Kinematics Questions and Answers

Physics
Kinematics38 A ball is dropped from a bridge of 122 5 metre above a river After the ball has been falling for two seconds a second ball is thrown straight down after it Initial velocity of second ball so that both hit the water at the same time is 1 49 m s 2 55 5 m s 3 26 1 m s 4 9 8 m s

Physics
Kinematics39 A boy throws balls into air at regular interval of 2 second The next ball is thrown when the velocity of first ball is zero How high do the ball rise above his hand Take g 9 8 m s 1 4 9 m 4 29 4 m 2 9 8 m 3 19 6 m

Physics
Kinematics47 A particle is dropped under gravity from rest from a height hg 9 8 m sec and it travels a distance 9 25 in the last second the height is a 100 m b 122 5 m c 145 m d 167 5 m Flight of Dreams

Physics
KinematicsTwo disc A and B made up of the sam material having radii a and b a rotatir about their center of mass as shown in th figure if there is no sliping between the disc then the ratio of their kinetic energies w be b OG a 2 a b b a

Physics
Kinematicshas the Note that in one direction as shown the acceleration of an object are always along the same straight line either in the same di rection or in the opposite direction However for motion in two or three dimensions veloc ity and acceleration vectors may have any angle between 0 and 180 between them dimension the ve velocity and 8

Physics
KinematicsU1 Two particles A and B move with constant velocities v and along two straight lines inclined at angle 0 towards the intersection point O At the moment t 0 the particles were located at the distance 1 and 1 from the point O as shown in the figure Find the shortest distance between the particles U V B

Physics
KinematicsA man can swim with a velocity v relative to water and can run on the ground with a velocity w The flow velocity of the river is u The width of the river is d The man is at a point A on one bank and wants to reach point B lying right across on the other bank of the river as shown in the figure Find the minimum time in which the man can reach the destination d B

Physics
Kinematics53 Predict the motion of an object on the basis of given information i Change in the speed of the object is zero and its direction of motion is fixed ii Change in the velocity of the object is zero during any time interval iii Change in the speed of the object is not zero but its direction of motion is fixed

Physics
KinematicsA particle starts from rest with zero initial acceleration The acceleration increases uniformly with time Find the time average and distance average of velocity upto a certain instant when the velocity becomes v

Physics
KinematicsA man standing on a horizontal road holds an umbrella a 30 with the vertical to keep himself dry He then runs at speed of 10 m s and find the rain drops to be hitting vertically The velocity of rain w r t man is 20 m s 30 m s 10 m s 5 m s

Physics
Kinematics2 9 When brakes are applied the speed of a train decreases from 96 kmh 1 to 48 kmh 1 in 800 m How much further will the train move before coming to rest Assuming the retardation to be constant 266 66

Physics
Kinematics8 A ladder 3m in length and weighing 200N is placed on a rough wall at an inclination of 60 as shown Coefficient of friction between ladder and wall is 0 28 and between ladder and floor is 0 34 A man weighing 600N is to reach to the top of the ladder Calculate the horizontal force to be applied to the ladder at floor level to prevent the ladder from slipping 600N 200N

Physics
KinematicsA block of mass mis attached with a massless spring of force constant k The block is placed over a fixed rough inclined surface for which the coefficient of friction is The block of mass mis initially at rest The block of mass Mis released suddenly from rest with spring in unstretched state The minimum value of M required to move the block up the plane is neglect mass of string and pulley and friction in pulley J m 37 3 5 m mmmm M

Physics
KinematicsWhen a deer was 48 m from a leopard the leopard starts chasing the deer and the deer immediately starts running away from the leopard with constant velocity A leopard cannot run at high speeds for a long time and has to slow down due to fatigue If we assume that the leopard starts with an initial speed of 30 m s and reduces its speed in equal steps of 5 m s after every 2 s interval at what minimum speed must the deer run to escape from the leopard

Physics
KinematicsA particle is thrown with a speed of 12m sec at an angle of 60 with the horizontal The time interval between the moments when its speed is 10m sec is g 10m sec 1 1 sec 3 1 4 sec 2 1 2 sec 4 1 6 sec

Physics
Kinematics1 A ball is bouncing elastically with a speed 1 m s between walls of a railway compartment of size 10 m in a direction perpendicular to walls The train is moving at a constant velocity of 10 m s parallel to the direction of motion of the ball As seen from the ground a the direction of motion of the ball changes every 10 seconds b speed of ball changes every 10 seconds c average speed of ball over any 20 second interval is fixed d the acceleration of ball is the same as from the train

