Kinematics Questions and Answers

Physics
KinematicsThe quantities remaining constant in a collision are a momentum kinetic energy and temperature b momentum and kinetic energy but not temperature c momentum and temperature but not kinetic energy d momentum but neither kinetic energy nor tempe rature

Physics
KinematicsThe x and y coordinates of the particle at any time are x 5t 2t and y 10r respectively where x and y are in meters and t in seconds The acceleration of the particle at t 2s is 1 8m s 2 0 NEET 2017 3 5m s 4 4m s An object is projected with a velocity of 20ms making an angle of 45 with horizontal The equation for the trajectory is h Ax Bx where h is height x is horizontal distance A and B are constants The ratio A and B is 1 1 5 2 5 1 3 1 40 g 10 ms 4 40 1

Physics
Kinematicsa Which of the following graph represents non uniform motion treaph B show non uniform motion b Which of the following graph will represent motion of second hand of a clock Distance D

Physics
KinematicsFigure shows a particle P of mass m moving on a smooth circular wire of radius 5 cm being acted upon by attractive force conservative in nature directed towards O which 4 m dynes is 3 cm from centre C as shown in the figure and having magnitude 3 OP 3 cm P A

Physics
KinematicsA motor cycle rider moves some distance with a uniform speed of 30 m sec He immediately comes back to the starting point by the same path with a uniform speed of 20 m sec Find out the average velocity of the motor cycle rider A 12 m sec B 50 m sec C 24 m sec DX25 m sc0

Physics
Kinematics15 A block of mass m 2 kg is resting on a rough inclined plane of inclination 30 as shown in figure The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is 0 5 What minimum force F should be applied perpendicular to the plane on the block so that block does not slip on the plane g 10 m s a Zero c 2 68 N 30 b 6 24 N d 4 34 N

Physics
Kinematics13 A grasshopper on the bottom of a cubical box has to jump out of If each side of the box is h 52 cm and the grasshopper can ju a maximum initial velocity u 3 m s what should the minin angle the box be so that the grasshopper can jump out of Acceleration due to gravity is g 10 m s

Physics
KinematicsWater flows out in all directions with the same speed from a sprinkler consisting of a perforated spherical shell fixed at the end of a hose When the sprinkler is fixed at the ground maximum height attained by a water stream is h If the sprinkler is shifted to height h above the ground by what factor will the watered area on the ground change Neglect diameter of the spherical shell as compared to the height h
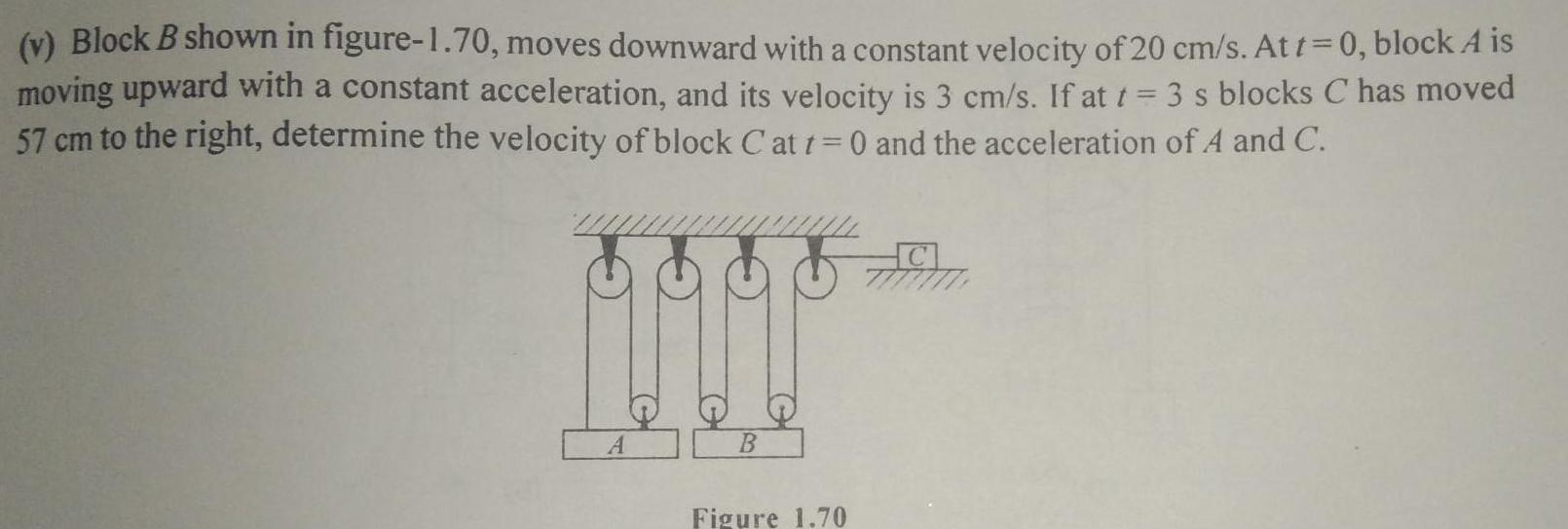
Physics
Kinematicsv Block B shown in figure 1 70 moves downward with a constant velocity of 20 cm s At t 0 block A is moving upward with a constant acceleration and its velocity is 3 cm s If at t 57 cm to the right determine the velocity of block C at t 0 and the acceleration 3 s blocks C has moved of A and C MUUT A Figure 1 70

