Kinematics Questions and Answers

Physics
KinematicsA particle is projected from point A A fly is standing at a tower at point B as shown in figure When particle passes from B fly starts flying in horizontal direction with constant speed of 2 m sec Both will meet at the same horizontal level at point C Then g 10 m sec 1 angle of projection is tan 3 angle of projection is 45 9 2 B 2m 4m C 2 angle of projection is tan 2 4 None of these

Physics
Kinematics17 velocity of B with respect to A 1 20 m s 2 10 m s 3 10 m s 4 20 m s Variation of quantity P with quantity Q is plotted in given figure describes motion of particle in a straight line Then which of the following statement is wrong P tive Q 1 Quantity Q may represent time 2 Quantity P is velocity if motion is uniform 3 Quantity P may be displacement if motion is uniform 4 Quantity P may be velocity if motion is 17

Physics
KinematicsAn electron has an initial speed of 6 2 x 106 m s at point A The electron moves from point A and stops at point B Find the potential difference VA VB between the two points in volts

Physics
KinematicsA particle is moving along x axis experiences a constant acceleration of 4 m s in negative x direction At time t 3 sec it velocity was observed to be 8 m s in positive x direction The distance travelled by particle in time interval t 0 to t 7 sec will be 1 42 m 2 98 m 3 49 m 4 58 m

Physics
KinematicsALLEN 16 x m 90 80 70 60 50 30 201 2 3 B 56789 t sec 16 Displacement time graph of two particle A B is shown in the given figure Find relative velocity of B with respect to A 1 20 m s 2 10 m s 3 10 m s 4 20 m s of quantity P with quantity Q

Physics
Kinematics3 Both 1 and 2 4 Acceleration A ruler is dropped vertically through the gap 14 between your thumb and fore finger Then find reaction time if displacement of ruler is 21 0 cm 1 0 2 sec 3 0 8 sec 2 0 6 sec 4 0 9 sec wing graph represents ruler GEEK FREI Fil ruler fara 1 0 2 sec 3 0 8 sec For y 15 15

Physics
Kinematicsdisplacement if motion is uniform 4 Quantity P may be velocity if motion is uniformly accelerated A ball is dropped from a building of height 45m Simultaneously another ball is thrown up with a speed of 40 m s Calculate the magnitude of relative velocity of the balls when both balls are in air 1 0 m s 3 40 m s 2 20 m s 4 60 m s

Physics
KinematicsA ball dropped from a tower strikes the ground in 6s Find the velocity strikes the ground What is the distance travelled by the ball in the last 3s g 9 8 m s with which the ball 58 8 m s 132 3 m in the last second of

Physics
Kinematicsg 9 8m s 122 5 m A body is released from rest from a height of 490 m Find the time taken by the body to reach the ground How much distance does it cover in the 4th second of its motion p 9 8 m s 10 s 34 3 m

Physics
KinematicsA particle is projected from origin in x y plane x in horizontal direction y in vertical direction If there exists a field that exert a force on the particle equal to weight of particle in vertically upward direction then particle passes through point 3 4 after 0 2 sec If this particle moves only under gravity of earth then the equation of path followed by particle will be x x 45 4 1 y x 3 80 4 2 y x 3 x 4 80 3 3 y x 3 4 y x 4 x 45

Physics
KinematicsThe path of a projectile is defined by the equation r 3t t 30 and 0 1600 t Find its velocity and acceleration after 30 sec r 3t t 30 0 1600 430 PR

Physics
KinematicsA ball of mass m is thrown at an angle is with the horizontal with an initial velocity The change in its momentum during its time of flight T is A mgT B 2musin 0 C mu sin D Mg

Physics
Kinematicsstrikes the ground What is the distance travelled by the ball in the last 3s g 9 8 m s 58 8 m s 132 3 m A body is dropped from a height of 176 4 m Find the distance covered by it in the last second of its motion With what velocity will the body strike the ground g 9 8 m s 53 9 m 58 8 m s lost second of its motion Find

Physics
KinematicsA man standing at the top of a building throws a ball vertically upwards with a velocity of 14 m s The ball reaches the ground 4 6s later What is the maximum height reached by the ball How high is the building With what velocity will the ball strike the ground g 9 8 m s 49 2 m above ground 39 2 m 31 05 m s

