Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the volume percent v v of Br in a solution preparec by dissolving 22 2 milliliters of liquid bromine Br in the solvent carbon tetrachloride CCl4 to make 295 6 milliliters of solution Include the correct unit symbol with your answer choice

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the molar concentration of the following solution 100 0 mL solution containing 77 2 g Al2 SO4 3

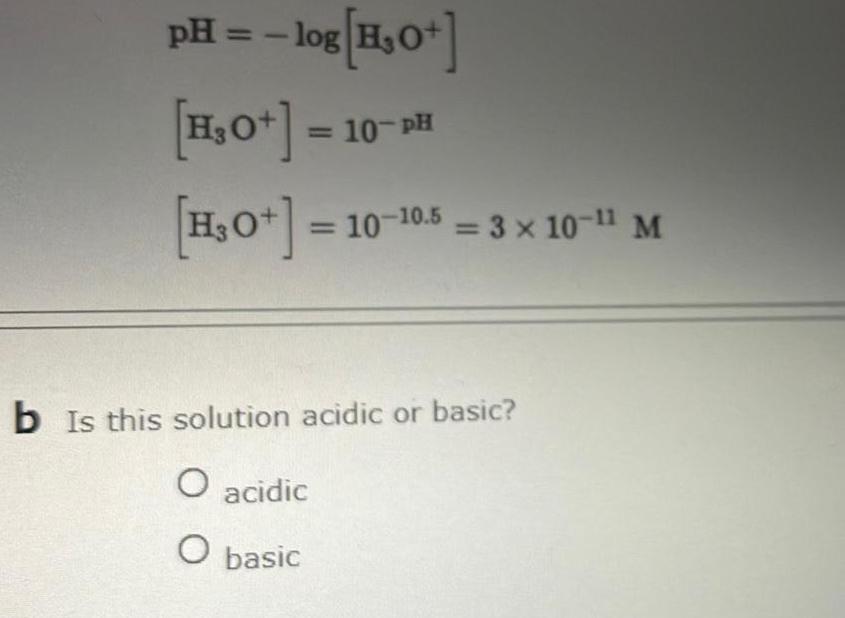
Physical Chemistry
SolutionspH log H 0 H O H 0 10 PH 10 10 10 5 3 x 10 1 M b Is this solution acidic or basic O acidic O basic

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsChemical Soluble in oll Conductivity when dissolved in water PF CF PCI AIF No Yes No No Not conductive Not conductive Not conductive Conductive Melting point 152 C 184 C 94 C 1291 C Boiling point 151 C 198 C 76 C Using principles of bonding and states of matter which is the best constructed argument about which of the below would best dissolve in room temperature water and why AIF3 would dissolve best in polar water at room temperature because it is conductive when dissolved in water which means it is ionic It is also a gas at room temperature and gases dissolve better in water PCI3 would dissolve best in polar water at room temperature because it does not dissolve in oil which makes it a polar compound polar compounds dissolve in polar compounds and it is a liquid at room temperature and liquids dissolve better in water than gases CF4 would dissolve best in polar water at room temperature It dissolves in oil so it must be a nonpolar molecule and nonpolar molecules dissolve better in polar molecules In addition it is a gas and gasses dissolve better in water PF3 would dissolve best in polar water at room temperature because it is a polar molecule polar molecules dissolve in polar molecules and it is a liquid at room

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA cell with a total of 0 3 osmol L is placed into a solution with a total of 0 2 osmol L It is assumed that the osmotic particles cannot pass through the cell membrane Answer the following true or false questions a true b false Osmoles are the total particles in a solution regardless of identity When particles are placed into a solvent solvent particles are displaced When solvent particles are displaced the concentration of the solvent increases 4

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many mL of a 5 00 ppb solution are needed to have 1 00 g The concentration will always be the conversion factor Like m m ppm and related concentrations are all in g ml 5 00 ppm means 5 00 g in a million mL or 5 00 g 106 mL or 5 00 g mL x 105 mL a 0 00 i 10 00 r 10 6 aa 20 0 b 1 00 j 2000 S 10 9 hb 10 0 gx C 2 00 k 10 t 10 12 CC 22 d 3 00 I 10 u 108 m 106 e 4 00 V 10 1 dd 0767 8 2 00 x n 10 f 5 00 w 101 0 1012 X 30 0 g 6 00 P 10 2 y 0 100 h 8 00 9 10 3 mL z 0 200