Physics
Kinematics27 A particle is projected with velocity 10 m s at an angle of 60 from ground Then the vertical component of velocity vector when instantaneous velocity becomes perpendicular to initial velocity is 5 3 3 5 m s 1 m s 10 3 4 5 3 m s 2 m s

Physics
Kinematics5 A body thrown vertically up from the ground passes the height of 10 2 m twice in an interval of 10 s What was its initial velocity a 52 ms b 61ms c 45 ms 1 d 26 ms 1

Physics
KinematicsThe projectile motion of a particle of mass 5 g is shown in the figure A ven er 45 45 B The initial velocity of the particle is 5 2 ms and the air resistance is assumed to be negligible The magnitude of the change in momentum between the points A and B is xx10 2kgms 1 The value of x to the nearest integer is

Physics
KinematicsA ball of mass 4 kg moving with a velocity of 10 ms 1 collides with a spring of length 8 m and force constant 100 Nm 1 The length of the compressed spring is x m The value of x to the nearest integer is en 1

Physics
KinematicsA car runs at constant speed on a circular track of radius 100 m taking 62 8 s on each lap What is the average speed and average velocity on each complete lap 3 14 A velocity 10m s speed 10 m s C velocity zero speed zero B velocity zero speed 10 m s D velocity 10 m s speed zero

Physics
Kinematicsa 750 W b 1050 W c 1150 Two springs P and Q having stiffness constants k and k k respectively are stretched equally Then a More work is done on Q b More work is done on P c Their force constants will become equal d Equal work is done on both the springs

Physics
Kinematics5 A particle moving with constant speed turns left by an angle of 74 after travelling every 1 m distance If it returns back to its starting point after 18 sec then the magnitude of average acceleration of the particle from it s initial position to just before it takes it s second turn is 10 k m s Find the value of k

Physics
KinematicsIf the maximum vertical height and horizontal ranges of a projectile are same the angle of projection will be 1 450 2 Tan 4 3 Tan 2 4 300

Physics
KinematicsA team at SQU fires a rocket beside the college of science from rest at an angle 30 and accelerates at 30 m s2 for 3 0 s The engine shuts off at a height 202 5 m above the ground a Calculate the speed of the rocket after 3s b At what time after t O will the maximum height be reached c What maximum height will the rocket reach

Physics
KinematicsA body falling vertically downwards under gravity breaks in two parts of unequal masses The centre of mass of the two parts taken together shifts horizontally towards a heavier piece b lighter piece c does not shift horizontally d depends on the vertical velocity at the time of

Physics
Kinematics17 v versus s graph of a particle moving in a straly shown in the figure From the graph some conclusions are drawn State which statement is wrong v2 bab nak S 40 00510 niw orivom a The given graph shows a uniformly accelerated motion b Initial velocity of particle is zero Beqills 15 c Corresponding s t graph will be a parabola nga d None of the above

Physics
KinematicsA man applies a force of 20N to kill a fly wit h a flat stick If the area over which force is acting is 2 cm square then Calculate the pr essure on that area

Physics
KinematicsExample 9 43 A hollow sphere of mass M lies on a rough horizontal plane when a particle of mass m travelling with speed v collides and sticks with it If line of motion of the particle is at height h above the centre of sphere find h if th body rolls without slipping after collision