Physics
KinematicsA particle moves in an xy plane in such a way that its distance r from the origin depends upon time t as r 3t The angle 9 made by its position vector with the positive x axis at any time t is given as 9 2t Here r is in metre 0 in rad and t in second y 0 V R P The particle moves in Straight line At time t 0 5 s its speed is 2 m s At time 0 5 s its velocity vector makes an angle 45 with its position vector at the same time At time t 0 5 s its velocity vector makes an angle 30 with its position vector at the same time

Physics
KinematicsOne Integer Value Correct Type Direction Q Nos 11 23 This section contains 13 questions When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 both inclusive 11 A stone is to be projected horizontally from top of a 1 7 m high pole Calculate initial velocity of projection in ms if it strikes perpendicularly an inclined plane as shown in the figure 1 7 m 37 137

Physics
Kinematics16 A 150 m long train is moving to north at a speed of 1 m s A parrot flying towards south with a speed of 5 m crosses the train The time taken by the parrot the cross train would be 1 30 s 2 15 s 3 8 s 4 10 s

Physics
KinematicsThe cylindrical vessel is kept on horizontal surface as shown in fig The speed of water coming out through small hole M 45kg 1 Question Type Single Correct Type 2 h 10m 3 6 m s 0 6 m s 4m 11 m s Piston m 5kg A 1m

Physics
KinematicsA 1 50 kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0 250 Figure a The object has a speed of v 3 30 m s when it makes contact with a light spring Figure b that has a force constant of 50 0 N m The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed a distance d Figure c The object is then forced toward the left by the spring Figure d and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring s unstretched position Finally the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring Figure e a b d e V 01 V 0

Physics
Kinematics2 8 A graph of x versus t is shown in figure Choose correct alternatives given below A B C I DY a The particle was released from rest at t 0 b At B the acceleration a 0 c Average velocity for the motion between A and D is positive d The speed at D exceeds that at E

Physics
KinematicsA toy plane with mass 20kg spent 2 minutes in flight with 20 m s speed If it lunched from rest What is the average power delivered by the engine in Watt 33 O 360

Physics
KinematicsA helicopter rises from rest on the ground vertically upwards with a constant acceleration g A food packet is dropped from the helicopter when it is at a height h The time taken by the packet to reach the ground is close to fg is the acceleration due to gravity Options

Physics
Kinematicsastion 31 The magnitude of pairs of displacement vectors are given Which pairs of displacement vectors o give a resultant vector of magnitude 13 cm 1 4 cm 16 cm 2 20 cm 7 cm 3 1 cm 15 cm 4 6 cm 8 cm n

Physics
KinematicsThree identical blocks A B and C are placed on horizontal frictionless surface The block B C are at rest But A is approaching towards B with a speed 10 m s The coefficient of restitution for all collision is 0 5 The speed of the block C just after collision is approximately Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 A 10m s B 4 5 6 m s 6 4 m s 3 2 m s 4 6 m s C

Physics
KinematicsA carriage of mass M and length I is joined to the end of a slope as shown in the figure A block of mass m is released from the slope from height h It slides till end of the carriage The friction between the body and the slope and also friction between the carriage and horizontal floor is negligible Coefficient of friction between block and carriage is u Find minimum h in the given terms h M smooth

Physics
Kinematics41 A train starting from rest is accelerated by 0 5 m s for 10s then it moves with constant speed for the next 10s and finally retarding at a rate of 1 0 m s it stops i Draw speed time graph of the train i Calculate from the graph the total distance travelled the average speed during first 20 seconds and the maximum speed of the train 87 5 m 3 75 m s 5 m s

Physics
KinematicsA boy observes the motion of a tennis ball dropped from some height The ball bounces from the ground several times During the motion the acceleration of the ball Assume downward direction as positive O is constant always and equal to g O is constant always and equal to g O is not constant O varies uniformly between g and g

Physics
Kinematics99 7 3 F L x L A block is dragged on a smooth plane with th help of a rope which moves with a velocity v a shown in figure The horizontal velocity of th block is 1 v m 2 V sin 0

Physics
KinematicsIn the fig the ends P and Q of an unstr string move downward with uniform speed v Mass M moves upwards with speed P 1 v cose 3 2v cos www F 1 I olo M E 201 oprinioibA YIL T i tenisps V B ari jud How Webold 2 v cose 4 2 v cose

Physics
Kinematics128 The displacement time graph for two particles A and B are straight lines inclined at angles of 30 and 60 with the time axis The ratio of velocity of particle A B V V is 1 1 2 3 3 1 B S K 60 130 O A 2 1 3 4 1 3

Physics
KinematicsA skater glides off a frozen pond onto a patch of ground at a velocity of 2 8 m s to the left Here she is slowed at a constant rate of 3 0 m s 2 to the right Find the skater s velocity when she has slid 1 2 m to the left across the ground 1 Point

