Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Electric Field and Potential4 A positive point charge is placed inside a spherical metallic shell The electric field lines are represented by 2003 A B C D

Physics
Geometrical OpticsA ray of light travelling in the direction i 31 onvon M sido is incident on a plane mirror After reflection it travels along the direction 1 31 The angle of incidence is 1 2 2

Physics
Current ElectricityI shown in fig E F G and H are cells of emf 2 1 3 and 1 volts and their internal resistances JEE 1981 are 2 1 3 and 1 ohm respectively Calculate 1 F D value of n will be E 252 3 D B C HI i The potential difference between B and D is given by 13 n 13 MAHT SHOM ii The ratio of potential difference across the terminals of the cell G to cell H is given by Volt then valu of n will be n 2 19 the

Physics
Geometrical OpticsA plano convex lens made of material of refractive index with radius of curvature R is silvered on the curved side How far away from the lens mirror must you place a object so that the image coincides with the object KVPY 2011 R a b R c R 1 d R

Physics
KinematicsIn the above problem if reaches the ground at a horizontal distance d the second ball reaches the ground at a horizontal distance 3 12 d 1 6d 2 3d 4 4d A ball is projected horizontally from the top of a building 19 6 m high If the line joining the point of projection to the point where it hits the ground makes an angle of 45 to the horizontal the initial velocity of the ball is 1 4 9 ms 1 2 9 8 ms 1 3 19 6 ms 1 4 14 7 ms

Physics
Newton's law of motionset into oscill What is the trajectory of the bob of its extreme positions b at its mean positio 3 A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving a upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s b downwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s2 c upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s What would be the readings on the scale in each case d What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity article of mass 4 kg What is

Physics
Current ElectricityA step up transformer operates on 220 V line and supplies 2 2 A The ratio of primary and secondary winding is 11 50 The output voltage in the secondary is 1 220 V 2 100 V 3 1000 V 4 Zero

Physics
Experiments3 0 50 mm A student measures the time period of 100 oscillations of a simple pendulum four times The data set is 90s 91s 95s and 92s If the minimum division in the measuring clock is 1s then the reported mean time should be 2016 1 92 5 0s 4 0 75 mm 101 9 A scr Main Circu Giver The c 1 C

Physics
KinematicsIllustration 8 A wire of resistance 0 5 m 1 is bent into a circle of radius 1 m The same wire is connected across a diameter AB as shown in figure The equivalent resistance is in ohms 1 T A C D 2 1 3 B TC 2 4 T 4

Physics
Electric Field and Potential1 54 8 Figure 1 54 shows four point charges at the of a square of side 2 cm Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the centre O of the square if Q 0 02 C 2Q 2 cm Use 2 cm 1 41E0 DE Q 2Q B Q 2 cm 2 cm 9x10 Nm C ISCE 98 Ans 9 2 x 105NC 1 parallel to BA

Physics
FrictionWhich of the following forces is not conservative A F 3i 4 C F 3yi 4xj B F 3xi 4yi D F 3x 1 4y j on raxis has potential energy U 2 20 X 5x2 Joules along x axis The particl
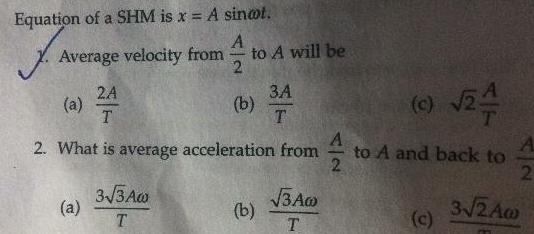
Physics
Simple harmonic motionEquation of a SHM is x A sintot A Average velocity from 2 a 2A T 2 What is average acceleration from a to A will be 3 3 Aw T b 34 3A T b 3AG T A 2 c 24 to A and back to c 2 3 2Aw

Physics
Newton's law of motionThe coefficient of static friction between your hand and a pie plate is about 0 8 If you want to put a cream pie in someone s face what minimum acceleration do you need to keep it from sliding down your vertica hand A 4g 5 2g B 5 C 5 g 2 D 5g 4

Physics
Sound Waves7 When two tuning forks fork 1 and fork 2 are sounded together 4 beats per second are heard Now some tape is attached on the prong of the fork 602 When the tuning forks are sounded again 6 beats per second are heard If the frequency of fork 1 is 200 Hz then what was the original frequency of fork 2 1 204 Hz 3 202 Hz 2 196 Hz 4 200 Hz

Physics
Current ElectricityA potentiometer is being used to compare two resistances The balancing length for a standard resistor R 10 0 2 is 58 3 cm while that for an unknown resistance X is 68 5 cm Determine the value of X What would you do if you failed to find a null point on the potentiometer wire AB

