Center of mass and momentum Questions and Answers

Physics
Center of mass and momentum6 0 points Let the mass density in kilogram per unit area of a disk of radius one meter be given by f x 1 e where x is the distance from the center of the disk in meter a 5 points calculate the total mass of this disk

Physics
Center of mass and momentumIn the figure shown a ball is released from top of the smooth track If the ball strikes the smooth horizontal surface of the track and bounces off it again strikes the horizontal surface at some distance R from B and rises to a height maximum of h above the surface If the coefficient of restitution for the collision is e R is maximum for e 1 3 R is maximum for e 1 for all values of e h h for e 1

Physics
Center of mass and momentumIn uniform circular motion 1 Both the angular velocity and the angular momentum vary 2 The angular velocity varies but the angular momentum remains const 3 Both the angular velocity and the angular momentum stay constant

Physics
Center of mass and momentum20 Two blocks M and M having equal r are to move on a horizontal frictionless surface Mis attached to a massless spring as shown in figure Initially M is at rest and M is moving toward M with speed v and collides head on with M M m M m booooo a While spring is fully compressed all the kinetic energy of M is stored as potential energy of spring b While spring is fully compressed the system s momentum is not conserved though final momentum is equal to initial momentum If spring is massless the final state of the Mis state of rest c d If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction then collision cannot be elastic A block of mass m 2 kg is resting on a rough

Physics
Center of mass and momentum1 In uniform circular motion a both the angular velocity and the angular momentum vary the velocity varies but the momentum remains constant c magnitude of both the velocity and the momentum stay constant d the momentum varies but the velocity remains constant b

Physics
Center of mass and momentum6 For the same mass which of the following will have the largest moment of inertia about an axis passing through the centre of gravity and perpendicular to the plane of the body a A disc of radius a A ring of radius a b c A square lamina of side a d Four identical rods forming square of side a 21

Physics
Center of mass and momentum44 A ball is thrown at an angle of incidence 0 on a horizontal plane such that the incident direction and the reflected direction are at right angles to each other If the coefficient of restitution is e then e is equal to 1 tan e 2 tan 2e 3 tan 2 e 4 tan e

Physics
Center of mass and momentum12 A particle strikes a horizontal frictionless floor with a speed u at an angle 0 with the vertical and rebounds with a speed v at an angle a with the vertical Find the value of v if e is the coefficient of restitution 1 v u e sin 0 co 02 v u e cos 0 sin 0 2 3 v u e cos0 ta 0 4 v uycot 0 e cos

Physics
Center of mass and momentum45 Consider the collision depicted in fig to be between two billiard balls with equal masses m m The first ball is called the target The billiard player wants to sink the target ball in a corner pocket which is at an angle 0 37 Assume that the collision is elastic and that friction and rotational motion are not important then is m 1 278 y axis m 2190 0 0 V V 3 45 x axis 4 53 irontal ground

Physics
Center of mass and momentumAs shown in the figure a 60 cm length of uniform wire of mass 60 g is bent into a right triangle What are the x and y coordinates of the center of mass or center of gravity of this triangle 10 cm 0 26 cm 24 cm 8 0 cm 3 0 cm 9 0 cm 4 0 cm 8 0 cm 5 0 cm 10 cm 3 0 cm 10 cm 5 0 cm

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA ball projected horizontally from a large inclined plane collides successively with the plane Coefficient of friction between the plane and the ball during these collisions is u What should be inclination of the plane and coefficient of restitution for the collisions so that between every two successive bounces the ball follows identical trajectories tan 1 16

Physics
Center of mass and momentumNEET 19 A particle of mass m strikes elastically on a wall with velocity v at an angle of 60 from the wall then magn e in momentum of ball along the wall is change 1 Zero 3 3mv Laws of Motion 2 2mv 4 mv

Physics
Center of mass and momentumd 2 1 3 Figure shows position and velocities of two particles moving under mutual gravitational attraction in space at time t 0 YA 2 kg 8ms l2ms 13 kg x x 2m x 12 m The position of centre of mass after one second is a x 4m b c x 8m d x 6m x 10 m

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo equal and opposite forces are applied tangentially to a uniform disc of mass M and radius R as shown in the figure If the disc is pivoted at its centre and free to rotate in its plane the angular acceleration of the disc is MR 20 SMR

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA 5 kg stationary bomb is exploded in three parts having mass in the ratio 1 1 3 respectively If parts having same mass move in perpendicular directions with velocity 30 m s then the speed of the bigger part will be 1 10 2 m s 2 10 m s 3 13 2 m s 15 4 m s

