Fluids Questions and Answers

Physics
Fluidsn is completely filled with water The container is placed on a frictional surface with coefficient of friction and a small hole is punctured at a depth on container wall h If area of hole is a and area of base of container is A a A then the value of u for which the container remains stationary is g 10 m s 1 3 7 a A 3a 2 2a A 4 All of the above

Physics
FluidsA cylindrical tank having cross sectional area A is filled with two liquids of density p 2p to a height h 2h respectively A small hole having area a is made in vertical wall so as to achieve maximum range of effluxed liquid on ground If cylinder is massless p 1000 kg m h 0 5 m A 1 m a 1 cm 2h Read Less Height of hole under the condition mentioned in the paragraph is 1m

Physics
Fluids7 44 In the arrangement shown in figure 7 112 a viscous liquid whose density is 1 gm cm flows along a tube out of a wide tank A Find the velocity of the liquid flow if h 10 cm h 20 cm h 35 cm All the distances are equal hi 7 7 7

Physics
Fluids2 A ball floats on the surface of water in a container exposed to the atmosphere Volume V of its volume is inside the water The container is now covered and the air is pumped out Now let V be the volume immersed in water Then a V V c V V b V V d V 0

Physics
FluidsThe arrangement shown in the figure gure is of of a cylindrical tube of uniform cross sectional area The vertical limbs contain a liquid of density p to a height h each The lower horizontal part of length 2h of the tube contains a liquid of density 2p The arrangement is finally accelerated horizontally at NO m s Find the difference in the heights of the liquid in the two vertical limbs h 4h 2h 2 8h 7 h 2p

Physics
Fluids23 A wooden block with a coin placed on floats in water as shown in the figure The distances h and I are shown there After some time the coin falls into the water then Coin H 1 Both and h increase 2 Both and h decrease 3 decreases and h increases 4 increases and h decreases

Physics
FluidsSixty four spherical rain drops of equal size are falling vertically through air with a terminal speed of 2 5 m s If these drops coalesce to form a big spherical drop then terminal velocity of big drop is 10 m s 40 m s 20 m s 30 m s

Physics
FluidsConsider a U tube with liquids filled inside as shown in the figure If the system is at rest then the value of h will be approximately Poil 0 8 g cc Pmercury 13 6 g cc and Pglycerol 1 3 g cc Glycerol Oil 20 cm 12 8 cm 20 8 cm 7 3 cm 24 1 cm Mercury

Physics
Fluids139 A capillary tube of radius r is immersed in water and water rises in it to a height h The mass of the water in the capillary is 5 g Another capillary tube of radius 2r is immersed in water The mass of water that will rise in this tube is h 1 2 5 g 5 0 g 3 4 10 0 g 20 0 g t s 27 egr hi 2 mix The Fi

Physics
Fluidswith water Now the container is accelerated horizontally with 9 a L No water will spill out Volume of water spill out 0 05 L L3 Volume of water spill out 0 1 L L 5 a

Physics
FluidsAs shown in figure a compressed gas at gauge pressure Pis enclosed in the container above liquid of density P2 Liquid of density to height of h is immiscible with liquid of density extending to height above liquid 1 Are of cross section at 1 is 1 3 of area of cross section at 2 Consider atmospheric pressure as Po P LP The speed at point 1 is V The speed at point 1 is V P 10 Q 9 P gloh p l 4P ZP gph ph 13p The height P pm If a is the area of cross section at point 1 then rate of flow of liquid out of container is 19a

Physics
FluidsS The pressure acting on a submarine is 3 105 Pa at a certain depth If the depth is doubled the percentage increase in the pressure acting on the submarine would be Assume that atmospheric pressure is 1 105 Pa density of water is 10 kg m 3 1 2 3 200 3 3 200 200 5 5 0 10 g 10 ms 2

Physics
FluidsA fountain pen works on the principle of O flow of liquids from higher to lower potential O capillary action Bernoulli s principle Quiccocity of liquido

Physics
FluidsA U tube is filled with two liquids A and B of densities pand 2p as shown in the figure initially Left arm is closed and air filled above the liquid at atmospheric pressure Po and right arm is open to atmosphere Now liquid of density pis slowly poured in right arm till the level of liquid of density 2p becomes equal in the two arms Neglect any variation in the temperature of the system Given Height hy is 2 2h Level of liquid B drop in right arm by 140 141 20 ho 2 2 Po 2h Area of cross section of left arm is 2S and that of right pg is S Assume that the length of right arm is sufficiently large 19 ho 3 Length of liquid A in right arm is ho 2 3h 3 3h 3 2h 3 2h 32h 4 4h 4 3h 2 ho 4 4h h

