Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA Kapiolani Community College student titrated 250 0 mL of a 0 1000 M NaOH solution against a solution of H SO4 What is the concentration of the H SO4 solution if titration required 221 0 mL H SO4 2 NaOH 2 H30 Na SO4 there is enough information to calculate the moles of 0 2500 LX mol NaOH mol NaOHX mol H SO4 1 mol NaOH mol H SO3 but not moles of acid mol NaOH mol H SO4

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsYour patient requires 620 mL of normal saline NS solution at 80 ml hour What s the infusion time in min Report answers with appropriate decimal places for professionals to dispense

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsFor each system listed in the first column of the table below decide if possible whether the change described in the second column will increase the entropy S of the system decrease S or leave S unchanged If you don t have enough information to decide check the not enough information button in the last column System A few grams of water vapor H O A few moles of nitrogen N gas Change The water condenses to a liquid at a constant temperature of 16 0 C The nitrogen is cooled from 11 0 C to 16 0 C and is also expanded from a volume of 6 0 L to a volume of 15 0 L The helium is heated from 5 0 C to 27 0 while the volume is held constant at 6 0 L AS O AS 0 AS 0 AS 0 not enough Information AS 0 AS 0 AS O not enough information AS 0 AS 0 AS O not enough information C da

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa Define each of the following terms solute solvent saturated unsaturated supersaturated h What are three methods to increase the rate of solubility

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsExplain the osmolarity of the solution What determines the osmotic pressure the mass of molecules of an open substance or the number of molecules per unit volume Find equal solutions of osmolarity among the following 1M NaCl 3M AI 1M CaCl2 1M Fe SO4 6GI 2M GI 4M AI 2M NaCl Explain tonicity hypertonic isotonic and hypotonic solutions what is the difference between osmolarity and tonicity What kind of solution should be used for intravenous infusion during excess fluid loss by the body Why What is the concentration of NaCl in in the physiological solution

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 Titration of 20 0 mL of an NaOH solution required 9 0 mL of a 0 30 M KNO3 solution What i the molarity of the NaOH solution

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances O True False

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemist analyzed a sample for citric acid but it actually contained malic acid What part of the calculation will be different Predict whether the true molarity value is larger or smaller than the calculated value

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA student is trying to calculate v v for a solution made by dissolving 20 mL of acetone in 90 mL of water What should be the correct way of calculating v v O 20 mL divided by 110 mL and then multiplied by 100 to change it to percent O 20 mL divided by 90 mL and then multiplied by 100 to change it to percent O 90 mL divided by 110 mL and then multiplied by 100 to change it to percent O 20 mL divided by 70 mL and then multiplied by 100 to change it to percent

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsChlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of manganese dioxide with hydrochloric acid HCl aq as described by the chemical equation MnO s 4HCl aq MnCl aq 2 H O 1 Cl g How much MnO s should be added to excess HCl aq to obtain 375 ml Cl g at 25 C and 1 00 x 10 kPa

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the concentration of solution in mass percent 49 2 g C12 H22O11 in 478 g H O Express your answer as a percentage 9 33 9 3 10 3 10

Physical Chemistry
Solutions5 Write a complete balanced chemical equation for when solutions of calcium chloride and sodium sulfate are allowed to react according to the following equation Balance the equation and work the problems that follow Na SO aq CaCl aq NaCl aq CaSO s a Identify the precipitate formed during this reaction by giving the chemical formula and chemical name for this substance b The above reaction is completed by allowing 45 0 ml of 0 250 M sodium sulfate to react with 25 0 ml of 0 450 M calcium chloride The percent yield for this reaction is reported to be 92 7 Calculate the experimental mass of the precipitate that can be expected to be recovered from this reaction 1 42 g

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCombining 0 228 mol Fe O3 with excess carbon produced 19 3 g Fe Fe O3 3C2Fe 3CO What is the actual yield of iron in moles actual yield 0 17232 Incorrect What is the theoretical yield of iron in moles theoretical yield percent yield 0 456 What is the percent yield 81 7

