Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentAmagnet is suspended horizontally in the earth s magnetic flux When it is displaced and then released it oscillates in a horizontal plane with a period T If a piece of wood of the same moment of inertia about the axis of rotation as the magnet is attached to the magnet what would the new period of oscillation of the system become b a T I 3 T c 2 T 1 2 d T 2 1 1

Physics
Work, power & energyD A particle of mass 100g is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 5 m s The work done by the force of gravity during the time the particle goes up is a 0 5 J 1 25 J me the partic VIC b c 1 25 J 0 5 J d simple

Physics
RotationThe ratio of the accelerations for a solid sphere mass m and radius R rolling down an incline of angle 0 without slipping and slipping down the incline without rolling is 1 5 7 3 2 5 2 2 3 4 7 5 159

Physics
Sound WavesA source is moving across a circle given by the equation x y R with constant speed m s in clockwise sense A detector is stationary at the point 2R 0 w r t the centre of the 330T Vs 6 3 circle The frequency emitted by the source is fs a What are the co ordinates of the source when the detector records the maximum and minimum frequencies b Find these frequencies Take speed of sound v 330 m s

Physics
NucleusBinding energy of deuterium is 2 23 Mev then its mass defect in a m u is 1 0 0024 3 0 0012 2 0 0012 4 0 0024

Physics
Simple harmonic motionblock attached to an end of a vertical spring whose other end is fixed to the ceiling of a stationary lift stretches the spring by length equilibrium It s time period when lift moves up with an acceleration g 2 is

Physics
KinematicsAn aeroplane is travelling horizontally at a height of 2000 m from the ground The aeroplane when at a point P drops a bomb to hit a stationary target Q on the ground In order that the bomb hits the target what angle e must the line PQ make with the vertical kg 10 m s AIPMT Mains 2007 Solution Lett be the time taken by bomb to hit the target h 2000 11 291 t 20s R ut 100 20 2000m R 2000 h 2000 tan e 1 0 45 Q 100m s R 100ms P 2000 h 2000m

Physics
Newton's law of motion8 Calculate the maximum possible value of mass m of block Cupto which block A will remain stationary relative to B If the length of block B is equal to 1 50 cm and mass of block C is m3 2mo then calculate the time t when block A will topple from block B if the system is released from rest A B Fig 7 256 C

Physics
Thermodynamics38 A cylindrical rod is used to conduct heat energy If it conducts Q cal sec then what energy will it conduct if its all linear dimensions are halved 1 Q 2Q 3 Q 4Q 2 Q 4 Q ON OT 2 Q

Physics
KinematicsFor a man walking with speed 3 2 km h rain appears to fall vertically downward When he starts running with 5 2 km h rain appears to fa on him at an angle of 45 with vertical The spee of rain w r t ground in km h is 1 22 2 2 6 3 26 0 2 5

Physics
Simple harmonic motionA man of mass 60 kg standing on a plateform executing S H M in the vertical plane Th displacement from the mean position varies a y 0 5 sin 2 ft The minimum value of f fe which the man will feel weightlessness at th highest point is y is in metres 1 3 g 4 T 2g2MA 2T 2 4 ng 4 2 2g

Physics
FrictionL 4 and m of different Three blocks A B and C of mass m 2 densities and dimensions are placed over each other as shown in the figure The coefficients of friction are shown Blocks placed in a vertical line are made to move towards right with same velocity at the same instant Find the time in sec taken by the upper block A ta L topple from the middle block B Assume that blocks B and C don t stop sliding before A topples from B given L 36 m 0 4 and g 10 m s L 2 2 B C

Physics
RadioactivityWhen Th238 changes into Bi222 then the number 90 of emitted a and B particles are 2 4a 7B 4 4a 18 1 8a 7B 3 4a 4p men 5 svig toolqmsa 83 16 107

Physics
Rotation1 A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N 1 0 25 rad s 3 5 m s 2 25 rad s 4 25 m s

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo particle of mass 4 kg 2kg are located as shown in figure then find out the position of centre of mass y 5m 4kg 37 0 0 2kg X

Physics
Properties of matterThe diagram shows a simple mercury barometer The mercury level is at a heighth when the atmospherich P pressure is 100000 Pa What is the pressure at P A 40000 Pa B 60000 Pa C 100000 Pa D 140000 Pa 0 4 h

