Kinematics Questions and Answers

Physics
KinematicsFigure 3 15 represents a multiple flash photo of two balls Describe each ball s motion Does either ball pass the other When Do they ever have the same speed When

Physics
KinematicsA plane is travelling S35 W at an airspeed speed in still air of 250 km h A wind of 95km h is blowing from SE Determine the resultant ground velocity Include the vector diagram in your solution


Physics
KinematicsZoom Link Parent Graphs There is a second hot spot in the lower right corner of the iFrame Dragging this hot spot allows you to change the size of i dimensions you prefer EDylan Young Type A projectile is launched horizontally from a cliff top at 16 m s Determine the values of the velocity components at 1 second intervals of time Using g 9 8 m s s Enter for left and down time s 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 0 E A C Vx m s 16 B D F Ms Donohue Science BASD Virtual Acade C Clever Portal Gm B D Vy m s 0 0 LL E H Once satisfied with your entries tap on Check Answers Check Studer d young stude Le Veloci Progres Ques Motion Diagram V H Tap for Ques He View

Physics
KinematicsVelocity m s 50 40 30 20 10 1 A 9 Velocity 2 B 3 4 Time s 5 6 C 7 8 Time Graph a How do you get velocity from this graph b How do you get acceleration from this graph

Physics
KinematicsQuestion 21 of 45 Step 2 of 5 01 00 47 A BB is shot from a BB gun at a rate of 195 mph at an angle of 20 from the horizontal The BB gun sits on a platform 7 feet above the ground Step 2 of 5 How high is the BB 4 seconds after leaving the BB gun Round your answer to the nearest integer AnswerHow to enter your answer opens in new window 1 Point Keypad Keyboard Shortcuts

Physics
KinematicsFor general projectile motion with no air resistance the horizontal component of a projectile s velocity first decreases and then increases remains a non zero constant remains zero continuously decreases continuously increases

Physics
Kinematicsevacuated tube which can be drop baseball cized objecte How long te object in free fall 102 the b what is its speed just as it reaches a catching device at the bottom tower int the object experiences 26 9 g as c When caught an average it s tops Through what distance does i travel during the deceleration 2 Ciam deceleration of

Physics
Kinematicsin object is thrown vertically downward at a rate of 15 m s from a structure whose height is 1400 m Calculate its total time of flig SHOW AN ORIGINAL PICTURE ON THIS PAGE WITH YOUR CALCULATIONS

Physics
KinematicsSpeed m s 0 10 20 30 40 50 0 2 4 6 10 Time sec 1 As time increases what happens to the speed 2 What is the speed at 5 seconds 3 Assuming constant acceleration what would be the speed at 14 seconds 4 At what time would the object reach a speed of 45 m s 5 What is the object s acceleration 6 What would the shape of the graph be if a speed of 50 m s is maintained from 10s to 20 s 7 Based on the information in Problem 6 calculate the acceleration from 10 s to 20 s 8 What would the shape of the graph b if the speed of the object decreased from 50 m s at 20 s to 30 m s at 10 9

Physics
Kinematics2 A 18 kg cart is pulled by a force of 23 N at an angle of 32 to the horizon along a frictionless surface a distance traveled by the cart in 4 3 s if it started from rest and has a final velocity of 5 3 m s b calculate the work done on the cart in 4 3 s and the power generated in pulling the cart

Physics
KinematicsA rod of mass M kg and init mass m 0 004 kg is moving with a speed v0 2300 m sec towards the rod at a distance d 0 5 m from the pivot The mass m then gets embedded in the mass m and the system begins to rotate about the pivot after the collision What is the kinetic energy of the system before the collision The moment of inertia of a rod about one of its ends is I M and the moment of inertia of a particle is I mr Initial m d vo 10580 J 30580 J 50580 J 70580 J pivot M e d Final pivot M me W

Physics
Kinematics1 Consider the following graph for the motion of a particle moving along the x axis 8 pts 10F 8 X m 6 2 0 0 0 0 5 1 0 1 5 2 a Calculate the average velocity in the time interval 0 5 s 1 5 s b Calculate the velocity at t 1 5 s c During what time interval s is the particle speeding up d What is the average speed in the interval 0 08 15 12 tsl

Physics
KinematicsA massive unknown object is moving at a speed of 59 96 m s and must be stopped before it wrecks a building What force should Ironman apply to it in 4 s if it weighs 1493 22 kg

Physics
KinematicsIsla s change in velocity is 30 m s and Hazel has the same change in velocity Which best explains why they would have different accelerations O Isla had negative acceleration and Hazel had positive O Isla had a different time than Hazel O Isla had positive acceleration and Hazel had negative O Isla went a farther distance than Hazel

