Basic Physics Questions and Answers

Physics
Basic PhysicsQuestion No 37 Single Correct Three products are being considered as possible thermal insulators The thicknesses and conductivities of the three products are as follows Product I Product II Product III A B Conductivity arbitrary units Product I LANGUAGE ENGLISH 12 6 4 Product II Thickne For a given cross sectional area which product would make the best thermal insulator arbitrary 4 6 2 PHYSICS 1 6 11 16 21 26 31 36 41 2 7 12 17 22 27 32 37 42 CHEMISTRY BIOLOGY 3 8 13 18 23 28 33 38 43 4 9 14 19 24 29 34 39 44 1 N 2 3 3 4 4

Physics
Basic PhysicsTwo particles of equal masses are revolving in circular paths of radii r and r respectively with the same speed The ratio of their centripetal forces is NCERT 1984 Kerala PMT 2004 b a c r2 r1 r 2 d r r 2 r 2

Physics
Basic PhysicsQuestion In free space a particle A of charge 14C is held fixed at a point P Another particle B of the same charge and mass 49s ke at a distance of 1 mm from P If B is released then its velocity at a distance of 9mm from P is 1 4T g Take A 1 0 m s 9 10 Nm C 2 0 x 10 m s B 3 0 x 104 m s 15 x 10 m s JEE Main 20

Physics
Basic Physics4 In an hydrogen atom the electron revolves around the nucleus in an orbit of radius 0 53 x 10 10 m Then the electrical potential produced by the nucleus at the position of the electron is loh Sids 11 b 27 2 V a 13 6 V c 27 2 V d 13 6 V

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe primary and secondary coils of a transformer have 500 and 1000 turns respectively If magnetic flux linked with each turn of primary coil given by 2 2t where is in weber t is time in second The output voltage across the secondary coil will be 1000 V 1500 V 750 V

Physics
Basic PhysicsFour marbles are dropped from the top of a tower one after the other with an interval of one second The first one reaches the ground after 4 seconds When the first one reaches the ground the distances between the first and second the second and third and the third and fourth will be respectively Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 4 35 25 and 15 m 30 20 and 10 m 20 10 and 5 m 40 30 and 20 m

Physics
Basic PhysicsProblem 3 Using a forked rod a 0 5 kg smooth peg P is forced to move along the vertical slotted path r 0 50 m where is in radians If the angular position of the arm is 0 0 125r t2 rad where t is in seconds determine the force of the rod on the peg and the normal force of the slot on the peg at the instant t 2 s The peg is in contact with only one edge of the rod and slot at any instant 050 m

Physics
Basic PhysicsGiven 6 96x10 C a 2 5 10 C Specific heat of Cu 0 092 Cal g C Specific heat of Al 0 230Cal g C Symbols have their usual meanings One night a boy of height h 1 5 mis standing on the bank of a straight canal o the other bank of which a lamp is installed at a height H 6 mon a pole There a no ripples on the water surface so light emanated from the lamp appears as a flar bright spot after reflection from the water surface When the boy starts walking along the bank the flare appears to him moving at a constant speed u 3 m s relative to the ground Find speed of the boy in m s

Physics
Basic PhysicsA plano convex lens fits exactly into a plano concave lens Their plane surfaces are parallel to each other If lenses are made of different materials of refractive indices u and and Ris the radius of curvature of the curved surface of the lenses then the focal length of the combination is NEET 2013 a c R 2 2R 11 11 b d R R

Physics
Basic PhysicsInside an electrical conductor there is a cavity and a charge q is suspended fixed inside the cavity space without any electrical contact with conductor Let E be the electrostatic field due to charge q at P be the electrostatic field at P due to induced charge on the inner surface of cavity E be the electrostatic field at P due the induced charge on the outer surface of conductor then A 3 0 B 0 C 3 0 D 0 Cavity

