Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Geometrical Optics44 Calculate the radius of the image of the moon formed by the objective of an astronomical telescope having focal length 10 m Given the diameter of the moon 3 48 103 km and its distance from the earth 3 84 x 105 km Ans 4 53 x 10 2 m 45 Two convex lenses of focal lengths 0 20 m and 0 01 m are provided to you How shall you arrange

Physics
Basic Physics2 Calculate the current produced in a small germanium plate of area 1 cm and of thickness 0 3 mm when a potential difference of 2V is applied across the faces Given concentration of free electrons in Ge is 2 x 10 m and mobilities of electrons and holes are 0 36 m V s and 0 17 m V s respectively 1 1 3 3 3 3 2 2 3 4 None of these

Physics
RotationA person is riding a bicycle in vertical portion accelerating forward without slipping on a straight horizontal road What is are the direction s of the total force exerted by the road on front P and the IJSO Stage II 2014 rear Q wheel P

Physics
KinematicsAn aeroplane flying horizontally with a velocity c 216 km h drops a food packet while flying at height of 980 m The total horizontal distance travelled by the packet is g 9 8 m s 1 600 m 2 600 2 m 3 216 m 4 432 2 m

Physics
ThermodynamicsA refrigerator has to transfer an average of 268 Joule of heat per second from temperature 5 C t 35 C What is the average power consumed assuming ideal reversible cycle and no other losses Select one a 308 J S 1 b 288 J S c 309 J S 1 d 298 J S 1
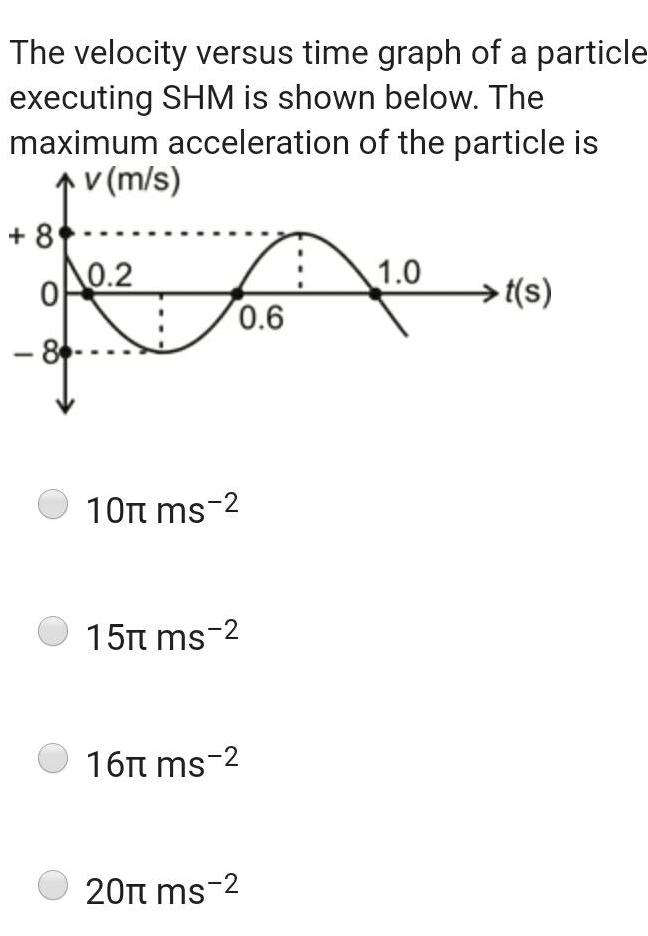
Physics
Simple harmonic motionThe velocity versus time graph of a particle executing SHM is shown below The maximum acceleration of the particle is v m s 8 0 86 0 2 7 foo 0 6 10 ms 2 15 ms 2 16 ms 2 20 ms 2 1 0 t s

Physics
Geometrical Optics5 The refractive index of the material of a prism is 2 and the angle of the prism is 30 One of the two refracting surfaces of the prism is made a mirror inwards by silver coating A beam of monochromatic light entering the prism from the other face will retrace its path after reflection from the silvered surface if its angle of incidence on the prism is 1 60 3 30 2 45 4 zero

Physics
Optical InstrumentsAn analyser blocks the light coming from a polariser as Select one a None b The pass axis of the analyser and the polariser is oriented 90 to each other e The light changes it path as it passes through the analyser d The pass axis of the analyser and the polariser is oriented 0 to each other