Physics
KinematicsA 4 the horizontal After 2 s the ball is moving at an angle of 30 with the horizontal The speed of projection of the projectile may be equal to 1 66 9 m s 2 17 9 m s 3 28 m s 4 Both 1 and 2

Physics
Kinematicsmeet After 4 s 78 4 m from top From a height of 98 m a body is dropped to fall freely and at the same instant a body is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 49 m s along the same path Find when and where the two bodies meet After 2 s height of 76 4 m

Physics
KinematicsFrom the top of a tower 100 m high a ball is dropped At the same time another ball is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m s Find when and where the two will After 4 s 78 4 m from top meet

Physics
Kinematics12 x m 24 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 t sec What is nature of acceleration between t 18 s and t 20 s is above diagram 1 Positive 2 Negative 3 Zero 4 None of these ph which of following physica

Physics
Kinematics4 s 2 s 29 4 m s Find the velocity at which a rifle bullet must be fired vertically so as to reach a height of 1 km What time will elapse before the bullet passes through the firing point on its return journey 08m 140 m s 200 7 s

Physics
KinematicsA particle moving in a straight line covers half the distance with speed of 10 m s The other half of the distance is covered in two equal time intervals with speed of 4 5 m s and 7 5 m s respectively The average speed of the particle during this motion is 1 8 0 m s 3 10 0 m s 2 12 0 m s 4 7 5 m s

Physics
KinematicsStewart kicks a soccer ball with initial velocity of 20 feet per second at an angle of 40 to the horizontal The parametric equation that describes the position of the ball as a function of time are 20 cos 40t y 16t 20 sin 40t If he is 25 feet away from a 5ft goal will the ball go in O No The ball will bounce first No The ball will be at a height of 24 ft Yes The ball will be at a height of 24 ft Yes The ball will go in

Physics
KinematicsBOAL BOVNCERT BASEDOBJECTIVE PHY3 MOTIONINASTRAIGHT UNE P65 11 x m 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 t What is nature of acceleration from t t 10 sec in above diagram 1 Positive 3 Zero 2 Negative 4 None of th

Physics
KinematicsTwo bodies of masses 1kg 10 kg are dropped from the top of a tower On the surface of earth simultaneously 1 Heavier will reach first 2 Lighter will reach first 3 Both will reach simultaneously 4 Any one will reach first

Physics
KinematicsA string of a material of length 1 m cross sectional area 0 2 cm requires 2000 N to extend it by 1 mm The same material is used to manufacture the legs of a robot of 50 cm length and of cross sectional area 0 5 cm each The mass of the robot is 50 kg When it jumps from a building of height h it experiences a strain 0 05 The maximum height through which the robot can jump without breaking its legs is g 10 ms 2 1 m 0 2 cm s progone in sargo 1 mm ad agos as d aus od 5 o Options 1 do 60 a sprego 0 5 cm og 50 kg a 553 0 05 3580 Dood de se ono drsne 3 12 5 m 2 2 5 m 10 m 2000 Ne5550 50 cm hegne 45502 5008 og Joh g 10 ms 4 7 5 m

Physics
KinematicsA load W is to be raised by a rope from rest to rest through a height a the greatest tension which the rope can safely bear is nW Then the least time in which the ascent can be made is 1 Zero 2 3 na n 1 2na n 1 g 1 2 of these

Physics
KinematicsA particle moves along a straight line w ith its velocity related to position as v xxx2 where a constant If at t 0 x 0 and v 0 then find the following i Acceleration in terms of displaceme nt ii Acceleration in terms of time

Physics
KinematicsPre Medical Physics 22 A child climbs up a step waited f on step and comes down and process Choose x t graph for th X 0 M 1 2 3 4 X t m In hmm X 0

Physics
KinematicsBalloons with constant ascending velocity can be used to investigate wind velocities at various heights The given graph of elevation angle against time was obtained by observing a such balloon The balloon was released at distance L 1 km from the point of observation and it seemed to be rising dir ectly upwards Knowing that wind velocity near the ground was zero find the balloon s height at time t 7 min after its start and wind velocity at this height a deg 60 40 20 0 2 4 6 8 t min

