Newton's law of motion Questions and Answers

Physics
Newton's law of motionng 1 h g A stone is dropped from a certain height and another stone is dropped from the same height after 2s Wha will be their separation after 10 more seconds 1 115 6 m 2 156 5 m 3 172 3 m 4 215 6 m de if gravity disappears find the total time it would

Physics
Newton's law of motionA fighter plane is yung horizontally at an altitude of 1 5 km with speed 720 km h At what angle of sight w r t horizontal when the target is seen should the pilot drop the bomb in order to attack the target Take g 10 ms2 tan23 0 43 O O O O 23 32 12 42

Physics
Newton's law of motion3 A man measure his weight by standing on a weigh ing machine If he leaps on the left side of the ma 2xco chine then its reading 12 mgr 1 remains same 2 increases 3 decreases to to zoro 610

Physics
Newton's law of motion3 ALLEN An iron ball of mass 100 g moving with a 28 velocity of 10 m s collides with a wall at an angle 30 with wall rebounds at the same angle with the same speed If period of contact between the ball the wall is 0 1 sec the force experienced by the wall is 1 10 N 3 IN 2 100 N 4 0 1 N A mass M is suspended by a rope from a rigid 29 100 gm fe ang yon alan 30 ufa na sit alam 0 1 sec dar a sua for 1 10 N 3 IN Manta 10 m s 2 4 100 N 0 1 N

Physics
Newton's law of motionA block of mass m is placed in a container as shown Height of the block is very close to the height of the container A time dependent force F acts on the system such that resultant downward accel eration of system is given by a at a 0 where t is time Which of the following graphs represents normal reaction of tube on block Take downward direction as positive for for normal reaction N 1 3 Z4 N Z 2 4 Z4 N Z4

Physics
Newton's law of motionA block of mass 6 kg kept on a horizontal smooth surface is act B 16kg ya horizontal force of 48N Find the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the block What is the force applied by the block on the surface and in which direction

Physics
Newton's law of motioncalculate the force acting on the body if its mass is 10 kg A force of 2 N gives a mass m an acceleration of 5 m s2 and a mass m an acceler acceleration would be produced if both the masses are tied together

Physics
Newton's law of motionF pushes wedge of mass M on a smooth horizontal surface A block of mass m is stationary relative to the wedge then F mF M m D The reaction between M and m is M A Frictional force is equal to mg between M and m B Minimum coefficient of friction between M and m is M m 8 F C Minimum force required to prevent relative sliding between M and m is M m m plane Ignoring the friction at the pulley an

Physics
Newton's law of motiondirection Mass of block A is 4 kg and that of B is 6 kg a Draw the FBD of each block b Find the contact force between the blocks c find the force given by the block B on the ground BON A 4kg 6kg B

Physics
Newton's law of motionWhich of the following statements is are INCORRECT about reference frames In a non inertial reference frame an A isolated particle does not retain a constant velocity B C A reference frame travelling with acceleration relative to an inertial reference frame is a non inertial reference frame In an inertial reference frame velocity vector of an isolated particle changes neither in direction nor in magnitude with time If a block is stationary with respect to an D elevator then reference frame fixed to elevator must be inertial

Physics
Newton's law of motion5 A car travels first 1 3 of the distance AB at 30 km h next 1 3 of the distance at 40 km h and last 1 3 of the distance at 24 km h its average speed in km h for the whole journey is a 40 b 35 c 30 d 28

Physics
Newton's law of motionA particle direction is moving on a straight line along A graph between square of velocity position is drawn as shown Find t magnitude of acceleration in m s of particle v m s 100 25 x m

Physics
Newton's law of motion157 Two bodies are projected from the same point with equal speeds in such directions that they both strike the same point on a plane whose inclination is If x be the angle of projection of the first body with the horizontal the ratio of their times of flight is COS X sin x 3 b sin x B a COS X COL c COS X sin x B d sin x B COS X

Physics
Newton's law of motionFor the equilibrium condition shown the chords are strong enough to withstand a maximum tension 100 N What is the largest value of W in Newton that can be suspended 53 A 53 W Question Type Numerical Type

Physics
Newton's law of motionThree blocks A B and C of masses 3 kg 2 kg and 4 kg respectively are hanging on a string passing over a fixed frictionless pulley as shown in the figure Tension in the string connecting block B and C is 1 3 2g 3 4g 3 A B 2 4 8g 3 6g 3 Enthusiast Le