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many liters of a 5 00 M solution of Na3PO4 are needed to have 4 00 osmoles First we need the equation for dissolving the salt Na3PO4 3 Na 1 PO4 An osmole is a mole of dissolved particles the conversion factor is 1 mol First convert osmoles into moles Then calculate the liters osmol 1 mol 1 L osmol osmol mol

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the molecular weight of an unknown nonionic solute if 5 78 g are dissolved in 525 mL of solution and the osmotic pressure is 47 torr at 30 C unit Question Help Written Example Submit Question

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the pH of a solution that has H O 8 4 x 10 5 M Enter your answer in the provided bo Your Answer

Physical Chemistry
Solutions13 If you react 3 4 g of Aluminum with 5 2 g of Copper Sulfate a Which one is the limiting reagent b How many grams of Copper will you obtain 2AI 3CuSO4 Al2 SO4 3 3Cu

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsLactic acid C3H603 occurs in sour milk as a result of the metabolism of certain bacteria Calculate the pH of a solution of 40 mg lactic acid in 250 0 mL water Ka for D lactic acid is 1 4 x 10 4 pH

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 0 040 M solution of cyanic acid has a pH of 2 44 Calculate the ionization constant Ka of the acid Ka

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 Fill in the missing information 0 5pts each 10pts total H OH POH pH 4 96 x 10 1 M 5 55 x 10 M 11 O Acid Base or Neutral Neutral

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHydrogen gas has a Henry s law constant of 1 07x10 6 M mmHg at 30 0 C when dissolving in water If the total pressure of gas H2 gas plus water vapor over water is 1 00 atm what is the concentration of H in the water in grams per milliliter Pressure of the water vapor at 30 0 C 31 8 mmHg a ml

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsby Calculate the concentration of the sucrose solution in g L when 2 50 g are dissolved in 100 ML g L

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsPepsin is an enzyme involved in the process of digestion Its molar mass is about 3 50 x 104 g mol What is the osmotic pressure in mmHg at 30 C of a 0 400 g sample of pepsin in 55 0 mL of an aqueous solution

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsList these aqueous solutions in order of increasing melting point by ranking them from 1 lowest to 4 greatest The last three are all assumed to dissociate completely into ions in water 0 1 m sugar 0 04 m NaCl 0 04 m CaCl2

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 10 0 L tank at 4 23 C is filled with 15 6 g of chlorine pentafluoride gas and 10 5 g of boron trifluoride gas You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas in the tank Be sure your answers have the correct number of significant digits chlorine pentafluoride boron trifluoride mole fraction partial pressure mole fraction partial pressure 0 0 atm 0 0 atm X

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsM W A solution is prepared by dissolving 29 05 g of an unknown non electrolyte solute in sufficient water to yield 4 830 L of solution At 23 41 C the osmotic pressure of the solution is found to be 502 1 mm Hg What is the molar mass of the unknown solute in g mol Please use R 0 0820574 Latm molk Please report your answer with 4 significant figures g mol Which of the following is likely to increase the rate of a reaction

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the concentration in mol L of dissolved nitrogen N in water at 22 8 C and 678 mm Hg The Henry s Law constant for dissolved nitrogen in water at 22 8 C is 6 98x10 4 mol L atm Please report your answer with 3 significant figures such as 1 23E 3 mol L M A solution is prepared by dissolving 29 05 g of an unknown non electrolyte solute in sufficient water 4 830 L of solution At 23 41 C the osmotic pressure of the solution is found to be 502 1 mm Hg W

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsO a 4 11 O b 4 1 C 4 106 O d 4 e 4 1060 At 25 0 C Kw 1 0 x 10 14 and neutral water has a pH of 7 00 At 9 80 C Kw 2 76 x 10 15 and neutral water has a pH of Record your answer to 3 decimal places K for HX