Physics
Unit & DimensionsD Dimensional formula of universal gravita constant 1 M L T r 2 M LT co pripra 26 Hal yarala 1 M L T 3 IM 1 1 1441146 961 1941943 2 M LT 4 ML T 1

Physics
Work, power & energy1 A water pump lifts water from a level 10 m below the ground Water is pumped at a rate of 30 kg minute with negligible velocity Calculate the minimum horsepower the engine should have to do this na

Physics
Geometrical OpticsAn object 2 4 m in front of a lens forms a sharp image on a film 12 cm behind the lens A glass plate 1 cm thick of refractive index 1 50 is interposed between lens and film with its plane faces parallel to film At what distance from AIEEE 2012 lens should object shifted to be in sharp focus on film 1 7 2 m 2 2 4 m 3 3 2 m 4 5 6 m

Physics
Magnetism and MatterThe value of earth magnetic field BH 0 3 gauss In this magnetic field a magnet is oscillating with 5 oscillation min To increase the oscillation of magnet upto 10 oscillation min The value of earth magnetic field increased by Question Type Single Correct Type 1 0 3 gauss 2 0 6 gauss 3 0 9 gauss 4 0 12 gauss

Physics
KinematicsTwo bulbs of volume V and 4V contain gas at pressures of Satm 1 atm and at temperatures of 300K and 400K respectively When these bulbs are joined by narrow tube keeping their temperatures at their initial values The pressure of the system is 1 latm 2 2 atm 3 2 5atm 4 3 atm

Physics
Current ElectricityA group of six identical cells each of emf E and internal resistance r are joined in series to form a loop The terminal voltage across each cells OE O 6E LU CO Zero

Physics
Newton's law of motionIn the given figure a mass Mis attached to a horizontal spring which is fixed on one side to a rigid support The spring constant of the spring is k The mass oscillates on a frictionless surface with time period T and amplitude A When the mass is in equilibrium position as shown in the figure another mass m is gently fixed upon it The new amplitude of oscillation will be M m a A b A M M c A d A M m M M M mm

Physics
Circular MotionA smooth table is placed horizontally and a spring of unstreched length and force constant k has one end fixed to its centre To the other end of the spring is attached a mass m which is making n revolutions per second around the centre Tension in the spring will be A 47 m k n2 k 4 m n B 4 m k n k 4 m n C 2 m kln k 4 m n D 2 m kn k 4 m n

Physics
Geometrical OpticsA transparent solid cylindrical rod has a refractive index of mid point of one end of the rod as shown in the figure front The incident angle 0 for which the light ray grazes along the wall of the rod is 3 2 1 sin 2 sin 2 3 3 sin It is surrounded by air A light ray is incident at the AIEEE 2009 1 3 4 siny 1

Physics
Geometrical OpticsA transparent cube contains a small air bubble Its apparent distance is 2 cm when seen through one face and 5 cm when seen through other face If the refractive index of the material of the cube is 1 5 the real length of the edge of cube must be 1 7 cm 2 7 5 cm 3 10 5 cm 14 cm

Physics
Gauss Law9 Consider two concentric conducting spheres The outer sphere is hollow and initially has a charge 70 on it The inner sphere is solid and has a charge 20 on it a How much charge is on the outer surface and inner surface of the outer sphere b If a wire is connected between the inner and outer sphere after electrostatic equilibrium is established how much total charge is on the outer sphere How much charge is on the outer surface and inner surface of the outer sphere Does the electric field at the surface of the inside sphere change when the wire is connected

Physics
Fluids3 2 x 10 J 4 1 10 J In Poiseuilli s method of determination of coefficient of viscosity the physical quantity that requires greater accuracy in measurement is 1 Pressure difference 3 Length of the capillary tube 2 Volume of the liquid collected 4 Inner radius of the capillary tube tube The velocity distribution of the fluid is best represented by th zutta

Physics
Geometrical OpticsImage formed on retina of eye is proportional to 1 size of object 2 area of object The phenomena of total internal reflectic size of object 3 size of image who 4 size of ima size of obj

Physics
Simple harmonic motionWedge A is fixed while wedge B slides down on a smooth surface The vessel C having a simple pendulum of length I can slide down vertically on a smooth surface of wedge B Find the time period of the pendulum 90 111 C A O2n O O Zero Infinity

Physics
Center of mass and momentumThere is a uniform circular disc of radius R and a concentric disc of radius r where r R is cut off from it The distance of the new position of centre of mass of hollow disc from the centre of disc is O