Physics
Basic Physics90 ATI a B 90 O 11 Oxygen assume it to be ideal gas is filled in a closed container of constant volume If the temperature of the gas is increased by a significant amount some of the molecules dissociate into atoms If the specific heat changes by 8 what fraction of initial amount of oxygen has been dissociated Do not consider vibrational degree of freedom 12 In the figure ammeters read a current of 1A each as shown while the voltmeter reads a potential difference of 3V The ammeters are identical the internal

Physics
Basic Physics15 A charged particle of mass m and charge q is released 15 m G F FOR A lit from rest in an electric field of constant magnitude E The kinetic energy of the particle after time t is proportional to 1 1 2 E 3 q m uso 1 mv 1 mg 1 m 2 3 q m 4 am q 25

Physics
Basic PhysicsA body is thrown with the velocity v at an angle of 0 to the horizon Determine v in ms if the maximum height attained by the body is 5 m and at the highest point of its trajectory the radius of curvature is r 3 m Neglect air resistance Use 80 as 9

Physics
Basic Physics5 pts In a synthetic chemical reaction the theoretical yield refers to The efficiency of a synthetic procedure producing the given products The actual amounts of products that can be produced in a reaction The maximum amount of products that can be produced in a reaction The minimum amount of products that can be produced in a reaction

Physics
Basic PhysicsMonochromatic light of wavelength 6000A is used in a Young s double slit experiment One of the slits is covered by a transparent sheet of thickness 1 8 x 105m made of a material of refractive index 1 6 How many fringes will shift due to the introduction of the sheet A 16 B 18 C 20 D 24

Physics
Basic Physics36 d Here L 1 H C 20 F 20 x 10 6 F 50 R 300 S2 v Hz T The inductive reactance is X 2 vL 2 1 1002 gorb egatlo 004 TOP A8 The capacitive reactance is Xc 50quency 1 2AVC 11001 0 919H b 500 S 50 2x xx20x10 6 TC The impedance of the series LCR circuit is vR Xc XL v 300 500 100 2

Physics
Basic PhysicsA positively charged ring having uniform charge density is shown in the figure Two elements of ring of length 1 and 12 subtend same angle very small at point A Point A is in the plane of ring but not at the centre The elements 1 and 1 are at distance r and r2 respectively from the point A A The ratio of charges of elements and 2 is 1 B Net electric field at point A is zero C The elements and 2 produce same potential at A D The direction of net electric field at A is towards 2

Physics
Basic PhysicsA thin walled glass container is filled with water u 4 water A point source is fixed inside water A thin equiconvex lens u 1 5 and concave mirror are arranged with mutual separation as shown in figure R B R 2 R 2 The distance of lens from the plane surface of the container is also R 2 Here R is radius of curvature of all curved surfaces If the distance of the source from the 3 reflection at the concave mirror will be A 2R B 4R C 4R 2R point A is the separation between the source and the image formed after D 7R

Physics
Basic PhysicsA particle of mass m is confined in a two dimensional square well potential of dimensional a This potential V x y is given by V x y 0 for a x a and a y a elsewhere What is the energy of the second excited state for this particle

Physics
Basic PhysicsA free particle of mass m moves along the x direction At t 0 th normalized wave function of the particle is given by 4 x 0 2m 1 4 exp ix where a is a real constant 1 2 4 What is the expectation value of the momentum in this state What is the expectation value of the particle energy i ii

Physics
Basic PhysicsAn ideal gas expands from state P V to state P2 V2 where P2 2P1 and V 2V The path of the gas is expressed by the following relation P P 1 4 TO O V V V C Work done is 1 V V P PI 1 x x P P 1 V P2 2P1 A P1 V1 B 4 3 P1V1 2P1 V1 D 4P1 V1 P V V 2V1 faral sid af

Physics
Basic PhysicsA small transparent slab containing material of 1 5 is placed along AS as shown in figure The distance of the principal maxima and the first minima from point O on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab is respectively AC CO D S C S C d D S L d 4 C 10 a 0 19 D and 0 33 D b 0 19 D and 0 55 D c 0 33 D and 0 65 D d 0 33 D and 0 75 D P O Screen