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsreach the equivalence point Based on the titration curve it is determined that Ka 1 7 x 10 7 for the weak acid Based on this information what was the pH after 48 38 mL of NaOH was added Write your answer to 2 decimal places ie 1 23 or 12 34 Answer At a certain temperature manganese II hydroxide Mn OH 2 has a value of Ksp 3 3 x 10 13 At this temperature what is the molar solubility of Mn OH 2 in a solution buffered at pH 11 99 Report your answer to two significant figures i e 1 2E 8 M Answer Which of the following salts would be more soluble in 0 10 M HCI aq than in pure water

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 26 58 mL solution of weak acid is titrated with 0 0426 M NaOH It requires 42 45 mL of the NaOH titrant to reach the equivalence point Based on the titration curve it is determined that Ka 1 7 x 10 7 for the weak acid Based on this information what was the pH after 48 38 mL of NaOH was added Write your answer to 2 decimal places ie 1 23 or 12 34 Answer At a certain temperature manganese II hydroxide Mn OH 2 has a value of Ksp 3 3 x 10 13 At this roture what is the molar solubility of Mn OH 2 in a solution buffered at pH 11 99

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConsider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases name hydrofluoric acid hypochlorous acid acid 0 1 M KF 0 1 M NACIO solution 0 1 M KBr formula 0 1 M C5H5NHCI HF HCIO X Ka 6 8 10 3 0 10 4 pH 8 Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH In other words select a 1 next to the solution that will have the lowest pH a 2 next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH and so on choose one S choose one choose one choose one base name pyridine ammonia K formula C H N 1 7 x 10 NH3 1 8 10 9 5

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsUTOR Boiling Point Elevation positive K A solution is prepared by dissolving 14 10 g of ordinary sugar sucrose C12H22011 342 3 g mol in 41 10 g of water Calculate the boiling point of the solution Sucrose is a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte Solvent Benzene C He Camphor C 0H16 O Cyclohexane C6H12 Nitrobenzene C6H5NO Water H O Tb C 80 1 204 80 88 210 8 100 0 Kb C kg mol 2 53 5 95 2 79 5 24 0 512 T C 5 5 176 6 50 5 7 0 00 K C kg mol 5 10 37 7 20 2 8 1 1 86

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA solution is prepared by dissolving 17 55 g of an unknown non electrolyte solute in 70 75 g of cyclohexane The freezing point of the solution is found to be 0 52 C What is the molar mass of the unknown solute in g mol Data for Cyclohexane molar mass Kf normal freezing point Kb normal boiling point 84 16 g mol 20 0 C m 6 47 C 2 79 C m 80 74 C Please report your answer with 3 significant figures g mol

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid HCI has a concentration of 2 87 mol L and has a density of 1 05 g mL What are the mass percent and melality of HC this solution Mass percent HCI Molality HCI mol HCI kg H2 O

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSTEP 1 Convert volume to L How many Lof solution Your answer STEP 2 Solve for mole of Ca NO2 2 How many mol of Ca NO2 2 are in the 2 solution Your answer STEP 3a Find the molar mass of Ca NO2 2 What is the molar mass of Ca NO2 2 include units Your answer moler mass to solve How many g should you add to the

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many milliliters of a 6 00 M stock solution of NH3 would you need to prepare 100 00 mL of a 0 30 M NH3

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many mL would of a 1 M NaCl stock solution would you add to water to make 250 mL of 0 30 M Naci

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 Describe two of the four ways you could make a buffer solution with 50 ml of 0 1 M Na HPO4 and any other substances

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIndicate with a Y yes or an N no which apply dipole forces induced dipole London dispersion forces V hydrogen bonding

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsPhysiological saline solution has an osmolarity of 0 30 osmol L An aqueous solution of barium nitrate is made by dissoving 15 9 g Ba NO3 2 in enough water to make a liter of solution Assuming that the cell membrane is not permeable to its ions is this Ba NO3 2 solution hypertonic hypotonic or isotonic to red blood cells If normal red blood cells were suspended in this Ba NO3 2 solution what would be the expected outcome

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA solution contains 67 g of sodium sulfide Na2S in 1500 mL of solution Calculate the molarity of the solution O 0 38 M 44 7 M O 0 0447 M O 0 57 M