Physics
Kinematics5 A man standing on a road has to hold his umbrella at 30 with the vertical to keep the rain away He throws the umbrella and starts running at 10 kmh He finds that raindrops are hitting his head vertically What is the speed of rain with respect to ground a 10 3 kmh 1 b 20 kmh 10 kmh 1 d kmh 1 3 c 20 3

Physics
Kinematicsand the distance covered by the particles in the following figures i and ii while a particle travelsi to B as shown by the arrows A B E C a A B a

Physics
Kinematics7 A heavy particle is suspended by a 1 5 m long string It is given a horizontal velocity of 57 m s a Find the angle made by the string with the upward vertical when it becomes slack b Find the speed of the particle at this instant c Find the maximum height reached by the particle over the point of suspension Take

Physics
Kinematics10 A sphere of mass is dropped from the top of a building and reaches the ground before achieving terminal velocity The force of air resistance that acts on the sphere as it falls is given by F kv where k is a positive constant and y is the velocity of the sphere What happens to the magnitude of the sphere s velocity and acceleration and to the distance it falls during each second as the sphere approaches the ground Magnitude of Velocity Magnitude of Acceleration Distance of Fall Each Second A E Increases Increases Increases Decreases Decreases Increases Decreases Decreases Increases Decreases Increases Increases Decreases Decreases Increases

Physics
KinematicsA sphere of mass m is kept in equilibrium with th help of several springs as shown in the figure Measurements show that one of the springs applie a force F on the sphere With what acceleratio the sphere will move immediately after thi particular spring is cut F 1 zero 2 F m 3 F m Fu rrrrrrr Q elllllllll mmmmmmm bearbornas 26 vallug apinoitant nesvy

Physics
KinematicsIn the figure is shown a motion diagram of an object moving along the x direction with constant acceleration The dots 1 2 3 position of the object after successive equal time intervals The object is moving with O Negative velocity and positive acceleration Negative velocity and negative acceleration Positive velocity and positive acceleration Positive velocity and negative acceleration USO x 0 3 21 x sho

Physics
KinematicsA particle starts from rest Its acceleration is varying with time as shown in the figure When the particle comes to rest its distance from its starting point is a m s 2 4 1 2 4 6 t s

Physics
KinematicsAn object A of mass 2 kg in dropped from a height 30 m and at the same time another object B of mass 4 kg is projected upwards with an initial velocity of 15 m s The maximum height above the ground level attained by the centre of mass of A and B system is g 10 m s Options 35 m O 30 m 25 m

Physics
KinematicsA ball is projected upwards from a height h above the surface of the earth with velocit u The time at which the ball strikes the ground is Choose only 1 answer 2hg A 1 2 2h B g g 1 C 1 g 2gh 12 Your Answer

Physics
Kinematics12 The velocity of a particle moving along y axis is given by 2y 2 The time after which the particle starts retracing its own path is 1 1 s 2 2 s 1 4 1

Physics
Kinematics8 A carrom board 4 ft x 4 ft square has the queen at the centre The queen hit by the striker moves to the front edge rebounds and goes in the hole behind the striking line Find the magnitude of displacement of the queen a from the centre to the front edge b from the front edge to the hole and c from the centre to the hole on it 19 Give 20 Draw at x Verif tange

Physics
Kinematics10 A person walking at 4m s finds rain drops falling slantwise in to his face with a speed of 4m s at an angle of 30 with the vertical Show that the actual speed of the rain drops is 4 m s Ans 4 m s

Physics
Kinematics12 The range of a projectile for a given initial velocity a Decreases as the launch angle increases indefinitely B Increases as the cast angle increases indefinitely C Decreases as the launch angle increases to a certain limit value D Increases as the launch angle increases to a certain limit value 13 Figure 8 shows a projectile launched with a certain initial velocity vo above horizontal speed and also positions P Q R and S In which of the positions listed below is the projectile speed less a P b Q C R d S

Physics
KinematicsA rock is thrown from the edge of a cliff with an initial velocity u at an angle 6 with the horizontal as shown above Point P is the highest point in the rock s trajectory and point is level with the starting point Assume air resistance is negligible 7 Which of the following correctly describes the horizontal and vertical speeds and the acceleration of the rock at point P1 by l com had Horizontal Vertical Speed Speed A B D C cos8 D Cos8 cos 6 sin 4 cos 6 Which of the following correctly describes the horizontal and vertical speeds and the acceleration of the rock at point Horizontal Vertical Speed Speed A cos U C cos D 2 cos Acceleration sind Acceleration