Physics
Current Electricity12 cells each of emf 1 5 V and internal resistance 0 5 2 are arranged in m rows each containing n cells connected in series Calculate the values of n and m for which this combination would send maximum current through an external resistance of 1 5 2 Sample Paper 6 2 R 1 502 H

Physics
FluidsThe mass of a body is 70 kg When completely immersed in water it displaces 2000 cm water What is the relative density of the material of the body

Physics
CapacitorsIn the given circuit a charge of 80 C is given to the upper plate of the 4 F capacitor Then in the steady state the charge on the upper plate of the 3 uF capacitor is A 32 C C 48 C B 40 C D 80 C 80 C 2 F HF I 4 F

Physics
FluidsExample 16 17 Water flows through the tube as shown in figure The areas of 2 cm respectively The rate of flow of water through the tube is 500 cm Is Find cross section of the wide and the narrow portions of the tube are 5 cm and the difference of mercury levels in the U tube 2 Fig 16 56

Physics
Wave OpticsA plate of thickness t made of a material of refractive index u is placed in front of one of the slits in a double slit experiment a Find the change in the optical path due to introduction of the plate b What should be the minimum thickness t which will make the intensity at the centre of the fringe pattern zero Wavelength of the light used is 2 Neglect any absorption of light in the plate

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe power of spectacles lens required for a person is 5 dioptre when separation between spectacles and eye is 2 cm What will be the power of contact lens required by him 1 5 25 D 3 3 2 D 2 4 75 D 4 5 75 D

Physics
Current ElectricityIn a hydrogen tube it is observed that through a given cross section 3 13 x 10 5 electrons per sec moving from right to left and 3 12 x 10 5 protons per sec are moving from left to right The electric current in the discharge tube and its direction is

Physics
Current ElectricityFind the equivalent resistance between A and B of given wire mesh of 14 resistances each wire having resistance R A R 2 5R 6 C B 2R 3R D 2 H A B

Physics
Unit & DimensionsA physical quantity P is related to four observables a b c and d as follows P The percentage errors of Vcd measurement in a b c and d are 1 3 4 anc 2 respectively What is the percentage error in the quantity P

Physics
KinematicsA car moving with a speed of 50 km h can be stopped by brakes after atleast 6 m If the same car is moving at a speed of 100 km h the minimum stopping distance is a 6 m c 18 m b 12 m d 24 m

Physics
Current ElectricityA copper wire has a resistance of 0 5 22 Another copper wire of the same mass as the first one double in length of the first Find the resistance of the second wire

Physics
RotationD In Column I situations are given in which a constant force starts acting on a body initially at rest on a rough horizontal surface Match with the observations given in Column II Column I Column II A B C D Ring d Disc 5 Solid Sphere Solid Cylinder F F P 9 R S Body accelerates forward Rotation about the centre of mass is clockwise lo cudrom Friction force acts backward No friction acts 2 Rotational M

Physics
Newton's law of motionIn the figure the vertical sections of the string are long A is released from rest from the position shown Then DCE 2006 m vol 1 2 m A m a The system will remain in equilibrium b The central block will move down continuously c The central block will undergo simple harmonic motion d The central block will undergo periodic motion but not

Physics
Geometrical OpticsFor the equation vuf for a lens if 1 u v 4f wty 3f to be applicable 2 u v 2f 4 u v 5f

Physics
Current Electricity12 Find the potential difference VA VB for the circuit shown in the figure B IV 2 IV 350 1350 192 IV 192 4 19 SIR A

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentolenginio D The magnetic field at all points inside the pipe is the same but not zero Figure shows cross section view of a infinite cylindrical wire with a cylinderical cavity current density is uniform J jok as shown in figure Of notl A Field inside cavity is uniform B Field inside cavity is along a Only Inpirov enam C Field inside cavity is perpendicular to a ning oldst Istuoshod a no iqail ofbeen moo A qnd won ai zasqmoo bas noit od 11 Istroshod wolad 00 jedroxized of olyns fedy D If an electron is projected with velocity vo j it will move undeviated before colliding with cavity wall

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentFigure shows a long straight wire of a circular cross section radius a carrying steady current I The current is uniformly distributed across this cross section Calculate the magnetic field in the region r a and r a P

Physics
Current Electricityas shown below Arrange Three resistances of equal value are arranged in them in the increasing order of power dissipation different combinations www I III 1 III I N I 3 I IV III II i II IV 2 II III IV I 4 I III II IV