Physics
Kinematics4 ting at an initial angular velocity at 3 rev s and is accelerating at a constant rate of 2 97 Pads Fmover a wheel whisse radius is 41 cm a point on the belt has a velocity of 14 19 m s find the velocity 18 Question 20 116 Add your answer A truck s wheel R 0 76 m is traveling at an initial angular velocity of 16 54 rad s and is constantly decelerating at a rate of 9 02 rad s How far in meters will a point on the outer rim of the wheel travel by the time it stops Round your answer to 2 decimal places Screens 25 png 3 Points Screens 26 png i

Physics
KinematicsAriana is accelerating her car at a rate of 4 6 m s2 for 10 seconds Her starting velocity was 0 m s What was her final velocity 0 m s 2 3 m s 4 6 m s 46 m s

Physics
KinematicsThe graph represents velocity over time Velocity m s 22216H2086420 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Time sec What is the acceleration 0 4 m s 0 2 m s 0 2 m s 0 4 m s k

Physics
KinematicsThe graph depicts the velocity and times of Elan and Anna during a race 30 Velocity m s 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 12 4 Anna 16 Elan 8 10 Which best depicts the data From 0 to 2 seconds Anna experienced negative acceleration From 3 to 6 seconds Elan accelerated while Anna di not From 6 to 8 seconds Elan accelerated faster than Anna From 8 to 10 seconds Elan experienced negative acceleration

Physics
KinematicsHow long does it take a radio signal to travel from Chicago to Saint Louis 500 km hint what is the speed of a radio signal approximately

Physics
KinematicsA student is bouncing on a trampoline At her highest point her feet are 45 cm above the trampoline When she lands the trampoline sags 15 cm before propelling her back up Part A For how long is she in contact with the trampoline Express your answer with the appropriate units

Physics
Kinematics1 EXPLAIN the difference in motion represented by a straight line and a curving line on a distance vs time in terms of constant or changing speed 2 Changing speed is called acceleration speeding up or deceleration slowing down Describe the shape of an acceleration line on a Distance vs Time graph of acceleration

Physics
KinematicsSKETCH 3 A man standing still at 4 m SKETCH 4 A man moving from Om to 10m at a steady fast pace then moving back to 0 m at a steady slow pace Sketch 5 A man moving from 0 to 10 meters at an ever increasing speed acceleration Sketch 6 A man moving from 10m to Om at a steady fast pace 1 e Distance m 5 10 10 Distance m 3 5 10 0 Distance m 7 Distance m 10 5 0 3 5 10 10 0 3 5 I Time s Time s Time s Time

Physics
KinematicsA Explore By either clicking on the man or the slider cause the man to move back and forth and observe what shows up on the graphs B Record Using the axis provided below make sketches of Distance vs Time and Velocity vs Time graphs for the actions described on the left side of each axis SKETCH 1 A man moving from Om to 10m at a slow steady pace SKETCH 2 A man moving from Om to 10m at a fast pace 10 Distance m 5 10 10 25 Distance m 0 5 10 Time 3 4


Physics
KinematicsA stone is dropped from a cliff and its velocity in feet per second at regular 0 25 second intervals is shown in the table Estimate the distance that the stone travels from t 0 to t 1 25 The distance that the stone travels from 0 to SCOOB Time sec Velocity ft sec 0 0 25 0 5 0 75 1 1 25 0 2 8 2 5 13 26 39 52 65

Physics
KinematicsWhich graph below illustrates an object moving at constant non zero acceleration V Which graph below illustrates an object moving at constant acceleration t Graph A V t

Physics
KinematicsLeft endpoint approximation You decide to use a left endpoint Riemann um to estimate the total displacement So you pick up a blue pen and draw rectangles whose height is determined by the velocity measurement at the left endpoint of each one second interval By using the left endpoint Riemann sum as an approximation you are assuming that the actual velocity is approximately constant on each one second interval or equivalently that the actual acceleration is approximately zero on each one second interval and that the velocity and acceleration have discontinuous jumps every second This assumption is probably incorrect because it is likely that the velocity and acceleration change continuously over time However you decide to use this approximation anyway since it seems like a reasonable approximation to the actual velocity given the limited amount of data A Using the left endpoint Riemann sum find approximately how far the object traveled Your answers must include the correct units Total displacement Total distance traveled

Physics
KinematicsA particle moves in a straight line with the given velocity u t 12 4r in m s Find the displacement and distance traveled over the time interval 0 9 Give your answers as whole or exact numbers displacement m