Physics
Fluids131 A simple pendulum has a time period T The pendulum is completely immersed in a non viscous liquid whose density is 1 T the material of the bob The time period of the pendulum immersed in the liquid is 2 20 T 19 20 3 20 th of that of T 19 918 20 T 134 A par motic 32 When an oscillator completes 100 oscillation its The 1 3 135 A

Physics
Fluids0 A liquid stands at the plane level in U tube when a rest If areas of cross section of both the limbs are equal what will be the difference in heights h of the system liquid in the two limbs of U tube when the s given an acceleration a in horizontal direction towards right as shown T2 H T L T2 a La

Physics
Fluidsdrical tube of uniform cross sectional area A is fitted with two air tight frictionless pistons wire The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire Initially the pressure of the gas is po and Po temperature is To atmospheric pressure is also po Now the temperature of the gas is increased to 2To the tension in the wire will be a 2 PA b PA c PA 2 d 4 PA

Physics
FluidsA razor blade floats on the surface of water contained in a glass When the glass is gently shaken the razor blade sinks Mark the incorrect statement 1 Volume of displaced water is lesser than blades own volume 2 When the razor blade sinks the height of the water decreases 3 For a floating body of greater density than water its weight is balanced by the compressive forces of the water below it 4 Weight of razor blade is equal to the weight of the displaced water due to volume occupied by the razor blade and some additional region affected by cunfoo

Physics
Fluids12 A ferry boat has internal volume 1 m and weight 50 kg a Neglecting the thickness of the wood find the fraction of the volume of the boat immersed in water b If a leak develops in the bottom and water starts coming in what fraction of the boat s volume will be filled with water before water starts coming in from the sides

Physics
Fluids11 A metal piece of mass 160 g lies in equilibrium inside a glass of water figure 13 E4 The piece touches the bottom of the glass at a small number of points If the density of the metal is 8000 kg m find the normal force exerted by the bottom of the glass on the metal piece

Physics
Fluids28 Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross section figure 13 E7 The area of cross section at A and 2 and 2 mm respectively If 1 cc of water Bare 4 mm enters per second through A find a the speed of water at A b the speed of water at B and c the pressure difference PA PB 2 A 0 94 cm B Figure 13 E7

Physics
Fluids5 A cubical box is to be constructed with iron sheets 1 mm in thickness What can be the minimum value of the external edge so that the cube does not sink in water Density of iron 8000 kg m 8 and density of water 1000 kg m

Physics
Fluidsin the two arms of the manometer shown in figure 13 E1 are 2 cm and 8 cm Atmospheric pressure 101 x 10 N m Find the pressure of the gas in the cylinder and the pressure of mercury at the bottom of the U tube The EU gas C Figure 13 E1 409X105 N m

Physics
Fluidssides 13 A cubical block of ice floating in water has to support a metal piece weighing 0 5 kg What can be the minimum edge of the block so that it does not sink in water Specific gravity of ice 0 9

Physics
FluidsA liquid is flowing in streamline manner in a pipe 1 with rate of x If the same liquid is flowing in a pipe of radius half of pipe 1 and length twice the pipe 1 with same pressure difference the rate of flow of liquid for this pipe is 1 3 23 3 X 25 2 4 X 22

Physics
Fluids15 Consider water moving through a pipe The diameter of the inlet is 10 cm and the diameter at the outlet is 7 cm What is the velocity at the outlet if the velocity at the inlet is 10 m s assume the pressure and temperature remain the same Cannot determined without knowing the density of water at the inlet 80 m s 5 m s 20 m s

Physics
FluidsAn inverted hollow cone of height H and radius at the top R is filled completely with a liquid of density d Neglect atmosphere pressure a Find horizontal component of the force which the liquid exerts on half curved side wall of the cone b Find the vertical downward component of the thrush force due to water pressure which the liquid exerts on half side curved wall of the cone R

Physics
Fluids1 A small block of material having relative density is immersed in a liquid and released The 3 block starts moving upwards with an acceleration a The value of a is Given g is acceleration due to gravity

Physics
Fluids5 Find out the correct direction for the flow of water in the given system A 1 3 Y 12 Y 9 AB CK TK OP 12 TP 7 Y 12 B W B C 2 4 A B TK B

Physics
FluidsQ 15 A liquid of density p is filled in a conical vessel as shown in Fig Force exerted by liquid on side wall is A R pgh B R pgh 3 h R C R pgh D 0