Physics
KinematicsTwo blocks A and B of masses 1 kg and 2 kg are connected together by a spring and are resting on a horizontal surface The blocks are pulled apart so as to strech the spring and then released The ratio of K Es of both the blocks is 1 1 2 2 3 BURT 1 4 1 4

Physics
Kinematics75 The power supplied by gravity to a projectile thrown from ground varies as AP P The projectile was of mass m and projected with speed u and angle with vertical Find Po and to 1 mgusin0 2 mgusine 3 mgucose usine g ucose g usine g

Physics
KinematicsFour particles A B C and D are projected simultaneously from O and O which are at the same level as shown The particles collide at the same point The velocity of B is half of the velocity of A and velocity of D is of the of the velocity of C Particles B and D are projected horizontally and particles A and C upwards at different angles with horizontal The particles A and C reach their maximum height in the same time Find the ratio of velocities of A and C B D

Physics
KinematicsA billiards player hits a stationary ball by an identical ball to pocket the target ball in a corner pocket that is at an angle of 40 with respect to the direction of motion of first ball Assuming the collision as elastic and friction and rotational motion are not important the angle made by the target ball with respect to the incoming ball is

Physics
Kinematics108 Cylindrical bucket B with water in it has mass 10 kg balances a mass of 12 kg A on horizontal surface as shown in the figure A place of cork of mass m 2 kg and specific gravity 0 5 is tied to the bottom of the bucket through a light string A is moved horizontally with constant velocity 4 m s as shown Find the ratica of tension T and T at the instant A reaches point C T 1 60 Im

Physics
Kinematics3 81 With what minimum speed v must a small ball should be pushed inside a smooth vertical tube from a height h so that it may reach the top of the tube Radius of the tube is R 106 A 2g h 2R C g 5R 2h R Figure 3 106 5 B R sd no D 2g 2R h olgen s 101

Physics
KinematicsA river is flowing towards west to east with 3 m sec A man wants to cross the river along the shortest path with velocity 5 m sec w r t still water In which direction person swims to cross the river from river current A B C D 37 53 127 143

Physics
Kinematics11 If the velocity time diagram for the rectilinear motion of a particle is the half wave of a sine curve as shown in Fig C find the total distance x that the particle travels during the half period time intervals 2 Ans x A Vmax 7 Fig C Vmax T 2

Physics
Kinematics94 95 In the system shown in the figure the acceleration of 1 kg mass is a downwards 4 b downwards 8 c upwards d upwards 96 Two blocks of masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light ipextensible string The string passes over a frictionless pulley The acceleration of the system is a 8 c b d 97 A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a massless rope which can stand a maximum tension of 500 N In which of the following cases will the rope break Take g 10 ms 8 a The monkey climbs up with an acceleration of 5 ms b The monkey climbs down with an acceleration of 5 ms mtG Objective NCERT Phys c The monkey climbs up with a uniform speed 5 ms d The monkey falls down the rope freely under gravity angl 98 A book is lying on the table What is the between the action of the book on the table and the reaction of the table on the book b 45 d 180 a 0 c 90 99 Two blocks of masses of 40 kg and 30 kg are connected by a weightless string passing over frictionless pulley as shown in the figure 40 kg 0 kg The acceleration of the system would be b 0 8 ms 2 a 0 7 ms c 0 6 ms d 0 5 ms 100 A mass of 1 kg is suspended by means of a thread The system is i lifted up with an acceleration of 4 9 ms ii lowered with an acceleration of 4 9 ms The ratio of tension in the first and second case is a 3 1 c 1 3 b 1 2 d 2 1

Physics
Kinematicsa 10 b 8 51 c 4 5 d 4 4 An object of mass m is released from rest from the top of a smooth inclined plane of height h Its speed at the bottom of the plane is proportional to a ma b m c m d m by the a 2 11 A uni