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAKCI solution containing 42 g of KCl per 100 g of water is cooled from 60 C to 0 C What happens during cooling O The excess will recrystallize The solution will bubble Nothing will change O The precipitate will dissolve Solubility g solute in 100 g H O BRRRRRRR 20 100 90 70 50 40 30 20 NaNO CaCl Pb NO NaC1 KNO KCI KCIO K Cr 07 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Temperature C

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA A 1 00 L solution is made of 0 40 mol L NaNO and 0 25 mol L HNO K 4 5 x 104 What is the pH of this solution

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSuppose there are two known compounds containing the generic elements X and Y You have a 1 00 g sample of each compound One sample contains 0 26 g of X and the other contains 0 35 g of X Identify plausible sets of formulas for these two compounds XY3 and XY4 XY and X3Y X3 Y and X4Y XY and X Y X Y and X3Y X Y3 and X3Y3 X4Y2 and X3Y Table

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many equivalents of Mg 2 are there in 6 00 mol of M83 PO4 2 First we have to convert moles into equivalents Mg3 PO4 2 1 mol 6 00 mol MP 3 Mg 2 a 250 b 100 0 j 1 k 6 00 x 10 3 p 1 80 x 10 2 2 PO4 equivalents eq mol C 2 1 3 60 x 102 q 7 65 x 10 10 r 2 63 d 30 00 f 33 e 6 m 6 00 x 10 2 S 7 89 n 5 8 3 t 5 26 eq Mg 2 h 36 0 3 0 x 10 2 u 1012 i 18 0

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAt STP 0 275 L of a gas weighs 0 398 g Calculate the molar mass of the gas g mol

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many grams of MgCl in 30 00 mL of a 25 5 ppt solution 30 00 mL a 25 5 b 100 0 j 1 k 6 00 x 10 3 q 7 65 x 10 10 r 2 63 W 106 X 103 8 C 2 1 3 60 x 10 2 S 7 89 y 10 mL d 30 00 e 6 m 6 00 x 102 t 5 26 Z 10 f 24 n 5 u 1012 8 8 3 o 3 0 x 10 2 V 10 h 36 i 18 0 p 1 80 x 10

Physical Chemistry
Solutionstwo reagents produce his compo yon 5 For all parameters listed below show show how you calculated them you may show that on the reverse side of this page or on the extra sheet of paper or right on the empty line next each answer A student while making aspirin just like you will combined 2 10 g of salicylic acid 4 00 mL of acetic anhydride and 5 drops of sulfuric acid Calculate the following and show your work a number of moles of salicylic acid b mass of acetic anhydride in grams it is not 4 00 g c number of moles of acetic anhydride d number of moles of aspirin that the student expects to get e mass grams of aspirin that the student expects to get f What was the limiting reagent salicylic acid or acetic anhydride The actual mass was of synthesized aspirin was 1 57 g g Calculate the yield of aspirin point Each line 0 5 pt keep all digits use the correct no of sig figs keep all digits keep all digits use all digits in calculations use the correct no of sig figs use the correct no of sig figs

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn the following acid base equation the reactant the Br nsted Lowry Acid HX H OX H3O O HX O H O OX O H3O is behaving as


Physical Chemistry
SolutionsD Question 5 The solubility of a gas in a liquid increases with temperature and in pressure O decrease increase O decrease decrease O increase increase O increase decrease in 4 p
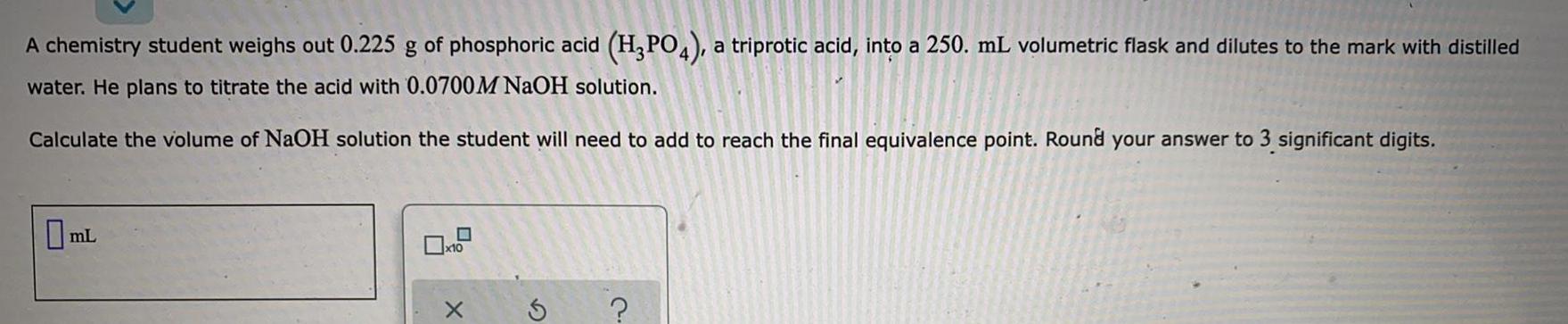
Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemistry student weighs out 0 225 g of phosphoric acid H PO4 a triprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water He plans to titrate the acid with 0 0700M NaOH solution Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point Round your answer to 3 significant digits mL x10 X