Physics
Fluidsm m pV P F F PA Pgauge P Po P Po pg F Pfluid9 Vsubmerged A V t Po 1 atm 1 0 x 105 Pa Pwater 1000 kg m g 9 8 m sec Acircle Tr Volume Flow Rate 1 1 Av A1v1 A202 P p v pgy P 3p v pgy2 Water 15 0 cm Mercury Water B Oil Barrier Problem 1 In the figure aboe on the left a U shaped tube open to the air at both ends contains some mercury the density of mercury is pm 13 600 kg m A quantity of water is carefully poured into the left arm of the U shaped tube until the vertical height of the water column is 15 0 cm a What is the gauge pressure at the water mercury interface Answer 1470 Pa b Calculate the vertical distance h from the top of the mercury in the righthand arm of the tube to the top of the water in the left hand arm Answer 13 9 cm

Physics
Fluidseffect An iron sphere is dropped into a viscous liquid Which of the following represents its acceleration a versus time t graph a4 1 3 f a4 2 4 a4 a4 VT t

Physics
FluidsA sealed vessel contains water p 1000 kg m upto height h 3 5 m The space above the water contains compressed air at pressure 4 2P Po atmospheric pressure 1 x 10 Pa The vessel is connected to a hose at the bottom as shown in the figure Assuming the area of cross section of hose to be uniform and small as compared to the area of the vessel 4 0 mb also assuming isothermal expansion of air as the liquid flows out of the vessel A initial speed of efflux of water is 26 6 m s B initial speed of efflux of water is 26 2 m s C initial speed of water at point P see figure is 26 2 m s D the height at which the flow of water stops is 1 74 m 4 2

Physics
FluidsA wooden plank of length I m and uniform cross section is hinged at one end to the bottom of a tank as shown The tank is filled with water up to a height of 0 5 The angle 9 that the plank makes with the vertical in the equilibrium position exclude cos 0 0 is 0 Find the value of x T X F C B mg

Physics
FluidsA vessel has cross section area A up to height 2h and area A for further height h A and B are two points in fluid at the bottom of the vessel as shown It is filled with liquid of density P Neglect atmospheric pressure A Pressure at A 3pgh B Pressure at B 3pgh M mi re TEL 2h C Pressure at A pressure at B A B D Force exerted by liquid at bottom of container is greater than weight of liquid

Physics
Fluids3 A cube of ice floats ice floats partly in water and partly in kerosene oil Find the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in kerosene oil Specific gravity to kerosene oil is 0 8 and that of ice is 0 9 K Oil Water

Physics
FluidsOne end of a long iron chain of linear mass density is fixed to a sphere of mass m and spec density 1 3 while the other end is free The sphere along with the chain is immersed in a deep la If specific density of iron is 7 the height h above the bed of the lake at which the sphere will f 7m in equilibrium is Find x Assume that the part of the chain lying on the bottom of the x exerts negligible force on the upper part of the chain COOP


Physics
Fluids38 A solid sphere of mass m suspended through a string in a liquid as shown The string has some tension Magni of net force due to liquid on upper hemisphere and that on lower hemisphere are FA and FB respectively Whi the following is are true A Density of material of the sphere is greater than density of liquid B Difference of FB and FA is dependent on atmospheric pressure C FB FA mg D FR FA mg

Physics
FluidsA vessel contains oil density 0 8 gm cm over mercury density 13 6 gm cm A homoge sphere floats with half its volume immersed in mercury and the other half in oil The density material of the sphere in gm cm is A 3 3 C 7 2 B 6 4 D 12 8

Physics
Fluids11 The surface tension of liquid is 5 N m If a film of this liquid is held in a ring of 0 02 m then total surface area potential energy is 1 0 02 J 30 2 J 2 0 01 J 4 0 1 J

Physics
Fluids10 The height of mercury column in a barometer in a Calcutta laboratory was recorded to be 75 cm Calculate this pressure in SI and CGS units using the following data Specific gravity of mercury 13 6 Density of water 10 kg m g 9 8 m s at Calcutta Pressure hpg in usual symbols