Physics
Newton's law of motionA wedge of mass M is kept on a smooth inclined plane in figure along with a block of mass m placed inside the wedge Block is free to move inside groove of the wedge Neglect friction between all the surfaces System is released from rest Mark the CORRECT option Block m Wedge M A Contact force between block and wedge is non zero B Acceleration of block is g sin 0 C Acceleration of wedge is greater than g sin 0 D Resultant acceleration of block is vertically downward

Physics
Newton's law of motionA body of mass 5 kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity u 30i 40j m s If a 5 constant force F i 5j N acts on the body the time in which the y component of the velocity becomes zero is 1 5 sec 2 20 sec 3 40 sec 4 80 sec 5 free ye fang sefore m 30i 40j m s fave F fy 1 5 sec 3 40 sec 2 20 sec 4 80 sec 1

Physics
Newton's law of motionthe tension in the rope of mass M length L at the given point P as shown in the figure 44 x drx xx X dml M 1 mg xg L 3 mg Mg M L m F my Tp di 1 2 Z M 2 mg L x g 4 Zero

Physics
Newton's law of motionA B What is the resultant force on the object 1N to the left 1 N to the right 7N to the left 7N to the right C The diagram shows a solid object on a flat surface with two forces acting on the object D 3N 4 N

Physics
Newton's law of motiong block is 3 meters from a light spring The coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the block is 0 25 the coefficient of friction is the same on the entire surface The block has a of 3 m s when it hits the spring that has a force constant of 50 N m The block comes to rest when it has compressed the spring a maximum distance d Find 1 The speed of the object at the beginning of the 3 meters 2 The value of the maximum compression d

Physics
Newton's law of motionTwo particles A and B are projected in same vertical plane as shown in diagram If B particle hits A then A A B C D 53 60m s 100m UB 45 m s UB 80 m s UB 37 Correct Answer Velocity of B when it hits A is 74 4m s B Velocity of A when it hits B is

Physics
Newton's law of motion45 Smooth B 10 5 10 57 45 rough The ratio of acceleration of blocks A placed on smooth incline with block B placed on rough incline is 2 efficient of kinetic friction between block B and incline is 2 0 75 4 None of these

Physics
Newton's law of motionon the pulley in the upward di A block of mass m placed on a smooth floor is connected to a fixed support with the help of a spring of force constant k It is pulled by a rope as shown in the figure Tension T of the rope is increased gradually without changing its direction until the block losses contact the floor The increase in rope tension T is so gradual that acceleration in the block can be neglected 7 0 a Draw its free body diagram well before the block losses contact with the floor b What is the necessary tension in the rope so that the block looses contact with the floor c What is the extension in the spring when the block looses contact with the floor

Physics
Newton's law of motionIV The acceleration of a particle moving along a straight line at any time t is given by a 4 2v where v is the speed of particle at any time t The maximum velocity is 1 4 m s 3 6 m s 2 2 m s 4 Infinity

Physics
Newton's law of motionA block of mass 25kg is suspended to the ceiling by means of light string as shown in figure What is the tension developed in the string A light string is subjected to 25kg

Physics
Newton's law of motionTwo boats A and B having same speed relative to river are moving in a river Boat A moves normal to the river current as observed by an observer moving with velocity of river current Boat B moves normal to the river as observed by the observer on the ground A To a ground observer boat B moves faster than A C To a ground observer boat A moves faster than B C To the given moving observer boat B moves faster than A D To the given moving observer boat A moves faster than B

Physics
Newton's law of motiona 1 0kg mass hangs attached to a spring of length 50 cm the spring stretches by 2 cm The mass is pulled down until the length of the spring becomes 60 cm What is the amount of elastic energy stored in the spring in this condition if g 10 m s 1 1 5 Joule 2 2 0 Joule 3 2 5 Joule 4 3 0 Joule A 10 kg block is pulled in the vertical plane along a frictionless surface in the form of an arc of a circle of radius 10 m The applied force is of 200 N as shown in figure If the block had started from rest at A the velocity at B would be

Physics
Newton's law of motion4 A current loop consists of two identical semicrcular parts each of radius R one lying in the x y plane and the other in x z plane If the current in the loop is i the resultant magnetic field due to the two semicircular parts at their common centre is AIPMT 2011 Hoi 1 TER 2 Hoi Hoi 3 2 2R 2R 4 Hoi 4R