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsProblem H 2 00 L of a 3 0 M solution of HCI is prepared for a Chem 305 experiment using 34 00 mL of a concentrated solution of HCI a Determine the molarity of the concentrated solution of HCI

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsGrams of sc per 100 g H 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 NH37 KCI 3 KNO NH C KCI NaCl 10 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Temperature C Ce SO4 3 If a solution of KCI is saturated at 90 degrees Celsius and is heated to 100 degrees Celsius the solution is now

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemistry student weighs out 0 0226 g of acetic acid HCH3CO into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water He plans to titrate the acid with 0 0600M NaOH solution Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the equivalence point Round your answer to 3 significant digits mL x10

Physical Chemistry
Solutions9 Solution A is 8 15 M CaCl2 11 0 mL of solution A are diluted to 420 mL of solution B 222 0 mL of solution B are diluted to 335 mL of solution C What is the concentration in moles per liter of solution C 10 points total Solution C concentration

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the concentration of OH in a 0 20 M solution of ammonia weak base The Kb value for ammonia is 1 8 x 10 5

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 10 0 mL sample of sodium chloride solution that has a mass of 18 78 g is placed in an evaporating dish and evaporated to dryness The residue has a mass of 8 65 g Calculate the following concentrations for the NaCl solution mass mass m m percent mass volume m v percent

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 What is the pH of a 0 010 M solution of acetic acid CH3COOH Ka for acetic acid is 1 8 10 5

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 Why does the temperature of the water in the brine drop Hint Consider that when salt is added and the freezing point is lowered before the ice melts it is actually above its freezing point temperature and still must melt Also remember that melting is an endothermic process Consider the ice cube the system and the water around the ice the surroundings Fill out the LOL chart and provide a written explanation INITIAL IIII CII Temp Phase Chem Kinetic E Potential E attractions ENERGY FLOW FINAL SID IID III Temp Phase Chem Kinetic E Potential E attractions EVALUATE Revisit the anchor phenomenon from the Colligative Properties Unit Freeze Ice to String Watch the following video https youtu be 5w1Qb3PuXBg Explain the mechanism behind what happened given all that you have learned Also compare and contras what happened with the ice cream brine why did the string re freeze to the ice but the brine stayed a liquid slush Some useful words might include freezing point particles temperature melting freezing endothermic exothermic system surroundings heat

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa What is the concentration of a dextrose solution prepared by diluting 17 mL of a 4 0 M dextrose solution to 25 mL using 25 mL volumetric flask

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe molar solubility of Mg CN is 1 4 x 105 M at a certain temperature Determine the value of Ksp for Mg CN 1 Initial M Change M Equilibrium M Based on the given values fill in the ICE table to determine concentrations of all reactants and products Mg CN s 14 x 10 5 1 4 x 10 5 2 Mg aq 2 8 x 10 5 2 8 x 10 5 NEXT x 2 CN aq RESET 2x

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe common laboratory solvent diethyl ether ether is often used to purify substances dissolved in it The vapor pressure of diethyl ether CH3CH OCH CH3 is 463 57 mm Hg at 25 C In a laboratory experiment students synthesized a new compound and found that when 19 70 grams of the compound were dissolved in 194 6 grams of diethyl ether the vapor pressure of the solution was 451 15 mm Hg The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non electrolyte What is the molecular weight of this compound diethyl ether CH3CH OCH CH3 74 12 g mol MW g mol