Physics
KinematicsA projectile thrown from ground at some angle is having velocities u and V at two points during it If u and are perpendicular to each other then the minimum kinetic energy during the journey is of the projectile is m A 2 u v u v B m uv 2 u v C m u v 2 u v m u v uv D b

Physics
KinematicsA body is dropped from the top of a tower of height 3h The ratio of the intervals of time to cover the three equal heights h is Ot 12 t3 1 3 5 Ot t t3 1 2 5 t t O t t t3 3 2 1 O t t t3 1 2 1 3 2

Physics
Kinematics18 18 Pressure verses temperature graph of an ideal gas at constant volume is shown by a straight line A in figure If the mass of the gas is doubled and volume is halved the corresponding pressure verses temperature graph is givey by line P 1 A 2 B B C T 3 C 4 D farger a ten Aaferent TOUR 34 3 water ani 1 A B th 2 B 3

Physics
KinematicsThe following figure shows position time graph of an object moving along x axis Based on the information represented by the graph answer the following questions x m 4 t s 2 3 4 5 6 24 The position of the object at f 4 sis 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 25 The displacement of the object for the time interval t 0 to t 3 s is 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 2 5 26 The position of the particle is x 1 m at time instant t 1 1 1 s 3 1 s as well as 5 s 2 5 s 4 1 5 s as well as 53 27 The average velocity for the time interval t 0 to t 4 sis 1 1 m s 3 0 5 m s 28 The average speed and average velocity have same numerical value for the time interval Y0 2s 2 0 5s 3 Both 1 2 4 0 6 s 29 The average speed for the time interval 0 6 s is 0 67 m s 2 0 5 m s 2 2 m s 4 0 75 m s TIC

Physics
KinematicsHi there I m Harsh Vadher I say In si mple way that you please take cordin ate system and draw line with 1 obtu se slope 2 acute and 3 zero than I c ommited option 2 correct Cause for 1 case take xt graph upper X1 5 and down X2 3 and give t1 t2 time I got Vavg 2 At take mod but it s spee d avg is 3 At because it s distance fr om up measured 3m to down And rest 3 4 optio correct 1 Objective Type Questions More than one options are correct Select the correct statements For a particle moving on a straight line 1 Average speed is always equal to magnitude of average velocity 2 Average speed may be greater than magnitude of average velocity JE 3 Average velocity instantaneous velocity if velocity is constant 4 Moving with constant acceleration average velocity for a given time interval is arithmetic

Physics
Kinematicsan acceleration of 2 m s2 Answer the following questions As seen by a passenger in car A 36 9 37 Car ATTICAL 1517 1 Con 2 F increa 4 Fir backward and then backward and then ard finally ases and finally 43 No 44 45 decreases again 39 Taking the moment of start as t 0 the separation between the cars at the moment t 5 s is 37 5 m with A ahead of B 2 37 5 m with B ahead of A 3 50 m with B ahead of A 4 50 m with A ahead of B G 40 The position of car A at this moment t 5 s is 46

Physics
Kinematicsbody is projected vertically upwards with a velocity of 21m s Find the maximum height reached by the body the time taken by it to reach this height the velocity with which it passes a point A at a height of 10m H the time that elapses when the body passes through A on its downward journey from instant of projection g 9 8m s 22 5 m 2 14 s 15 65m s 3

Physics
KinematicsA stone dropped from a balloon at rest from a certain height passes through 81 m in the last s before it strikes the ground Find the height of the balloon and the velocity of the stone when it hits the ground 5207 m 319 5 m s

Physics
KinematicsA ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground level with a velocity of 19 6 m s How long does it take to reach the maximum height What maximum height does it reach What is the 28 19 6m 9 8 m s velocity of the ball at t 3s

Physics
Kinematicsinstant of projection g 9 8m s 22 5 m 2 14 s 15 65m s 3 745 s From the top of a structure 100m high a body is projected vertically upwards with a velocity of 39 2m s Find a how high it will rise b velocity with which it strikes the ground and c time it takes to reach the ground g 9 8 m s 178 4 m 59 13 m s 10 03 s