Physics
KinematicsA cyclist is moving on a track at a speed of 6km h After a while the raindrops fall vertically with a speed of 8km h Find the angle made by the umbrella with the verticle to protect the cyclist A tan B 1 tan 1 C tan 1 1 3 3
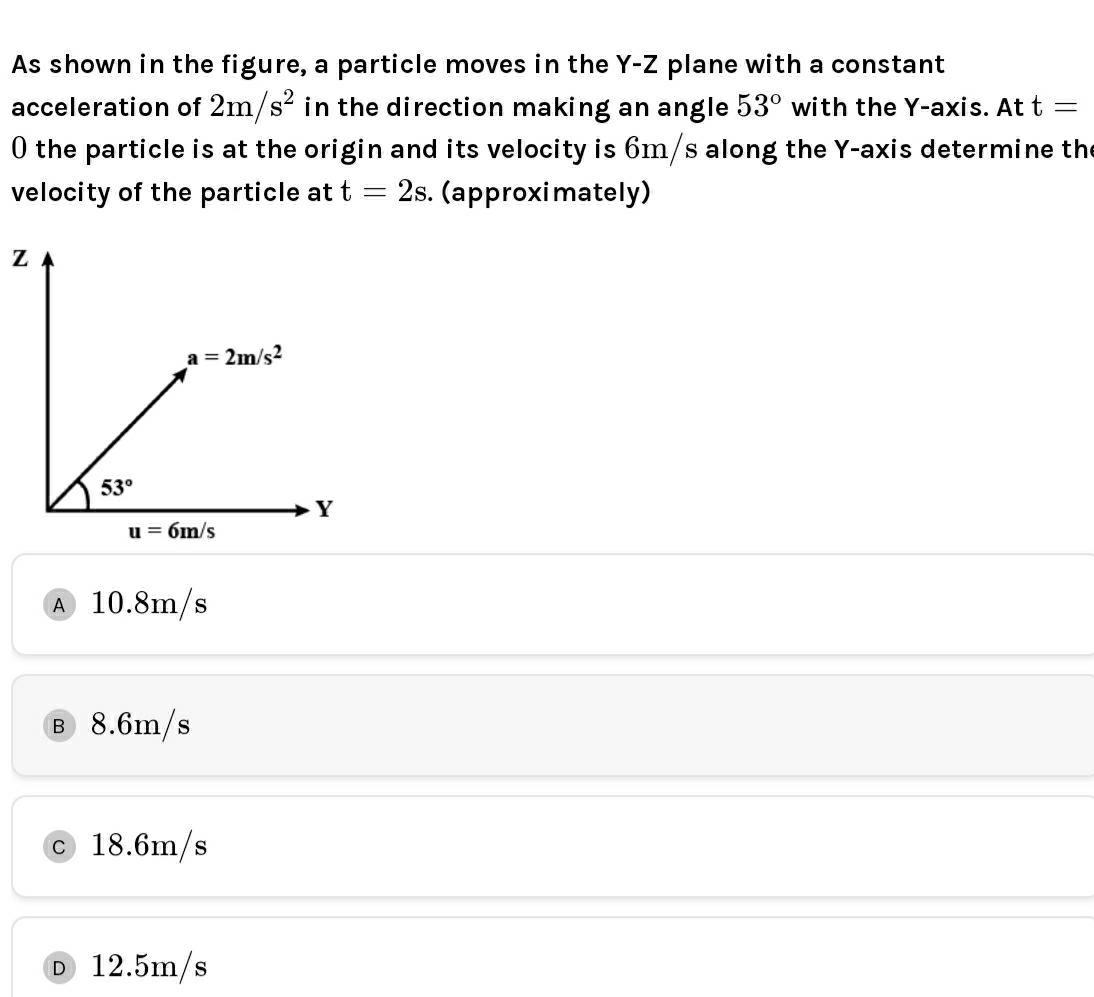
Physics
KinematicsAs shown in the figure a particle moves in the Y Z plane with a constant acceleration of 2m s in the direction making an angle 53 with the Y axis At t 0 the particle is at the origin and its velocity is 6m s along the Y axis determine the 2s approximately velocity of the particle at t ZA 53 a 2m s u 6m s A 10 8m s B 8 6m s C 18 6m s D 12 5m s

Physics
KinematicsA motorist with an expired license tag travels at a constant speed of 11 2 m s down a street and a policeman on a motorcycle taking another 4 93 s to finish his donut gives chase at an acceleration of 2 85 m s a Find the time required to catch the car t S b Find the distance the trooper travels while overtaking the motorist X m

Physics
KinematicsConsider a water sphere of radius R in a gravity free region Density of water is p at all points in the sphere Due to the self gravitational effects of the water sphere the pressure developed at its centre is A C 4G R D 6 B 2G R p 5 G R p 4 D 3G R p 8

Physics
Kinematics5 A A body moves along a coordinate line in such a way that its velocity at any time t where 0 ts is given by v t t 36 t Find its position function if it is initially located at the origin B Additionally find the average velocity on the interval 0 6

Physics
Kinematics461 faz 1 Ex 6 Particles are projected from a point 0 in a vertical plane with locity 2gk prove that the locus of the vertices of their paths is the ellipse 4y y k 0 a fond

Physics
KinematicsEx 2 The line joining C to D is inclined at an angle ato the horizon Show the least velocity required to shoot from Cto D is tan the least velocity required to shoot from D to C f f T time