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialA coil is suspended in a uniform magnetic field with the plane of the coil parallel to the magnetic lines of force When a current is passed through the coil it starts oscillating it is very difficult to stop But if an aluminium plate is placed near to the coil it stops This is due to Question Type Single Correct Type 1 Electromagnetic induction in the aluminium plate giving rise to electromagnetic damping 2 Development of air current when the plate is placed 3 Induction of electrical charge on the plate Shielding of magnetic lines of force as aluminium is a paramagnotic material

Physics
Wave Optics4 change depending upon the wave length 3 not change Diameter of human eye lens is 2 mm What will be the minimum distance between two points to resolve them which are situated at a distance of 50 meter from eye The wavelength of light is 5000 A 1 2 32 m AIPMT 2002 3 1 25 cm 4 12 48 cm 2 4 28 mm when the Young s double slit experiment is performed in water instead or air th

Physics
Basic PhysicsA viscous fluid is flowing through a cylindrical tube The velocity distribution of the fluid is best represented by the diagram 41612 particle 3412 1 2 Friction Tal de to adesive force llio hall of radius r falling in a tank of liquid at the instant when its acceleration is one 4 None of these

Physics
Simple harmonic motionTwo object P and Q of masses 2m and m are connected to two springs of spring constant 2k and k respectively Other ends of springs are connected to rigid walls as shown Initially springs are compressed by length 2A and A respectively and then released 0 0 J 2h vooooo 2m 2AAQ Smooth surface k oooooo Time period of P and Q remains same before and after the collision irrespective of the fact whether collision between masses is perfectly elastic or perfectly inelastic Time period of P and Q remains same before and after the collision only if collision between the objects is perfectly elastic Time period of P and Q remains same before and after the collision only if collision between the objects is perfectly inelastic If collision is perfectly inelastic amplitude of SHM of combined mass is A

Physics
Basic Physicsate magnitude of the resultant of t forces having magnitude 100N a cting at an angle of 60 degrees 95 N 58 N CON 2 N

Physics
Unit & Dimensionsyour understanding of the vectors material covered in the course so far Use these quantities to demonstrate your learning of the topics listed below It will be up to you to clearly define the topics covered and to create your own questions Make sure that every solution includes at least one of the given vectors scalars or units Include additional Information as needed Some topics to include are Meaning of a vector Geometric vectors Magnitude of a vector Scalar multiplication of a vector Addition subtraction of vectors Properties of addition subtraction scalar multiplication of vectors Applications of vectors forces and velocity Vectors 76 km h N32 W 102 N down Scalars 24 706 Units N km h

Physics
Basic Physicsm Question 7 Initially spring is relaxed and m is released from rest When come to rest for a just after cutting thread moment string AB is cut at the same instant Find the acceleration of eeeeeee M B TITT A
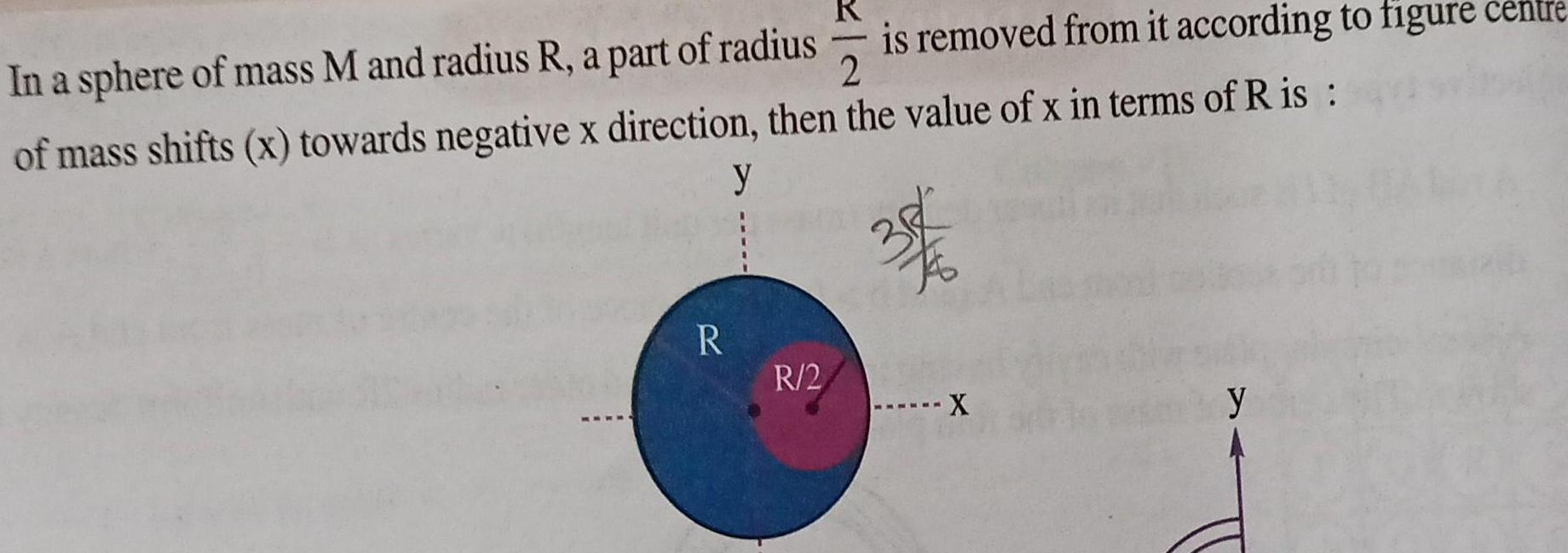
Physics
RotationR In a sphere of mass M and radius R a part of radius 2 of mass shifts x towards negative x direction then the value of x in terms of R is y 36 R 2 is removed from it according to figure centre X y