Physics
Basic PhysicsComplex Toh FeN3 U SCN 4 is hamed as Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 Azidosuperoxidotetrathiocyanato S ferrate II ion Azidodioxygentetrathiocyanato S ferrate III ion Azidoperoxidotetrathiocyanato S ferrate II ion

Physics
Basic PhysicsOne beam of coherent light travels path P1 in arriving at point Q and another coherent beam travels path P2 in arriving at the same point If these two beams are to interfere destructively the path difference P1 P2 must be equal to O an odd number of half wavelengths zero a whole number of wavelengths a whole number of half wavelengths 1
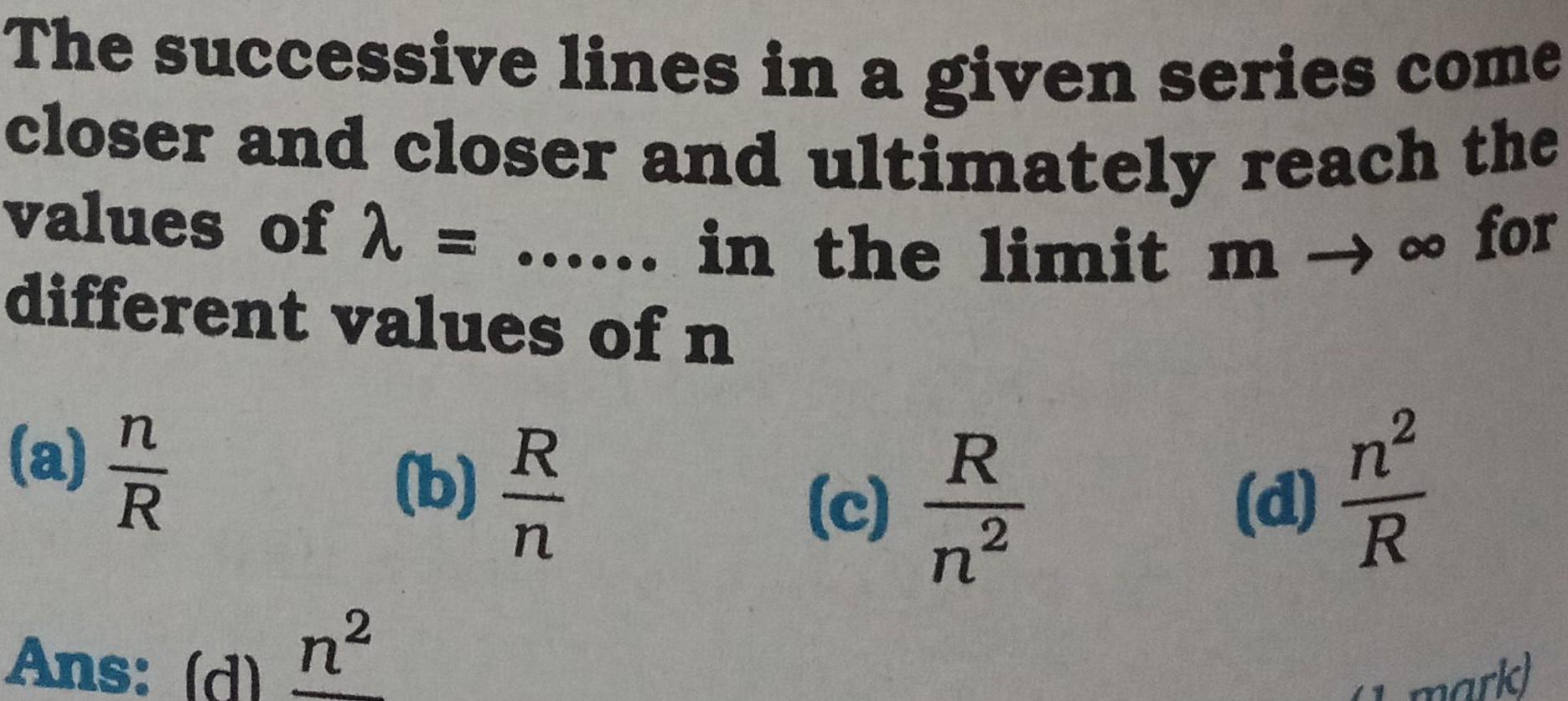
Physics
Basic PhysicsThe successive lines in a given series come closer and closer and ultimately reach the values of in the limit m for different values of n a R Ans d n b P R R c 7 n d R 1 mark