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn the laboratory you are asked to make a 0 150 m manganese II bromide solution using 15 9 grams of manganese II bromide How much water should you add grams

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous solution is made by dissolving 23 5 grams of sodium sulfide in 489 grams of water The molality of sodium sulfide in the solution is m

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the pH of a 0 35 M solution of trimethylamine CH N Kb 7 4 10 5 7 25 x

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe vapor pressure of ethanol is 54 68 mm Hg at 25 C A nonvolatile nonelectrolyte that dissolves in ethanol is saccharin Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 C when 12 60 grams of saccharin C7H5NO3S 183 2 g mol are dissolved in 275 3 grams of ethanol ethanol CH3CH OH 46 07 g mol VP solution mm Hg

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the molecular weight they determined for this compound g mol 2 02 C m The boiling point of diethyl ether CH3CH OCH CH3 is 34 500 C at 1 atmosphere K diethyl ether In a laboratory experiment students synthesized a new compound and found that when 10 79 grams of the compound were dissolved in 229 7 grams of diethyl ether the solution began to boil at 34 848 C The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non electrolyte

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 A pH meter is placed in a beaker containing 20 00 mL of aqueous HF and the sol aqueous KOH The equivalence point is reached after the addition of 34 15 mL of KOH solution Complete parts a e below 18 pts a Write a balanced chemical equation for the neutralization reaction that occurs Give the full chemical formula of each reactant and product b Calculate the concentration of the HF solution the original solution before the titration c At the beginning of the titration before any KOH is added is the pH of the solution in the beaker less than 7 00 equal to 7 00 or greater than 7 00 Circle your answer below Initial pH 7 00 7 00 7 00 d What is the pH of the solution in the beaker at the half equivalence point e At the equivalence point is the pH of the solution in the beaker less than 7 00 equal to 7 00 or greater than 7 00 Circle your answer below and then provide a brief explanation 7 00 7 00 7 00

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe boiling point of water is 100 00 C at 1 atmosphere A student dissolves 10 79 grams of potassium nitrate KNO3 101 1 g mol in 194 6 grams of water Use the table of boiling and freezing point constants to answer the questions below Solvent Water Ethanol Chloroform Benzene Formula H O CH3CH OH CHCl3 C6H6 Diethyl ether CH3CH OCH CH3 The molality of the solution is Kb C m Kf C m 0 512 1 86 1 22 1 99 3 67 2 53 2 02 m 5 12

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsPart 4 Calculate OH for each of the solutions 1 pH 8 55 2 pH 11 23 3 pH 2 87 4 pH 3 31 Part 5 Calculate the H for each of the following 1 pH 8 55 2 pH 11 23 3 pH 2 87

Physical Chemistry
SolutionspH comparison a Which is stronger apples with a pH 3 or human saliva with pH 6 How much stronger b Which is stronger eggs with a pH 8 or ammonia with pH 11 How much stronger

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous solution of 1 58 M silver nitrate AgNO3 has a density of 1 22 g mL The percent by mass of AgNO3 in the solution is

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsMatch the following aqueous solutions with the appropriate letter from the column on the right 1 0 24 m CrS04 A Lowest freezing point 2 0 19 m NH4 2S B Second lowest freezing point 3 0 13 m AICI 3 C Third lowest freezing point 4 0 50 m Glucose nonelectrolyte D Highest freezing point

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe nonvolatile nonelectrolyte aspirin CoH8O4 180 10 g mol is soluble in chloroform CHCI 3 Calculate the osmotic pressure generated when 14 8 grams of aspirin are dissolved in 235 ml of a chloroform solution at 298 K The molarity of the solution is The osmotic pressure of the solution is M atmospheres

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe freezing point of water is 0 00 C at 1 atmosphere If 11 78 grams of manganese II bromide 214 7 g mol are dissolved in 154 2 grams of water The molality of the solution is The freezing point of the solution is m C

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsTo prepare a solution 30 g of KcL is mixed with 50 g of water Determine P P of the solution

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf 22 2 grams of an aqueous solution of chromium II nitrate Cr NO3 2 contains 4 73 grams of chromium II nitrate what is the percentage by mass of chromium II nitrate in the solution Cr NO3 2