Physics
KinematicsQ3 A pendulum of length L 1 0 meter and bob with mass m 1 0 kg is released from rest at an angle 30 from the vertical When the pendulum reaches the vertical position the bob strikes a mass M 3 0 kg that is resting on a frictionless table that has a height h 0 85m A 8pts m L e M X a When the pendulum reaches the vertical position calculate the speed of the bob just before it strikes the box b Calculate the speed of the bob and the box just after they collide elastically c Determine the impulse acting on the box during the collision d Determine how far away from the bottom edge of the table Ay the boy will the box strike the floor

Physics
KinematicsQ2 An object of mass m 2 5 kg has a one dimensional collision with another object of mass m 7 5 kg Their initial speeds along x are v 16 0 m s and v 215 m s The two objects stick together after the collision Calculate the velocity after the collision

Physics
KinematicsTwo billiard balls with identical mass collide as shown Ball 1 has an initial speed of 8 3 m s and ball 2 has an initial speed of 10 6 m s After the collision ball 1 has a final speed of 3 6 m s What is the final velocity of ball 2 in m s The positive direction is to the right 1 Before 1 Note if you need to enter a number in scientific notation use e For example 1200 1 2e3 and 0 0012 1 2e 3 Include several decimal places in your calculations and your answer to avoid rounding error Do not include units with your answer After

Physics
KinematicsA ball dropped from a height of 20 meters takes 2s to fall to the ground Assuming it experiences free fall how long would a ball dropped from a height of 180 meters take to fall to the ground Use g 10m s O 3 3 s 6 s 5 s 4 s 2 8 S 9 5 s

Physics
KinematicsA motion diagram for some moving object is shown here Each frame dot of the motion diagram represents 1 s Over which of the labeled regions are the object s velocity and acceleration in opposite directions If there is more than one region you must select all of them t 11 s Region 2 Region 3 Region 1 Region 1 None of the regions Region 2 Region 3 t 0
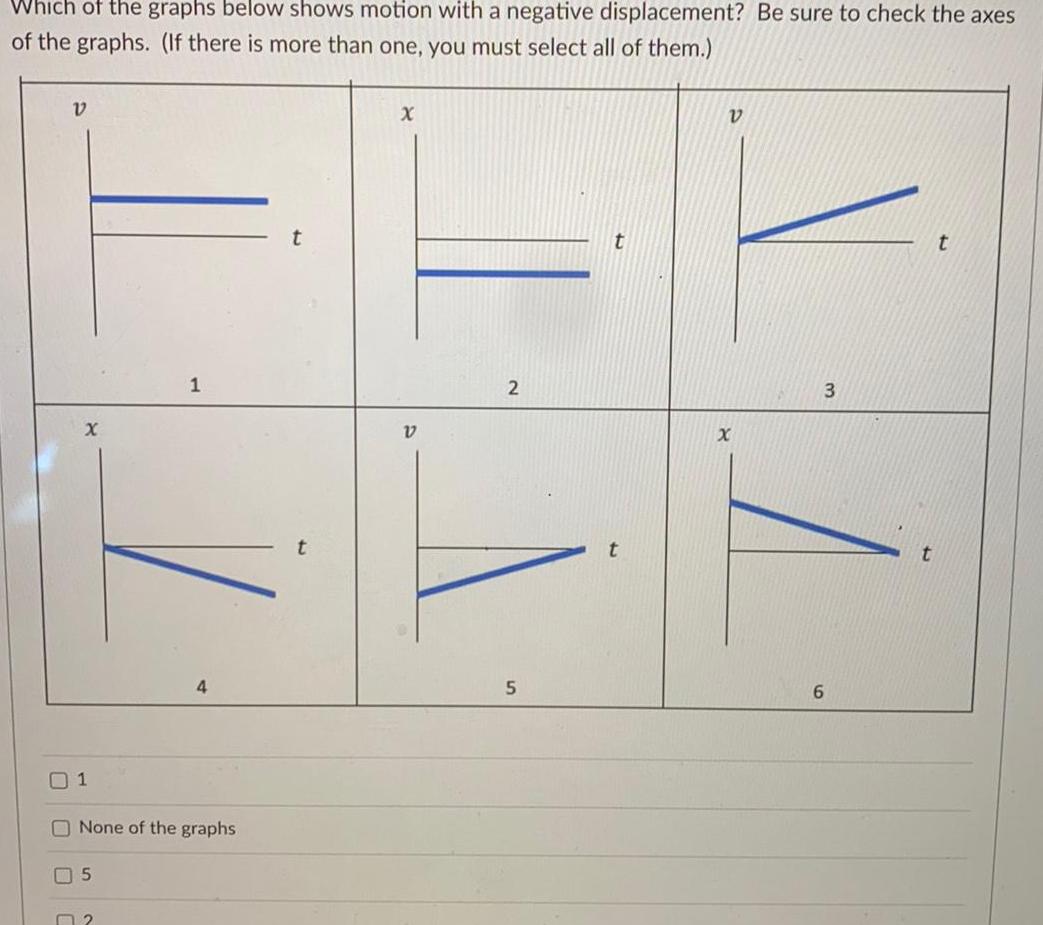
Physics
KinematicsWhich of the graphs below shows motion with a negative displacement Be sure to check the axes of the graphs If there is more than one you must select all of them V X 1 5 1 None of the graphs 2 4 t X V 2 5 t V 3 6 t t