Physics
Newton's law of motionA light inextensible straight thread of length 3 2m is placed on a frictionless horizontal floor A small block of mass m 3 kg placed on the floor is attached at one end of the thread With how much constant speed vo in m s the free end of the thread must be lifted vertically upwards so that the block leaves the floor when the thread makes an angle 0 30 with the floor Acceleration of free fall is g 10 m s

Physics
Newton's law of motion15 16 For Questions 15 16 A block of mass 2 kg is placed on a rough horizontal surface A spring is attached to the block whose other end is joined to rigid wall as shown in the figure A horizontal force is applied on the block so that it remains at rest while the spring is elongate mg k by x x2 Let Fmax and Fmin be the maximum and minimum values of force F for which the block remains in equilibrium For a particular x Fmax Fmin 4N Also shown is the variation Fmax Fmin versus x the elongation of the spring g 10 m s2 mmmmmmmm 2kg The spring constant of the spring is A 20 N m B 25 N m The value of Fmin if x 6 cm is A 1 50N B 0 d F Fm Fin 10N C 30 N m C 2N 0 2m X D 40 N m D 1N

Physics
Newton's law of motionThe wedge shown can slide without friction on a horizontal floor Mass of the wedge is M and its angle of inclination is 30 A block of mass m slides down the wedge without friction when released on its inclined face If path of the block relative to the ground makes an angle of 600 with the horizontal fin the ratio of mass of the block to that of the wedge m M M

Physics
Newton's law of motionWhile looking from the window you witness a squirrel moving with the speed of 18 m s on a horizontal ground The squirrel slides a distance of 18 m until it comes to a halt Considering the ground and the squirrel find the coefficient of friction 00 6 0 0 7 0 8 0 9

Physics
Newton's law of motionA row of blocks are lined up with masses of 1 94 kg 2 14 kg and 3 71 kg The masses are then pushed forward by a 11 5 N force applied to the 1 94 kg block If the table is frictionless how much force does the 2 14 kg block exert on the 3 71 kg block O5 48 N O 3 16 N 2 51 N 01 45 N

Physics
Newton's law of motion3 The force required to produce an acceleration of 2 m s on a mass of 2 kg is a 4 N b 10 N c 22 N d 18 N

Physics
Newton's law of motion89 A ball of mass m is dropped What is the formula for the impulse exerted on the ball from the instant it is dropped to an arbitrary time later Ignore air resistance 90 Repeat the preceding problem but including a drag force due to air of fdrag bv

Physics
Newton's law of motion1 The string shown in the figure is passing over small smooth pulley rigidly attached to trolley A If speed of trolley is constant and equal to VA Speed and magnitude of acceleration of block B at the instant shown in figure is A VB VA ap 0 3 C VB 11 5 VA B a 0 D ag 16V A 125 A OTO BO x 3cm h 4cm
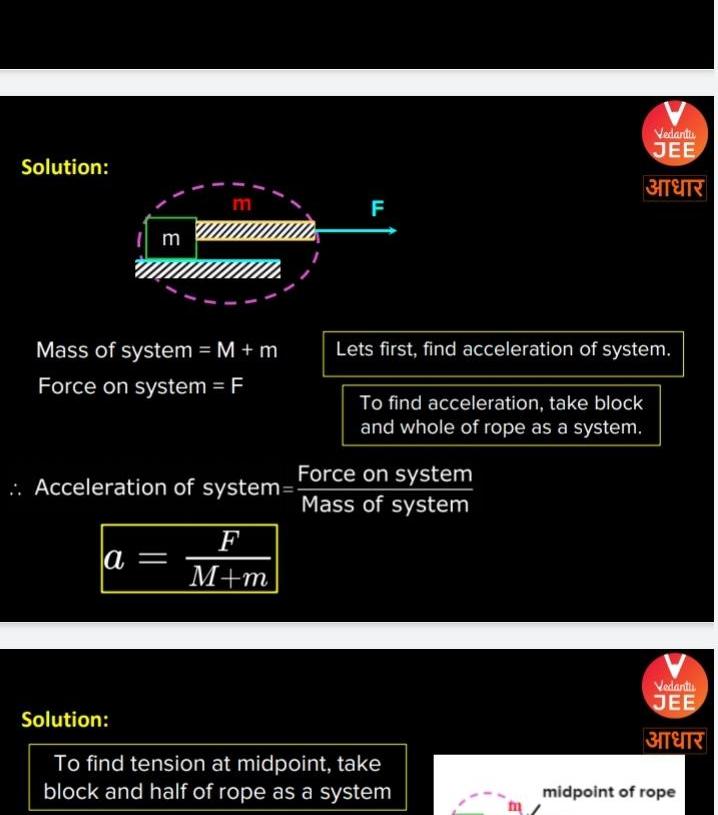
Physics
Newton's law of motionSolution m Mass of system M m Force on system F Acceleration of system a F M m F Force on system Mass of system Vedanti JEE Lets first find acceleration of system To find acceleration take block and whole of rope as a system Solution To find tension at midpoint take block and half of rope as a system 3 Vedanti JEE 3TER midpoint of rope