Physics
Center of mass and momentum2 PRACTICE P ractice Paper is an apt tool for scoring more these questions in exam like environment work upon Give yourself four marks for correcm given at the end that will help you plan your ne Time Allowed 50 min 1 Four particles of masses m 2m 3m and 4m are arranged at the corners of a parallelogram with each side equal to a and one of the angle between two adjacent sides as 60 The parallelogram lies in the x y plane with mass m at the origin and 4m on the x axis The centre of mass of the arrangement will be located at a 4 05 2 2 a 0 95a b 0 95a a 3a 3 4 5 A g subi 0 5 the E a c 6 A wa If wa equal

Physics
Center of mass and momentum7 Two masses m 3 60 kg and m 5 75 kg are connected by a thin rod of negligible mass with a length of 2 55 m as shown below m 3 60 kg 0 0 2 55 m m 5 75 kg a If we assume mi is located at x 0 m where is the center of mass of the system 10 points

Physics
Center of mass and momentum19 a massless ridgid rod has balls of mass m 2m 3m 4m and 5m evenly spaced in order of mass along the rod with the ball of mass m at the left end and the ball of mass 5m at the right end if the rod has a length L where is the location of the center of mass A L 3 b L 2 C 3L 5 D 2L 3 E 3L 4 6 A boy of mass 20kg stands on one side of a see saw a distance 2 5m from the pivot point how far from the pivot on the opposite side must his sister who has a mass of 55kg stand for the see saw to be balanced

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA particle of mass m moving with a velocity of 5m s collides head on with a stationary particle of mass m2 After collision both the particle move with a common velocity of 4m s then the value of m m is Question Type Single Correct Type 1 4 1 2 2 1 3 1 8

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA uniform cubical block of size a is moving with velocity v on the horizontal smooth plane as shown in figure It hits a small ridge at O The angular speed of the block after it hits O assuming it does not jump off is LO 3 3v 4a 3v Fa a H 2 3v 2a 4 Zero

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA particle of mass 2 kg is moving on a straight line y 2x 4 with velocity 2 m s Then magnitude of angular momentum of the particle w r t origin is 16 Kgm 1 5 sec 8 3 5 Kgm sec 2 32 Kgm 5 sec 4 32 5 Kgm sec

Physics
Center of mass and momentum813 The centre of mass of a non uniform rod of length 4 whose mass per unit length is K 3x kg m where x is in m The distance of centre of mass from its one enc which is at origin will be 53 m L 3 hr m

Physics
Center of mass and momentum4 55 A metre stick of length and mass M is placed on a frictionless horizontal table A hockey ball of mass m sliding along the table perpendicular to the stick with speed v strikes the stick elastically at distance d from the centre of the metre stick Find d if the ball is to be brought to rest immediately after the collision Fig 4 13 Fig 4 13 M

Physics
Center of mass and momentumThe moment of inertia of the two uniform joint rods about axis passing through P and perpendicular to plane is 1 Me 3 3Me M M l M l I s M 3 P 4 fu 4 2Me 3 5Me mi 12 19 S 2 2 V M

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA cylinder of mass M and raidus R moves with constant speed v through a region of space that contains dust particles of mass m which is at rest There are n number of particles per unit volume The cylinder moves in a direction perpendicular to its axis Assume m M and assume the particles do not interact with each other All the collision takes place is perfectly elastic and the surface of the cylinder is smooth The drag force per unit length of the cylinder require to K maintain the speed v constant for the cylinder when it has entered in the region is nm Rv2 Find the value of K 3 R

Physics
Center of mass and momentumc 5v0 2 oR d 2V0 51 The radius of gyration of a solid hemisphere of mass M and radius R about an axis parallel to the diameter at a distance Ris given by centre of mass 3 4 of the hemisphere lies at a height 3R 8 from the base 3R a 10 5R 8 c 3R 4 P b d O 5R R

Physics
Center of mass and momentumc R r t 49 A right triangular plate ABC of mass m is free to rotate in the vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis through A It is supported by a string such that C the side AB is horizontal The reaction at the support A is b a mg 3 d Data is insu 2mg 3 c mg 2 J A uniform sphere of radius Ris A B d mg

Physics
Center of mass and momentumCOMPREHEN A massless elastic cord that obeys Hooke s law will break if the tension in the cord exceeds Tmax One end of the cord is attached to a fixed point the other is attached to an object of mass 3m as shown in the figure If a second smaller object of mass m moving at an initial speed vo strikes the larger mass and the two stick together the cord will stretch and break but the final kinetic energy of the two masses will be zero If instead the two collide with a perfectly elastic one dimensional collision the cord will still break and the larger mass will move off with a final speed of v All motion occurs on a horizontal frictionless surface assume that Hooke s law is obeyed throughout until the cord breaks Find Y H