Physics
KinematicsA rabbit fleeing a fox runs 36 degrees west of north at 5 8 m s Using a coordinate system in which east is the x axis and north is the y axis what is the x component of the rabbit s velocity vector in units of m s Note if you need to enter a number in scientific notation use e For example 1200 1 2e3 and 0 0012 1 2e 3 Include several decimal places in your calculations and your answer to avoid rounding error Do not include units with your answer

Physics
Kinematics30 A particle is moving along the x axis The line graph shows the velocity of the particle over time velocity m s L3NTON 4 2 3 4 2 3 5 When is the instantaneous acceleration of the particle equal to 0 6 time sec

Physics
Kinematics5 From the top of a height of 25 m a bullet is thrown into the air vertically with an initial velocity of 20 m s After how many seconds does the direction of motion of the bullet change

Physics
Kinematics1 The velocity of a car changes from 5 m s to 7 m s at a constant rate in a time interval 5 s How long does the car move during this time period

Physics
KinematicsColumn A 1 2 3 4 5 v mtin the ball only has potential energy the ball only has kinetic energy as it hits the water the potential and kinetic energies are equal the ball has more potential energy than kinetic energy the ball has more kinetic energy than potential energy Column B a 3 b 5 c 1 d 4 e 2

Physics
Kinematics25 m s Sin 37 0 60 Cos 37 0 80 Tan 37 0 75 40m Goalpost 7 3m During a high school football game a field goal is attempted from just outside the thirty yard line The total distance from the ball to the goal posts is 40 meters since the goal posts are located at the back of the end zone The crossbar of the goal posts is 7 3 m high To be good a field goal attempt must pass over the crossbar The velocity of the ball after being kicked is 25 m s at an angle of 37 above the horizontal a Determine the horizontal component of the ball s velocity just after being kicked b Determine the vertical component of the ball s velocity just after being kicked c Determine the horizontal component of the ball s velocity at its highest point d Determine the vertical component of the ball s velocity at its highest point e Determine the highest point of the ball s path f Determine the time that it takes the ball to reach the goal posts g Determine the height of the ball when it reaches the goal posts Is the field goal attempt good h Determine the velocity of the ball as it passes the plane of the goal posts remember to include



Physics
KinematicsThe velocity of an object moving along an axis is given by the piecewise linear function v that is pictured in Figure 4 3 12 Assume that the object is moving to the right when its velocity is positive and moving to the left when its velocity is negative Assume that the given velocity function is valid for t 0 to t 4 a Write an expression involving defi nite integrals whose value is the to tal change in position of the object on the interval 0 4 b Use the provided graph of v to determine the value of the total change in position on 0 4 c Write an expression involving defi nite integrals whose value is the to tal distance traveled by the object on 0 4 What is the exact value of the total distance traveled on 0 4 d What is the object s exact average velocity on 0 4 e Find an algebraic formula for the object s position function on 0 1 5 that satisfies s 0 0 H 1 2 ft sec 1 2 3 y v t sec 4 Figure 4 3 12 The velocity function of a moving object

Physics
Kinematics4 A stone was dropped off a cliff and hit the ground with a speed of 120 ft s What is the height of the cliff Assume that there is no air resistance and that the acceleration of the ball is a t 32 ft s

Physics
KinematicsAn echo is heard from a cliff 5 05 s after a rifle is fired How many feet away is the cliff if the air temperature is 73 9 F ft

Physics
KinematicsWhich statement is true about the graph below The initial velocity is 0 m s O The initial acceleration is 4 m s The initial velocity is 4 m s 4 2 0 0 1 2 C 3 4 t s

Physics
Kinematics1 The position of a moving object at any instant is given by equation x 4t 6t 3 What is the average velocity of the object between t 1 sand t 4 s 2 A stone is thrown into the air vertically upward with an initial speed of 10 m s After how many seconds does its velocity become 5 m s downward


Physics
KinematicsA bicycle mechanic is checking a road bike s chain He applies force F 36 N to a pedal at the angle shown in Figure 1 while keeping the wheel from rotating The pedal is 17 cm from the center of the crank the gear has a diameter of 16 cm Figure 1000000 mm 110 1 of 1 Part A What is the tension in the chain Express your answer with the appropriate units T 63 75 Submit A Provide Feedback X Incorrect Try Again N Previous Answers Request Answer