Physics
Basic PhysicsAn aeroplane flying uniformly with a speed 400 km h 1 covers a distance of 50 km in easterly direction and then 70 km in northerly direction and finally reaches back to the starting point What is average velocity of the aeroplane a 400 km h c zero b 370 km h 1 d some other value

Physics
Frictionestion 39 d the value of frictional resistance if the dy is in limiting equilibrium Refer owing figure ote Click on image to enlarge it 400 N 46 14 N 00 00 N 200 N O P cos 30 O 400 cos 30 R

Physics
Electromagnetic InductionNEET PHYSICS All India Major Test Ser Q 129 A thin semicircular conducting ring PQR of Q 12 radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B as shown in figure O 1x x P B Rx The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed is v is 1 By and R is at higher potential 2 2rBv and R is at higher potential 3 Zero

Physics
Properties of matterA wire elongates by mm when a load W is hanged from it If the wire goes over a pulley and two weights W each are hung at the two ends the elongation of the wire will be in mm 4 zero 1 l 2 2 l 3 2 Y in mode of a material of density o It is falling through a liquid of density p p AIEEE 2006

Physics
Basic Physicsestion 16 ort lost in friction is given by Actual effort Ideal effort Ideal effort Actual effort Actual effort Actual load Actual load Actual effort

Physics
Basic Physics2 Velocity 3 Frequency 1 Wavelength Prism of which material is used for study of infrared spectrum 1 rock salt 2 flint glass 3 crown glass Image formed on retina of eve is proportional to 4 None 4 quarta

Physics
Basic PhysicsBHOLE RAJWARDHAN SANJAY Question 11 From a solid cylinder 150mm in diameter and 220mm height a hole having 45mm radius and height is drilled 220mm coaxially Calculate the Y for the remaining solid O 75mm O 110mm O 128 69mm O 146 23mm

Physics
Basic PhysicsA steel wire of 1 m long and 1 mm cross section area is hang from rigid end When weight of 1 kg is hung from it change in length will be given Y 2 10 N m 1 0 5 mm 2 0 25 mm 3 0 05 mm 4 5 mm C

Physics
Newton's law of motionAssertion Steel is more elastic than rubber Reason Under a given deforming force steel is deformed less than rubber 1 If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion 2 If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion 3 If both assertion is true but reason is false 4 If the assertion and reason both are false 5 If assertion is false but reason is true

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe potential difference V and the current I flowing through an instrument in an ac circuit of frequency f are given by V 5 cos wt volts and I 2 sin wt amperes where w 2 f The power dissipated in the instrument is Question Type Single Correct Type 1 Zero 2 10W 3 5W

Physics
Basic Physicsmple wheel and axle diameters of wh axle are 500 mm and 100 m ctively If load of 400 N is lifted by t of 100 N calculate the efficiency of ne at this load 6