Physics
Basic PhysicsA wide vessel with a small hole at the bottom is filled with two liquids The density and height of one liquid are p and h and that of the other are p2 and h P1 P2 The velocity of liquid coming out of the hole is Question Type Single Correct Type 1 v 2g h h 2 3 4 v 2g h p h p P P h P 28 h h2p P1 v 2g V M P 2g P h

Physics
Basic PhysicsA metal sphere A of radius a is charged to potential V What will be it s potential if it is enclosed by a conducting spherical shell B of radius b and two are connected by a conducting wire 1 V 3 1 v a B 2 3 4 None of these

Physics
Basic Physics23 A small particle of mass m is projected at an angle with the x axis with an initial velcoity v in the x y plane as shown in the figure At a time t v sine g the angular momentum of the particle is 0 A mgv t cos ej B mgv tcos Ok C mgv t cosok D mg D os O i mgv t cos AIEEE 2010 xv direction option

Physics
Basic PhysicsWhich experiment is responsible for finding out the charge on an electron a Millikan s oil drop experiment b Cathode ray discharge tube experiment c Rutherford s a rays scattering experiment d Photoelectric experiment

Physics
Basic Physics24 In figure battery B supplies 12 V Find the charge on each capacitor C C3 b S C B S C4 a first when only switch S is closed and b later when S is also closed Take C 10 C 20uF C 3 0 F and C4 4 0 F b

Physics
Basic PhysicsTwo forces are such that the sum of their magnitudes is 18 N and their resultant is perpendicular to the smaller force and magnitude of resultant is 12 N Then the magnitudes of the forces are 1 12 N 6 N 2 13 N 5N 3 10 N 8 N 4 16 N 2 N

Physics
Basic Physics6 If two objects of masses 2 5 kg and 100 kg experience the same force 5 N What is the acceleration experienced by each of them 7 What is called free body diagram 8 When an Apple falls it experiences Earth s gravitational force According to Newton s third law the Apple exerts equal and opposite force on the Earth Why does Earth appear to be stationary when an apple falls