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA proton of mass m collides with a heavy particle 4 at rest After collision proton bounces back with 9 of its initial kinetic energy Collision is perfectly elastic Find mass of heavy particle 1 5 m 2 6 m 3 3 m A small particle elastically strikes a fixed smooth cas 4 1 5 m mp

Physics
Center of mass and momentumFixed 16 Two particles of equal mass have velocities v 2 1 m s and v 23 m s First particle has an a 31 31 m s acceleration while the acceleration of the other particle is zero The centre of mass of the two particles moves in a vino a circle 1 c straight line b parabola d ellipse

Physics
Center of mass and momentum6 A particle of mass m moves with speed u and collides head on with a stationary particle of mass m The first particle continues to move in the same direction if is e coefficient of restitution m c e m a e 6 e d e

Physics
Center of mass and momentumners of s of each ystem is 3 Two blocks A and B of mass mand 2 m are connected by a massless spring of force constant k They are placed on a smooth horizontal plane Spring is stretched by an amount x and then released The relative velocity of the blocks when the spring comes to its natural length is a c 3k 2m 2kx m X b d 2k 3m 3km 2x X

Physics
Center of mass and momentum14 Initially two stable particles x and y start moving 1 towards each other under mutual attraction If at one time the velocities of x and y are V and 2V respectively what will be the velocity of centre of es mass of the system 1 V 3 3 2 Zero 4 V

Physics
Center of mass and momentum10 A ball of mass 4 kg strikes another 10 4 kg stationary ball of mass 2 kg with velocity Qua Beer Fot 600 83 10 ms Assuming perfectly elastic collision the velocity of 4 kg ball in ms 1 just after collision is 10 1 10
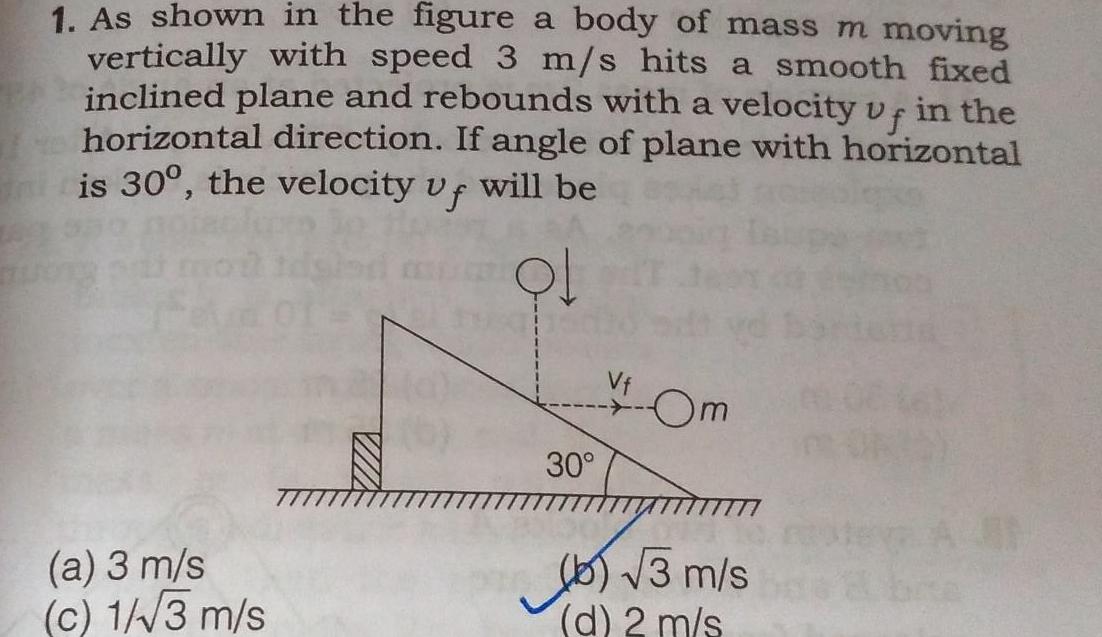
Physics
Center of mass and momentum1 As shown in the figure a body of mass m moving vertically with speed 3 m s hits a smooth fixed inclined plane and rebounds with a velocity vf in the horizontal direction If angle of plane with horizontal is 30 the velocity uf will be a 3 m s c 1 3 m s ma a 30 Om b 3 m s d 2 m s

Physics
Center of mass and momentum2 A hemisphere of radius R and of mass 4 m is free to slide with its base on a smooth horizontal table A particle of mass m is placed on the top of the hemisphere The angular velocity of the particle relative to centre of hemisphere at an angular displacement when velocity of hemisphere has become vis a 5v R cos 0 2V R cos 0 b c 3v R sin 0 d 5 v R sin 0