Physics
Newton's law of motionofv A ball of mass m moving horizontally which velocity u hits a wedge of mass M The wedge is situated on a smooth horizontal source If after striking with wedge the ball starts moving in vertical direction and the wedge starts moving in horizontal plane Calculate a the velocity of wedge V b the velocity v with which the ball moves in vertical direction the impulse imparted by the ball to the wedge d the coefficient of restitution e 0 m

Physics
Rotation2 149 The minimum force F needed to push the two 50 kg cylinders up the incline is 200x Newton The force acts parallel to the plane and the coefficients of friction at contacting surfaces are as A 0 3 between cylinder A and ground B 0 25 between cylinder B and ground and c 0 between two cylinders The cylinder A can rotate about its axis without friction Find the value of x F 37 AB

Physics
Simple harmonic motionA mass of 2 kg is suspended by a light spring of stiffness constant 20 Nm11 The energy associated with the vertical oscillation of the system is observed to decay 1 e of its initial value in 50 s Assuming the damping force proportional to the velocity the damping force constant is Select one a 0 2 Nsm 1 b 0 004 Nsm c 0 002 Nsm 1 d 0 04 Nsm 1

Physics
Current Electricity0 Consider a rectangular slab of length L and area of cross section A A current I is passed through it If the length is doubled the potential drop across the end faces a becomes half of the initial value b becomes one fourth of the initial value c becomes double the initial value d remains same J K CET

Physics
Transmission of heat30 gm of ice at 14 C is added to 200 gm of water at 25 C Find the equilibrium temperature Take specific heat of ice 0 5 cal g C specific heat of water 1 cal g C and latent heat of ice 80 cal g

Physics
Properties of matter38 A wire fixed at the upper end stretches by length by applying a force F The work done in stretching is AIEEE 2004 a F 21 b Fl FI

Physics
KinematicsFour persons K L M N are initially at the four corners of a square of side 20 m Each person now moves with a uniform speed v 5 m s in such a way that K always moves directly towards L L directly towards M M directly towards N and N directly towards K Find time in second after which four persons will meet

Physics
Simple harmonic motionA solid ball of mass m is made to fall from a height H on a pan suspended through a spring of spring constant K as shown in figure If the ball does not rebound and the pan is massless then amplitude of oscillation is ABA A mg K mg C K 2HK mg 1 2 B D mg k mg K 1 2HK mg 1 1 1 2 2HK mg 1 2 fmmx

Physics
KinematicsA ball of mass 0 2 kg is thrown vertically upwards by applying a force by hand If the hand moves 0 2 m while applying the force and the ball goes upto 2 m height further find the magnitude of the force Consider g 10 m s a 4N c 20N56 45 b 16N d 22 N

Physics
Center of mass and momentumInteger Type Questions 1 The magnitude of force f in Newton acting on a body varies with time t in millisecond as shown in the figure Find the magnitude of the total impulse in Ns of the force on the body from t 4 ms to t 16 ms IIT 1994 a 3 TON dioolov pdT F N 800 200 A B 0 EF 4 6 atbil b 4 d 6 D 16 t ms

Physics
Friction2 A block of mass 0 2 kg is held against by a wall by applying a horizontal force of 5 N on the block The coefficient of friction between the wall and block is 0 5 Find the magnitude in Newton of the frictional force acting on the block Take g 10 m s a 2 IIT 1994 b 4 c 8 d 0

Physics
Magnetic Field due to current3 In L C oscillation maximum charge on capacitor is Qo The current in the circuit when 50 energy is electrical and 50 magnetic is 1 Qo LC 9 C L 2 LC

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe relation between Einstein s B coefficient implies Select one a LASING is coherent b LASING is inefficient in natural crystals C All d Stimulated emission rate is equal to stimulated absorption rate

Physics
Magnetism and Mattercomponent of earth s field is 0 4 x 10 4 T 28 A magnet makes 12 oscillations per minute in the earth s magnetic field alone and 15 oscillations per minute when a short magnet with its axis horizontal and its south pole pointing north is placed with its centre 20 x 10 2 m directly above the oscillating magnet Find the magnetic moment of the short magnet Given BH 0 36 10 4 T 29 Two an I S C 04 Ans 0 81 J T have pole strength 60 Am When they cannot

Physics
Electric Field and Potential5 A system consists of two concentric conducting spheres with the inside sphere of radius a carrying a positive charge q What charge 92 has to be deposited on the outside sphere of radius b to reduce the potential of the inside sphere to zero How does the potential depend in this case on a distance r from the centre of the system Draw the approximate plot of this dependence 6 Four large metal plates are located at