Physics
RotationComprehension 3 The general motion of a rigid body can be considered to be a combination of i a motion of its centre of mass about an axis and ii its motion about an instantaneous axis passing through the centre of mass These axes need not be stationary Consider for example a thin uniform disc welded rigidly fixed horizontally at its rim to a massless stick as shown in the figure When the disc stick system is rotated about the origin on a horizontal frictionless plane with angular speed the motion at any instant can be taken as a combination of i a rotation of the centre of mass of the disc about the z axis and ii a rotation of the disc through an instantaneous vertical axis passing through its centre of mass as is seen from the changed orientation of points P and Q Both these motions have the same angular speed in this case 5 P 6 Z I Now consider two similar systems as shown in the figure Case a the disc with its face vertical and parallel to x z plane Case b the disc with its face making an angle of 45 with x y plane and its horizontal diameter parallel to x axis In both the cases the disc is welded at point P and the systems are rotated with constant angular speed about the z axis Q P Z 45 y Case a Case b Which of the following statements about the instantaneous axis passing through the centre of mass is correct 2012 y A It is vertical for both the cases a and b B It is vertical for case a and is at 45 to the x z plane and lies in the plane of the disc for case b C It is horizontal for case a and is at 45 to the x z plane and is normal to the plane of the disc for case b D It is vertical for case a and is 45 to the x z plane and is normal to the plane of the disc for case b B It is for case a and D It is m for h Which of the following statements regarding the angular speed about the instantaneous axis passing through the centre of mass is correct 2012 A It is 200 for both the cases C It is for case a and 2 for case b 0 for case b

Physics
Basic Physics21 A glass vessel contains air at 60 C To what temperature must it be heated to expel one third of the air the pressure remaining con stant Neglect the expansion of the vessel 1 127 C 3 327 C 2 226 5 C 4 427 C

Physics
Magnetism and MatterA beam of protons is moving horizontally towards you As it approaches it passes through a magnetic field directed downward The beam deflects 3 Does not deflect 1 To your left side 2 To your right side orporate Office B 58 Goal Building Budha Colony Patna 1 4 Nothing can be said

Physics
GravitationExample 18 In a double slit pattern 6000 the first order and tenth order maxima fall at 12 50 mm and 14 75 mm from a particular reference point If is changed to 5500 A find the position of zero order and tenth order fringes other arrangements remaining the same fris

Physics
Magnetic Field due to current25 An equilateral triangle of side length 1 is formed from a piece of wire of uniform resistance The current I is fed as shown in the figure Then the magnitude of the magnetic field at its centre O is b a 3 l 2 l c Hol 2 l C 3 3 l b 2 l d zero


Physics
Simple harmonic motionX The equation of a wave is given by Y A sin V k where is the angular velocity and v is the linear velocity The dimensions of k is

Physics
Electromagnetic InductionA uniform and constant magnetic field B coming out of the plane of the paper exists in a rectangular region as shown in figure A conducting rod PQ is rotated about its mid point O with a uniform angular speed win the plane of the paper The emf EpQ induced between P and Q is best represented by the graph PQ P B

Physics
Atomic StructureP 2 3 60 Consider a hydrogen like ionized atom with atomic number Z with a single electron In the emission spectrum of this atom the photon emitted in the n 2 to n 1 transition has energy 74 8 eV higher than the photon emitted in the n 3 to n 2 transition The ionization energy of the hydrogen atom is 13 6 eV The value of Z is JEE Advanced 2018 P 2 3 601

Physics
Electric Field and Potential20 A plane electromagnetic wave Ez 100 cos 6 10 t 4x V m propagates in a medium of dielectric constant 1 1 5 3 2 4 2 2 0 4 4 0