Physics
Basic PhysicsA semicircular disc of radius r is released from rest from the position shown If no slipping occurs between the disc and the horizontal surface determine the expression for the angular velocity w reached by the disc when its kinetic energy is maximum 16g 97 16
Physics
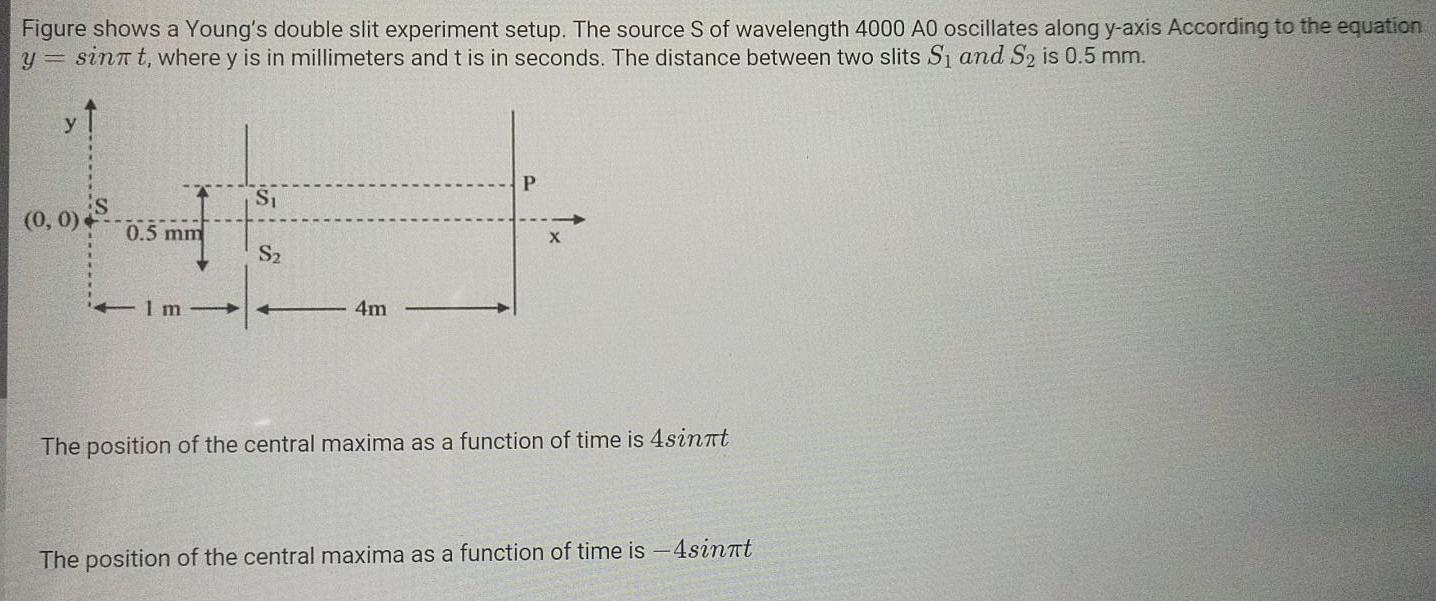
Basic PhysicsFigure shows a Young s double slit experiment setup The source S of wavelength 4000 A0 oscillates along y axis According to the equation y sinnt where y is in millimeters and t is in seconds The distance between two slits S and S2 is 0 5 mm y 0 0 0 5 mm S S 1m 4m P X The position of the central maxima as a function of time is 4sinnt The position of the central maxima as a function of time is 4sinnt

Physics
Basic Physics3 b c 8 1 d 16 1 29 In Young s double slit experiment one of the slits is wider than the other so that the amplitude of the light from one slit is double that from the other slit If I be the maximum intensity the resultant intensity when they interfere at phase difference o is given by a 1 2cos b 1 4 cos Im 1 8 cos 2 d 8 cos 9 9 c m 3

Physics
Basic PhysicsA smooth tube of certain mass closed at both ends is rotated in a gravity free space and released The two balls shown in figure moves towards the ends of the tube and stay there Then which statement is incorrect about this whole system 1 Total angular momentum will remain conserved 2 Total linear momentum will remain conserved 3 Total kinetic energy of system will decrease 4 Total mechanical energy will remain constant f fafted cur an feari zya an or to defeat fu s acs of fea farger and change yt facra fery Tera 1 ifua m 2 tea ander m 3 4 fara a fi fe

Physics
Basic PhysicsQ The instantaneous voltages at three terminals marked X Y and Z are given by Vx Vo sin wt Vy Vo sin wt 2 and 3 Vz Vo sin wt 4 An ideal voltmeter is configured to read rms value of the potential difference between its terminals It is connected between points X and Y and then between Y and Z The reading s of the voltmeter will be A VXY Vo B VW Vo C Independent of the choice of YZ the two terminals D Vms XY V 3 Vo

Physics
Basic Physics2 A convex lens of radii of curvature 20 cm and 30 cm respectively It is silvered at the surface which has smaller radius of curvature Then it will behave as 14 1 5 a concave mirror with equivalent focal length 30 11 b concave mirror with equivalent focal length 60 cm cm 11 c convex mirror with equivalent focal length 30 cm 11 d convex mirror with equivalent focal length 60 11 cm 68 Th an 3 of a c 69 Fa de an 2 70 A of the a