Physics
KinematicsVO A rock is thrown from the edge of a cliff with an initial velocity to at an angle with the horizontal as shown above Point P is the highest point in the rock s trajectory and point Q is level with the starting point Assume air resistance is negligible 7 Which of the following correctly describes the horizontal and vertical speeds and the acceleration of the rock at point P A vo cos 0 C u cos 0 D v cos com 0 Horizontal Speed Vertical Speed 0 0 0 sin 6 Acceleration g g 0

Physics
Kinematics8 A point traversed 3 4 th of the circle of radius R in timet The magnitude of the average velocity of the particle in this time interval is TR a c t R 2 00 b d 3 TR 2t R 2t

Physics
KinematicsThe position of a body moving along x axis at time t is given by x t 4t 6 m The distance travelled by body in time interval t 0 to t 3 sis 1 5 m 3 4 m 2 7m 4 3 m

Physics
Kinematics30 Which statement can be impossible cases in one two dimensional motion A body has zero velocity and still be accelerating b The velocity of an object reverses direction when acceleration is constant C An object be increasing in speed as its acceleration decreases a None of these d

Physics
Kinematicsrests against a smooth vertical wall as shown in figure The floor is also smooth Mass of ladder is 75 kg If upper end A is moving with velocity v vertically downward then the horizontal velocity of lower end B is 1 v V 3 T 6 m mmm 8 m 2 B 3 3v

Physics
KinematicsThe position of a particle at any instant t is given b s 18t 3t 2t3 where s is the total distanc travelled from the starting point in m at the end of second Find a velocity and the acceleration at start

Physics
Kinematics11 From a height two balls are thrown with equal speed one vertically upwards and other vertically downwards They take time t and to respectively to reach the ground If a third ball is dropped from same height then time taken to reach the ground will be 1 3 t t 2 2t t t t 2 t t 4 2 2 1 2

Physics
KinematicsMultiple CHOIC 1 A person travels along a straight road for the first half time with a velocity velocity v The mean velocity v of the person is v and v are in same direction 1 V 1 2 m s2 3 8 m s 3 V V V VV The velocity time v f graph for a particle moving along x axis is shown in the figure The acceleration at t 4 5 s is 3 6 If y x 2x then 1 2 dy dx v m s 16 at x 3 is B 6 B 2 A 16 2 A particle is at rest at origin at time t 0 s It is given an acceleration a 6t m s The position of the pa at t 2 s is 1 6 m 3 4 m 8 12 16 2 4 m s 4 6 m s t s 2 8 m 4 10 m 2 4 4 8 8 Then positition y time t relation is given by y t then velocity at time t 1 s in m s 3 1 Zero 2 8

Physics
Kinematics22 The displacement x of a particle varies with time as x ae at be t where a b a and B are positive constants The velocity of the particle will AIPMT Prelims 2005 1 Go on decreasing with time 2 Be independent of a and B 3 Drop to zero when B 4 Goon increasing with time

Physics
KinematicsA particle starts from rest and travels a distance d with uniform acceleration then it travels a distance 2d with uniform speed and finally it travels a distance 3d with uniform retardatron to come to rest Ratio of average velocity to maximum velocity is

Physics
KinematicsA slit is cut along the left bottom edge of a rectangular tank The slit is closed by a wooden wedge mass M and apex angle r as shown in diagram The vertical plane surface of the wedge is in the contact with the left vertical wall of the tank Coefficient of static friction between these surfaces in contact is To what maximum height can water be filled in tank without any leakage through the silt The width of tank is b and density of water is A 2M B 4M H

Physics
Kinematicsree forces F 6a1 8a N F 8b 3b N and F3 261 19 N acting simultaneously on a body keep it in translational equilibrium determine numerical value of 0 5 a b Backspace

Physics
Kinematics7 Two objects are dropped from rest from the same height Object A falls through a distance d during a time t and object B falls through a distance de during a time 21 If air resistance is negligible what is the relationship between d and d A d dB B d dB 2 C d 2d D d 4dB 10 E It cannot be determined from th

Physics
KinematicsA solid cylinder rolls from the back of a large truck travelling at 10 m s to the right The cylinder is travelling horizontal at 8 m s to the left relative to an observer in the truck The ball lands on the roadway 1 25 m below its starting level How far behind the truck does it land in m