Physics
Kinematics63 For a projectile projected at an angle are equal tan 4 u sin 20 u sin 0 2g sin 20 g 1 tan A 4 tan 4 sin 0 2 D the maximum height and horizontal range 470 R Tant 34 H
Physics
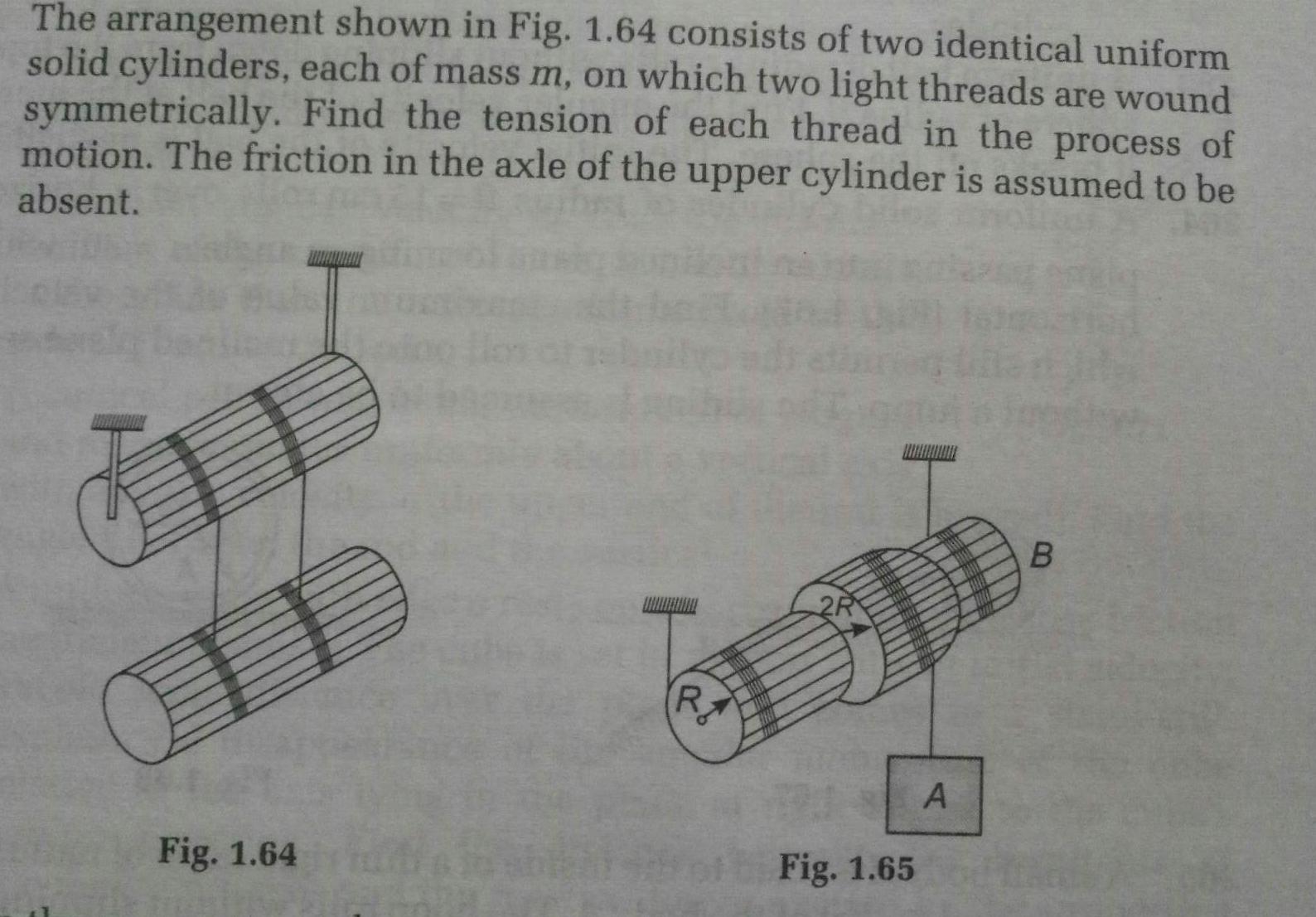
RotationThe arrangement shown in Fig 1 64 consists of two identical uniform solid cylinders each of mass m on which two light threads are wound symmetrically Find the tension of each thread in the process of motion The friction in the axle of the upper cylinder is assumed to be absent Fig 1 64 R 2R TORE BER TIME HOME THE Fig 1 65 N A B

Physics
Work, power & energyIs defined 1 Only in conservative fields 2 As the negative of work done by conservative forces 3 As the negative of workdone by external forces when AK 0 4 All of these

Physics
Properties of matter22 Aballoon of volumie V contains a gas of mass mat a pressure P and temperature 15 C Gas is pumped into the balloon so that its volume is doubled and the pressure is trebled If the temperature increases 6 C in the process finc the ratio of the increase in mass to the origi nal mass 1 34 5 2 239 49

Physics
Current Electricity7 Consider building the following resistor a square ABCD of side length and connect the centers of each side to form another square Connect the centers of each side of this square to form yet another square and so on to infinity Assume that all the wires in the circuit have the same cross section and resistivity Resistance of each side of square ABCD is R c A xR 3 A A3 A2 KA4 D D3 B B2 BKB BA B3 D4 D2 D B C4 C2 C3 C If the resistance between opposite corners A and C of the square ABCD is xR x is a numerical factor the resistance between corners A2 and C is a xR C b xR 2 d None of these

Physics
Basic PhysicsIf two vectors A 1 3 5k and A 1 31 ak are equal then the value of a is a 5 b 5 a 2

Physics
Magnetic Field due to current5 At a point on the right bisector of a magnetic dipole the magnetic a potential varies as 1 b potential is zero at all points on the right bisector c field varies as r d field is perpendicular to the axis of dipole