Physics
Newton's law of motionW t In the system shown in figure the block A is pulled towards right at a constant speed of 1 m s Find speed of block B w r t ground O O A B VA 1m s A B 6 m s 1 m s 2m s D 37m s

Physics
Newton's law of motionIn the system shown in figure the block A is pulled towards right at a constant speed of 1 m s Find speed of block B w r t ground D O A B V 1m s A B 6 m s 1 m s C 2m s D 37m s

Physics
Newton's law of motionThree forces with magnitudes of 75 pounds 35 pounds and 65 pounds act on an object at angles of 30 45 and 135 respectively with the positive x axis Find the direction and magnitude of the resultant of these forces Round your answers to one decimal place lb magnitude direction O

Physics
Newton's law of motion3 A body freely falling from the rest has a velocity u after it falls through a height h The distance it has to fall down for its velocity to become double is BHU 1999 a 2h b 4h c 6h d 8h

Physics
Newton's law of motion12 Two particles A and B mov velocity and v along two mutually perpendicular straight lines towards intersection point O as shown in figure At moment t 0 particles were located at distance and 1 respectively from O Then minimum distance between the particles and time taken are respectively 2 B 8 12 V t 14 1 vil 4x 12v 1 v 141 1 V 4 1 12 1 2 v v V O 14 1 1 V T 4 v 1 4 v v v 3 V 14 2 1 V 7 4 v 1 V 1

Physics
Newton's law of motion1 i ii iv stration 6 32 Two blocks A and B of mass M 3M re connected through a light string One end of the string is con nected to the block B and its other end is connected to a fixed point S as shown in Fig 6 144 Now a force F is applied block B Find the acceleration of block A B M A S B F 3M Segment AL Segment A Segmen A Segmen

Physics
Newton's law of motionP A particle of mass m is released from rest and follows a parabolic path as shown Assuming that the displacement of the mass from the origin is small which graph correctly depicts the position of the particle as a function of time V x a x t x t b o m x

Physics
Newton's law of motion30 30 1 0 0 m 4 kg 6 Two masses m 4 kg and m 2 kg are released from rest as shown in figure Find Famig my a F X i The distance travelled by centre of mass in 9 s i The speed of centre of mass after 9 s Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum m 2 kg b vat Vem 30 omponent system

Physics
Newton's law of motionA projectile is fired at angle of 45 with the horizontal Elevation angle of the projectile at its heighest point as seen from the point of proejection is A B tan 45 C 60 1 3 2 Correct Answer

Physics
Newton's law of motionball 4 58 A 10kg hammer strikes a nail at a velocity of 12 5 m s and comes to rest in a time interval of 0 004 sec Find the impulse imparted to the nail and the average force imparted to the nail Ans 125 N s 31300 N dio od to tro 10o edi le vitossib

Physics
Newton's law of motionA semi circular disc is moving rightward with velocity vo and acceleration ao both rightward at a certain moment Find the velocity and acceleration of rod at the same moment of time which is constrained to move in direction perpendicular to the direction of motion of disc as shown in the figure R TTTTTT 777777 P Vo

Physics
Newton's law of motionThe electric potential between a proton and an electron is given by V Voln where ro is a constant Assuming Bohr s model to be applicable write variation of In with n n being the principal quantum number 1 In x n 2 In x 1 n 3 rn xn 4 rn x 1 n

Physics
Newton's law of motion17 A particle of mass m moving with a constant velocity 20 v hits another identical stationary particle If coefficient of restitution is e then ratio of velocities of two particles after collision is 18 1 09 1 0 1 e 2 1 6 4 1