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 NaOCI aq 2 NaOH aq 2 Na SO4 aq 4 NaCl aq H O 1 22 A student performs an experiment to determine the value of the enthalpy change AH n for the oxidation reduction reaction represented by the balance equation above a Determine the oxidation number of Cl in NaOCI b Calculate the number of grams in Na S2O3 needed to prepare 100 00 mL of 0 500 M Na S O3 aq In the experiment the student uses the solutions shown in the table below Solution Na S O3 aq NaOCl aq NaOH aq Concentration M 0 500 0 500 0 500 Volume mL 5 00 5 00 5 00 c Using the balanced equation for the oxidation reduction reaction and the information in the table above determine which reactant is the limiting reactant win Justify your answer

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsFor a SOLID dissolved in a liquid solution as the temperature INCREASES the solubility generally This is a relations

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsUse the graph to answer the following 4 questions Solubility g of salt in 100 g H O 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 NaNO3 CaCl NaCl Pb NO3 2 KNO3 KCI KCIO3 K Cr O7 Ce SO4 3 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Temperature C

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConcentration of Fe NO3 3 in 0 10 M HNO3 solution Concentration of NaSCN in 0 10 M HNO3 solution Temperature of Solution Initial Concentrations Tube 0234 5 mL mL Fe NO3 3 NaSCN mL Total Solution Solution Volume 5 0 5 0 5 0 5 0 5 0 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 10 0 10 0 10 0 10 0 10 0 Initial Concentration of Fe NO3 3 M the 2 x 10 3 M Initial Concentration of NaSCN M

Physical Chemistry
Solutions20 A 0 50 L sample of fluorine gas contains 0 6 g of fluorine gas If more fluorine gas is added what mass of fluorine gas will be present in a volume of 2 5 L a 1 0 g b 2 0 g c 3 0 g d 4 0 g

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa Refer to figure below to determine whether this situation would result in an unsaturated saturated or supersaturated solution 120 g NaNO3 is dissolved in 100 g H 0 at 40 C OH BOOLA e B A 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 40 20 0 CsCl NaNO O unsaturated O saturated O supersaturated RbCl LICI NH C KCI NaCl U SO 20 40 60 80 100 Temperature C

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA buffer solution is prepared with 0 25 M of benzoic acid HC7H502 and 0 38 M of sodium benzoate NaC7H502 For HC7H502 Ka 5 7 x 10 5 What is the pH of this solution Please record your answer to two decimal places

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA container holds 0 6 moles of He g and 0 4 moles of Br g In ideal conditions wha is the partial pressure for Br g if the total pressure of the container is 5 0 atm a 4 atm b 3 atm c 2 atm d 1 atm 5 atm e

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsO 4 94 O 1 19 O 1 90 Question 21 Given that vapor pressure of water at 75 C is 290 mmHg calculate the vapor pressure of an aqueous solution of urea CO NH 2 containing 60 g or solute in 180 g of water O 150 mmHg O 190 mmHg 4 pts 230 mmHg

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn the diagram at right which position indicates the freezing point of the pure solvent 1 atm Pressure atm A A C Solid Select one a Point A b Point B Point C d Point D B Liquid Gas C Temperature C D

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsC12H22O11 12 0 12 CO 11 H O The body metabolizes sucrose C12H22O11 by burning it with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide water and energy If 3 0 moles of sucrose are burned what volume of carbon dioxide is produced O 1 584 L 0 16L O 56L 08061

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat mass in grams of CH3OH MM 32 04 g mol would need to be added to 200 1 g of water in order to lower the freezing point of water by 12 0 C Kf for water is 1 86 C m

Physical Chemistry
Solutionssulfate BaCl aq Na SO4 aq BaSO4 s 2NaCl aq 10 56 g BaSO4 of is precipitated from 500 mL of Na2SO4 What is the molarity of sodium sulfate 0 18 m 0 18 M 0 09 M 0 09 m

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsQuestion 5 In a titration experiment a student uses standard sodium hydroxide solution to titrate a hydrochloric acid solution with unknown concentration Known the volume of the acid is 5 00 mL The concentration of the sodium hydroxide is 0 1021 M Before titration the buret reading is 0 60 mL By the end of titration the buret reading is 25 75 mL What is the concentration of this hydrochloric acid

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe solubility of a compound defined as the maximum concentration of a substance that can be achieved under specified conditions True False Preous