Physics
Work, power & energyTwo smooth spheres made of identical material having masses m and 2m undergoes an oblique impact as shown in figure The initial velocities of the masses are also shown The impact force is along the line joining their centres along the x axis The coefficient of restitution is 5 9 The velocities of the masses after the impact and the approximate percentage loss in kinetic energy A 101 8 51 4 15 i 3 3 c 101 81 10 i 41 25 3 3 y axis 2m v 5m s m v 10m s 5 B 1 81 1 4 20 3 D 101 81 1 4 20 3 sin 4 5 x axi

Physics
KinematicsIn given figure speed of A D is 8 shown and speed of B with respect to A is m sec Speed in m s of c in vertical direction is x Then the value of x is Assume strings remains tight A B 53 C 5 m sec 8 53 m sec as D

Physics
Sound WavesWhen an open organ pipe resonates in its fundament mode then at the centre of the pipe The gas molecules undergo vibrations of maximum amplitude The gas molecules are in motion The pressure of the gas is constant The pressure of the gas undergoes maximum variation

Physics
Simple harmonic motionAn oscillator consists of a block attached to spring k 400 N m At some time t the position measured from the system s equilibrium location velocity and acceleration of the block are x 0 100m v 15 0 m s and a 90 m s The amplitude of the motion and the mass of the block are 1 0 2 m 0 84 kg 3 0 4 m 0 54 kg 2 0 3 m 0 76 kg 4 0 5 m 0 44 kg

Physics
Work, power & energy16 A particle of mass m is located in a unidimensional potential field where the potential energy of the particle depends on the coordinate x as U x U 1 cos ax Up and a are constants Find the period of small oscillations that the particle performs about the equilibrium position ba Solve the foregoing problem if the potential energy has the form x a x b x where a and b are positive constants

Physics
CapacitorsA l F capacitor is connected in the circuit shown below The e m f of the cell is 2 volts and internal resistance is 0 5 ohm The resistors R and R have values 4 ohm and 1 ohm respectively The charge on the capacitor must be 1uF HF 1 2 C 2 1 C 3 1 33 C 7010 E 2V r 0 50 R 192 www R 492 www

Physics
GravitationA ball is dropped from a spacecraft revolving around the earth at a height of 120 km What will happen to the ball a it will fall down to the earth gradually b it will go very far in the space c it will continue to move with the same speed along the original orbit of spacecraft d it will move with the same speed tangentially to the spacecraft 1996

Physics
Newton's law of motionSINGLE OPTION CORRECT TYPE When forces F F2 and F3 are acting on a particle of mass m such that F2 and F3 are mutually perpendicula hen the particle remains stationary If the force F is now removed then the acceleration of the particle is AIEEE 20 F F3 m A Flm B F2F3 mF1 C D F2lm the

Physics
Wavesind 2 30 5 cm OOP A tube 1 m long is closed at one end A stretched wire is placed near the open end The wire is 0 3m long and has a mass of 0 01kg It is held fixed at both ends and vibrates in its fundamental mode It sets the air column in the tube into vibration at its fundamental frequency by resonance Find a the frequency of oscillation of the air column b the tension in the wire If speed of sound in air is 330 m s mont if Y 300 m s n 500 Hz L 125 cm

Physics
Magnetism and MatterA bar magnet with its north N and south S poles is initially moving to the left along the axis of fixed circular conducting loop as shown A current is induced in the loop As seen from the magnet side lq er 0 0 of T 0 MICH S N 1 runs clockwise and acceleration of magnet is towards left 2 runs counterclockwise and acceleration of magnet is towards right 3 runs clockwise and acceleration of magnet is towards right 4 runs counterclockwise and acceleration of

Physics
ThermodynamicsA monoatomic gas undergoes a process given by 2dU 3dW 0 then the process is A isobaric B Adiabatic C polytropic processes with equation PV0 5 constant D polytropic processes with equation PV constant

Physics
Electric Field and Potentialfield intensity is zero 2 m Find the point C B S E 01 Ans 2 3 m 78 Two positive charges of 10 C each are situated 10 x 10 2 m apart from each other What is the increase in the electrostatic potential energy of the system when the two charges are brought closer by 2x 10 2 m Express your answer in S I unit Ans 2 25 J 79 An electric dipole of length 2 x 10 m is placed with A

Physics
Wave OpticsWhat is maximum number of possible interference maximas for YDSE in which slit separation is twice the wavelength of monochromatic light