Physics
KinematicsFrom the top of a tower 102 9 m high a body is thrown upwards with a velocity of 19 6 m s How high will it rise and in what time How much time will it take to hit the ground Find the position and velocity of the body 5 s after projection g 9 8 m s no

Physics
Kinematics1 1 22 The position of a particle moving along x axis given by x 2 3t 5 m The acceleration of particle at the instant its velocity becomes zero is 1 12 m s 2 12 m s 3 6 m s 4 Zero

Physics
Kinematicsm s A body is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity u How many times must the initial velocity be increased to secure double the height achieved in the first case If the body is to travel upwards for double the time how many times must the initial velocity be increased

Physics
Kinematics88 De broglie wavelength of an electron movin with a velocity of 1 5 x 108 ms is equal t that of a photon The ratio of kinetic energy o the electron to that of the photon is 1 2 2 4 3 1 4 1

Physics
Kinematics9 What is the launch angle that will produce the maximum range of a projectile if there is no air resistance If there is air resistance will the angle be less than equal to or greater than the launch angle with no air resistance
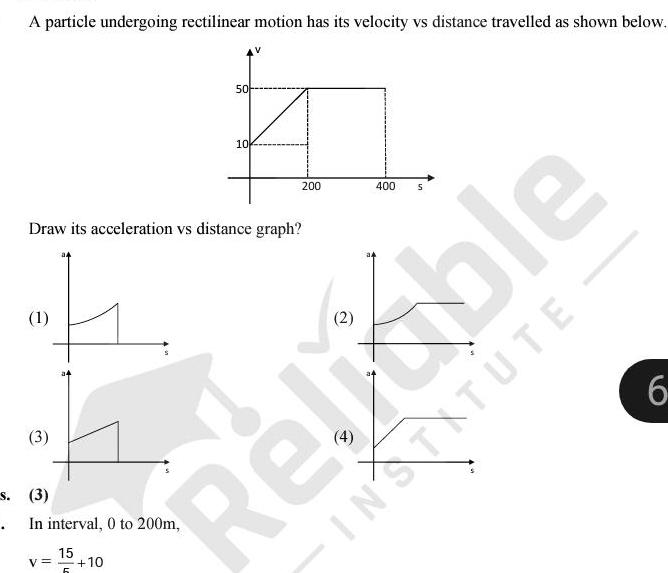
Physics
KinematicsA particle undergoing rectilinear motion has its velocity vs distance travelled as shown below 1 3 s 3 Draw its acceleration vs distance graph 50 In interval 0 to 200m 15 V 10 10 200 400 5 INSTITUTE 6 Rejoble

Physics
KinematicsA bullet of mass m embeds itself into a larger block of mass M If the maximum angle that the bullet block system rises after the collision is 60 the length of the string is 1 m and the velocity of the bullet before the collision is 4 142 m s find the energy loss during the collision Assume the bullet has a mass of 1 gram and the block has a mass of 1 kg Use g 10 m s Express answer to three decimal places OH M M m 1 0

Physics
Kinematicsuniform circular motion changes continuously A Angular displacement is vector quantity only for small values R The direction of angular displacement is perpendicular to plane of rotation of object

Physics
KinematicsAdvanced 1D and 2D Motion L 1 The acceleration of a particle varies with time as shown Assume the particle starts from rest at t 0 the displacement of the particle from t 2s to t 4s is Stage 2 10 a m b 20 3 m a c 25 m t ins d 28 m

Physics
KinematicsA ball is projected at an angle of 53 with horizontal at a speed of 20 m s on a planet named Eisteinium A horizontal wind starts blowing which gives a retardation to the ball in horizontal direction It was found that ball travels in a straight line Taking acceleration due to gravity on the planet to be 4 m s the magnitude of acceleration imparted by the wind is given by a m s The value of a is backspace

Physics
KinematicsIf both the blocks moving with constan acceleration then extension in spring K 1000 N m 32 N 1 3 cm 3 6 cm 7 kg oooooooo03 kg 72 N 2 2 cm 4 12 cm

Physics
KinematicsA force F k yi xj where k is a positive constant acts on a particle moving in the x y plane Starting from the origin the particle is taken along the positive X axis to the point a 0 and then parallel to the Y axis to the point a a The total work done by the force F on the particle is 1998 a 2ka b 2ka c ka d ka