Physics
Fluids13 The unit of the coefficient of viscosity in S I system is a m kg s b m s kg2 c kg m s kg m s 24 Systematic er a positive h negativ
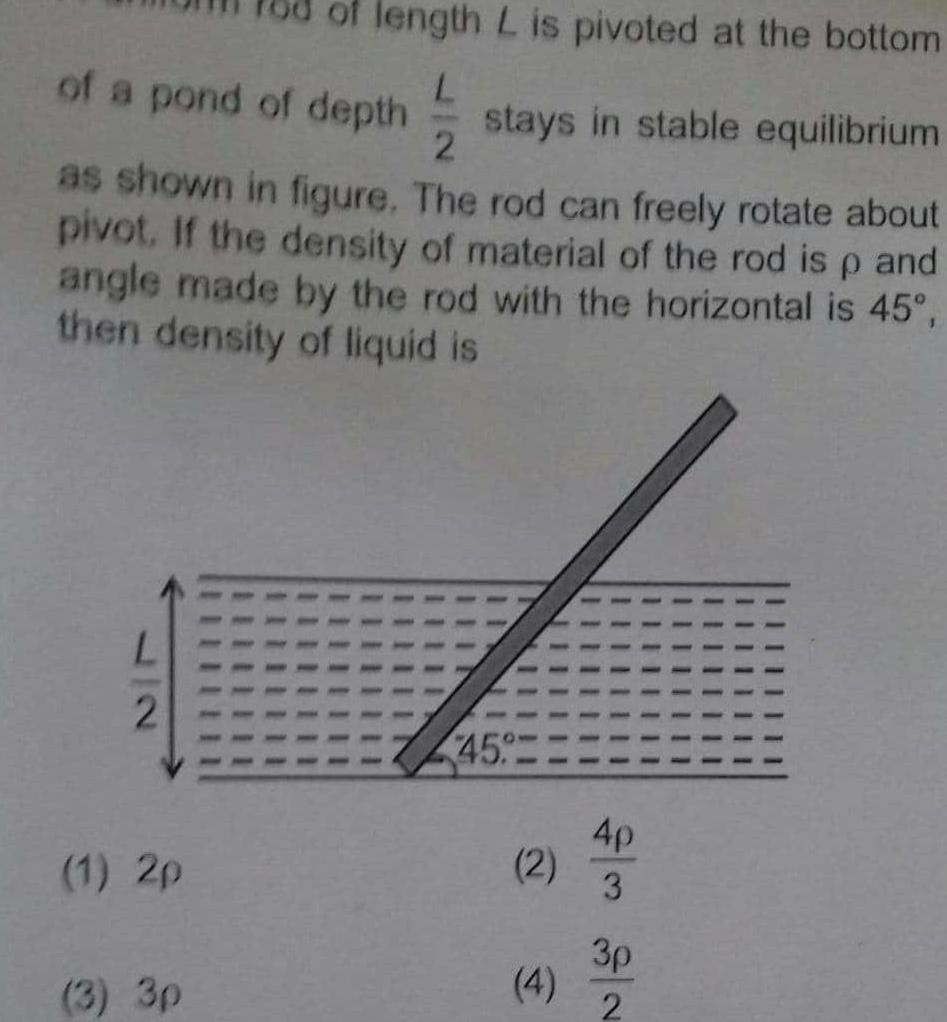
Physics
Fluidsof length L is pivoted at the bottom of a pond of depth stays in stable equilibrium 2 as shown in figure The rod can freely rotate about pivot If the density of material of the rod is p and angle made by the rod with the horizontal is 45 then density of liquid is 2 1 2p 3 3p 45 2 4 4p 3 3p 2
Physics
FluidsThe amount of work done in blowing a soap bubble such that its diameter increases from d to D is T surface tension of the solution 1 4n D2 d T 3 n D2 d2 T Vr 28n D2 d T 4 2n D d T

Physics
Fluids17 A film of soap solution is trapped between a vertical frame and a light wire ab of length 0 1 m If g 10 m s then the load W that should be suspended from the wire to keep it in equilibrium is XT 0 025 N m 1 0 25 g 2 0 2 g 3 0 5 g 4 04 a W b

Physics
FluidsA horizontal pipe 150 mm in diameter is joined by sudden enlargement to a 225 mm diameter pipe water is flowing through it at the rate of 0 05 m s What will be the change in pressure if the change of section is gradual without any loss 1377 m of woter D 3 027 m of water

Physics
Fluids2010 4 A uniform long tube is bent into a circle of radius R and it lies in vertical plane Two liquids of same volume but densities p and 8 fill half the tube The angle 0 is 8 WBJEE Samsung Triple Camera Gelary M20x R R

Physics
FluidsIn the setup shown two identical vessels A and B filled with water up to same level are connected by a horizontal tube equipped with a valve that is closed There are identical leak proof pistons in contact with the water in both the vessels The centres of the pistons are connected with the help of two taut elastic cords to the ends of a uniform lever arm supported on a fulcrum C that is fixed somewhere on the right half of the lever arm The cords are vertical and there is no friction between the pistons and the vessels If the valve is opened in which direction will the water flow through the connecting tube a From A to B c Water will not flow b From B to A d Insufficient information

Physics
Fluids9 A pump is used to deliver water at a certain rate from a given pipe To obtain n times water from the same pipe in the same time by what factor the force of the motor should be increased 1 n times 2 n times 1