Physics
Center of mass and momentum1 A ship of 5600 tonnes displacement is floating upright A weight of 30 tonnes is lifted from the port side of No 2 tween deck to the starboard side of No 2 shelter deck 10 m horizontally Find the weight of water to be transferred in No 3 double bottom tank from starboard to port to keep the ship upright The distance between the centres of gravity of the tanks is 6 m

Physics
Center of mass and momentumlar as d e 8 A small block of superdense material has a mass M 3 where M is the mass of earth It is released from rest from a height h radius of earth from the surface of earth The speed of the block at a height is h 2 a gh d 2gh b 3gh 2 c 2gh V 3 9

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA 7 A gun fires a bullet as shown in figure The barrel of the gun is inclined at an angle of 45 with horizontal When the bullet leaves the barrel it will be travelling at an angle to the horizontal of a 456 c more than 45 L b less than 45 d zero 45

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA bomb of mass 30 kg at rest explodes into two pieces of masses 18 kg and 12 kg The velocity of 18 kg mass is 6 m s The kinetic energy of other fragment is 524 J 486 J 312 J

Physics
Center of mass and momentum4 A ball of mass m approaches a wall of mass M m with speed 4 m s along the normal to the wall The speed of wall is 1 m s towards the ball The speed of the ball after an elastic collision with the wall is a 5 m s away from the wall b 9 m s away from the wall c 3 m s away from the wall 6 m s away from the wall dys

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo masses move towards each other as shown in figure They collide and stick together How much energy is converted to heat Assume energy loss is completely converted in to heat A mv cos 0 I m B mv sin 0 m C mv sin 0 D mv cos 0

Physics
Center of mass and momentum38 A non conducting sphere of radius R and uniformly distributed charge Q is fixed in a gravity free space and a particle having charge q is projected with a certain velocity vo from point P in such a way that it grazes the sphere at point A as shown in the figure with kinetic energy K The value of K is diameter AB is parallel to initial velocity vector vo k 1 a 4kQq 5R 9kQq 1 1 A 3R C 4R B b IN 9 P 5kQq 9R 3kQq 4TEO

Physics
Center of mass and momentumThe centre of mass of a non uniform rod of length 4 m whose mass per unit length is K 3 kg m where x is in m The distance of centre of mass from its one end which is at origin will be 813 5 3 3 213 m 5 m

Physics
Center of mass and momentuman ideal monatomic gas around the cycle ABCA as shown in the diagram The process BC is adiabatic Call the processes AB BC and CA as 1 2 and 3 and the heat AQ change in internal energy AU and the work done AW r r 1 2 3 respectively The temperature at A B C are T 300K T 600K and 455K T3 Indicate the pressure and volume at A B and C by Pr and Vr r 1 2 3 respectively Assume that initially pressure P 1 00atm Which of the following represents the

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA wedge of mass m with triangular cross section AB CB CA 2R is moving with a constant velocity Vi towards a sphere of radius R fixed on a smooth horizontal table as shown in the figure The wedge makes an elastic collision with the fixed sphere and returns along the same path without any rotation Neglect all friction and suppose that the wedge remains in contact with the sphere for a very short time At during which the sphere exerts a constant force F on the wedge 1998 a Find the force F and also the normal force N exerted by the table on the wedge b Let h denote the perpendicular distance between the centre of mass of the wedge and the line of ction of F Find the magnitude of the torque due to the normal force N about the centre of the edge during the interval At R B A C

Physics
Center of mass and momentumrigid massless rod of length 3 has two masses attached at each end as shown in the figure The rod is pivoted at pint p on the horizontal axis see figure When released from initia horizontal position its instantaneous angular acceleration will be a 9 13 b 9 5 M c 7g 3 2 M d 3

Physics
Center of mass and momentumd v 24 A molecule of mass m moving at a velocity v elastically impinges on the wall at an angle a with the wall then a the impulsive reaction of the wall is 2mvcos a b the impulsive reaction of the wall is 2mvsin a c the impulsive reaction of the wall is nonzero d given data is insufficient to calculate impulsive reaction of the wall

Physics
Center of mass and momentum8 Two billiard balls each of mass 50 g moving in opposite directions with a speed of 40 km h collide and rebound with the same velocity What will be the impulse imparted to each ball due to other ball

Physics
Center of mass and momentum28 The dimensional formula of farad ohm is 1 MOLOTOA 2 MOLTO 3 MOLOTA 4 MOLTA 29 The value of R in the given circuit is R 822 1 29 i 2 A 292 40 V 2 10 92 4 42