Physics
Basic Physics10 The potential difference across the terminals of a battery is 10 V when there is a current of 3A in the battery from the negative to the positive terminal When the current is 2 A in the reverse direction the potential difference becomes 15 V The internal resistance of the battery is a 2 5 Q b 5 0 d 19 c 2 83 9

Physics
Basic PhysicsIn Newton s ring experiment the diameter of the 10th ring changes from 1 40 to 1 23 cm when a liquid is introduced between the lens and glass plate What is the refractive index of the liquid O 1 05 O 1 15 O 1 25 O 1 35

Physics
Basic PhysicsLight of wavelength 580 nm is incident on a slit of width 0 300 mm An observing screen is placed 2 00m from the slit Find the position of the first order dark fringe from the center of the screen O 0 26 mm O 1 9 mm 3 9 mm 7 7 mm 2

Physics
Basic Physicserou tanya Academy 0 Two inclined planes OA and OB of inclinations to the horizontal area and B each equal to 30 as shown in the figure A particle is projected at an angle of 90 with plane OA from point A and its strikes the plane OB at point B normally Then find the speed of projection in m s given that OA OB 20 cm and g 10 m s u 90 ATI a B TITEXT 90

Physics
Basic Physics3 The accelaration due to gravity on a planet is 3 2 times that on the earth If length of seconds pendulum on earth is 1m length of seconds pendulum on the planet is 2 1m 4 1 5m 1 0 7 m 3 1 7m

Physics
Basic PhysicsA string fixed at both ends and under tension T vibrates in its 1 overtone with an amplitude A at the antinodes The total energy of the string is E and the maximum possible speed of a particle of the string is v If the same string were to vibrate in its fundamental mode under a tension 4T and with an amplitude A at the antinode then A The total energy of the string will be E B The total energy of the string will be 2E C The maximum possible speed of a particle on the string is v D The maximum possible speed of a particle on the string is 2v

Physics
Basic Physicsorder of and 7 order of 2 8 Young s double slit experiment uses a monochromatic source of light The shape of interference fringes formed on the screen is a parabola c circle b straight line d hyperbola

Physics
Basic Physicserect nd inverted c 25 justment a 91 A giant telescope in an observatory has an objective of focal length 19 m and an eye piece of focal length 1 0 cm In normal adjustment the telescope is used to view the moon What is the diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective The diameter of the moon is 3 5 x 10 m and the radius of the lunar orbit round the earth is 3 8 x 10 m he objective of this line ification of L 1 L 1 tronomical gth of the the least a c b 50 d 5 10 cm 15 cm b d MISCELLANEOUS 12 5 cm 17 5 cm

Physics
Basic Physics3 One of the combinations from the fundamental physical constants is hc G The unit of this expression is a kg2 b m c s 1 d none of the above National Standard Exam in Physics 2001 10 c 44 In th

Physics
Basic Physics227 tant 20 Light from two coherent sources of the same my of amplitude A and wavelength illuminates the screen The intensity of the central maximum is 1 If the sources were incoherent the intensity at the same point will be a 41 b 21 AVES bjects d

Physics
Basic PhysicsIn Young s double slit experiment the fringe width is 1 x 10 m If the distance between the slit and screen is doubled and the distance between the two slit is reduced to half and wavelength is changed from 6 4 x 10 7 m to 4 0 x 10 7 m the value of new fringe width will be 00 15 x 10 m 2 0 10 m 01 25 10 m 25 10 m 4 Marks 4 1

Physics
Basic PhysicsQ At time t 0 terminal A in the circuit shown in the figure is connected to B by a key and an alternating current I t Io cos wt with 10 1A and W 500rads starts flowing in it with the initial 7 6w the key is direction shown in the figure At switched from B to D Now onwards only A and D are connected A total charge Q flows from the battery to charge the capacitor fully If C 20 F R 100 and the battery is ideal with emf of 50 V identify the correct statement s BD A C 20 F www R 1022 A Magnitude of the maximum charge on the capacitor before t clockavice C in the part of the circuit just before t 7 is 1 x 10 C B The current 6w 50V 7T 6w is