Physics
Wave Optics005 m a real image is formed 0 20 m from the lens vision is 0 24 m ufication is produced by the lens when used as a magnifier The least distance Ans 7 2 x 102 m respectively The objective forms a real image at a distance of 20 x 10 2 m Calculate the 35 In a compound microscope the objective and eye piece have focal lengths of 5 x 10 3 m and magnifying power if the eye is held close to the eye piece and views a virtual image at a distance of 24 x 10 m its least distance of distinct vision Also find the distance between the object and the objective JAns 507 5 13 x 10 m 36 The f

Physics
Properties of matterA uniformly tapering circular bar has its diameter ranging from D a to D a along its length L The bar is subjected to an axial force P and young s modulus is Y The percentage error in the calculation of elongation of bar if mean diameter is used in calculation instead of actual diameter 2a A 100 D C a 10D B D 102 D a x 100

Physics
Simple harmonic motionwo simple harmonic motions are represented by the equations y 0 1 sin 100nt F 3 and Y 0 1 cos100nt The phase difference of the velocity of particle 1 with respect to the velocity of particle 2 is 1 2 3 3 3 4

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo particles A and B of masses m and 3m are moving along X and Y axes respectively with the same speed v They collide at the origin and coalesce into one body after the collision What is the velocity of this coalesced mass Hint X A m Bl3m Before collision y 14 4m After collision

Physics
KinematicsA dumbbell consists of two balls A and B each of mass m 1 kg and connected by a spring The whole system is placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure Initially the spring is at its natural length the ball m s in the B is imparted a velocity Vo 8 7 oooooooooooooooo 5000000 n 4 direction shown The spring constant of the spring is adjusted so that the length of the spring at maximum elongation is twice that of the natural length of the spring Find the maximum potential energy stored in Joule in the spring during the motion h horizontal fixed surface

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA sphere P of mass m and velocity undergoes an oblique and perfectly elastic collision with an identical sphere Q initially at rest The angle 9 between the velocities of the spheres after the collision shall be 1 0 2 45 3 90 4 180

Physics
Magnetism and MatterGiven BH 0 36 x 10 4 T 29 Two small identical magnets are 8 x 10 2 m long and have pole strength 60 Am When they cannot rotate it is possible to make one float 6 x 10 2 m above the other Find the force which the lower magnet exerts on the upper one J E E 00 Ans 0 16 N netic fields The angle between the field directions 30 A magnetic dipole is

Physics
Sound WavesTwo audio speakers are kept some distance apart and are driven by the same amplifier system A person is sitting at a place 6 0 m from one of the speakers and 6 4 m from the other If the sound signal is continuously varied from 500 Hz to 5000 Hz what are the frequencies for which there is a destructive interference at the place of the listener Speed of sound in air 320 m s produce five beats sec with neighbouring

Physics
Wave Optics16 Two wave are represented by equation 9 a sin oot 9 a cos cot the first wave 1 leads the second by t 2 lags the second by 3 leads the second by 4 lags the second by RIN 2 EIN 2 to y a u yu y to y k

Physics
GravitationA satellite revolve around the earth at a height 900 km above the surface of the earth in a circu orbit Calculate its orbital velocity G 6 67 x 10 11 Nm kg Mass of the earth 6 x 1024 radius of the earth 6400 km my 4MML

Physics
Basic PhysicsMagnetic field in a cylindrical region is given by B at Find emf across rod AB as shown in figure A O 2R B

Physics
Magnetism and MatterTwo geometrically identical bar magnets having their identical poles are together and allowed to magnetic moments 4M and 5M are joined such that oscillate in a magnetic field It is found that time the polarity of one of the magnet is reversed and taken in completing three oscillation is 3 second If the combination is again made to oscillate in same magnetic field then time period of oscillation will be 1 9 sec 3 3 3 sec 2 3 sec 1 4 3 sec

Physics
GravitationThe radius of the earth is 6370 km and radius of mars is 3440 km What is the acceleration due to gravity on mars if mass of the mars is 0 11 times the mass of earth g G Me boll

Physics
Electric Field and Potential40 An electric dipole consists of two point charges 4 C and 4 C placed 24 cm apart Find the electric potential at a point lying 4 x 10 2 m away from the centre of the dipole a on the dipole axis and b on the perpendicular bisector of the dipole c Determine also the electric potential at the point lying 20 x 10 2 m away from its mid point at an angle 60 with the dipole axis d What will be its minimum and maximum potential energy when placed in an electric field of intensity 2 x 105 V m Ans a 4 8 x 105 V b 0 c 0 9 V d 16 x 10 2 J 16 x 10 2 Jl