Thermodynamics Questions and Answers

Physics
ThermodynamicsQ 18 A perfect gas undergoes the following three separate and distinct processes to execute a cycle i Constant volume process during which 80 kJ of heat is supplied to the gas ii Constant pressure process during which 25 kJ of heat is lost to the surroundings and 20 kJ of work is done on it iii Adiabatic process which restores the gas back to its initial state Evaluate the work done during adiabatic process and the value of internal energy at all the state points if initially its value is 95 kJ

Physics
ThermodynamicsQ 16 A fluid is confined in a cylinder by a spring loaded friction less piston so that the pressure in the fluid is a linear function of the volume p a b V The internal energy of the fluid is given by the following equation U 34 3 15 p V where U is in kJ p in kPa and V in cubic meter If the fluid changes from an initial state of 170 kPa 0 03 m to a final state of 400 kPa 0 06 m with no work other than that done on the piston find the direction and magnitude of the work and heat transfer

Physics
ThermodynamicsAn ideal gas is taken through a cyclic thermodynamic process through four steps The amounts of heat given to the system in these steps are Q 1000 J Q 800 J Q 450 J Q 200 J respectively The efficiency of cycle is nearly NCERT Pg 322 1 31 2 45

Physics
Thermodynamicsby sound to travel fromx 0 to 1 is k M Y RT where k is take 2 1 41 A cylinder supports a piston of mass 5 kg and cross sectional area 5 10 m enclosing a gas at 27 C The gas is slowly heated to 77 C such that the piston rises by 0 1 m The piston is now clamped at this new position and the gas is cooled down to its initial temperature If atmospheric pressure is 1 atm then the difference in heat supplied during heating and heat rejected during cooling is J A ball of mass 1 kg moving with a speed of 10 m s on a smooth horizontal plane collides obliquely with another ball of same mass at rest as shown in fig If

Physics
ThermodynamicsTwo liquids A and B are at 36 C and 24 C When mixed in equal masses the temperature of the mixture is found to be 28 C Their specific heats are in ratio of O 314 C le
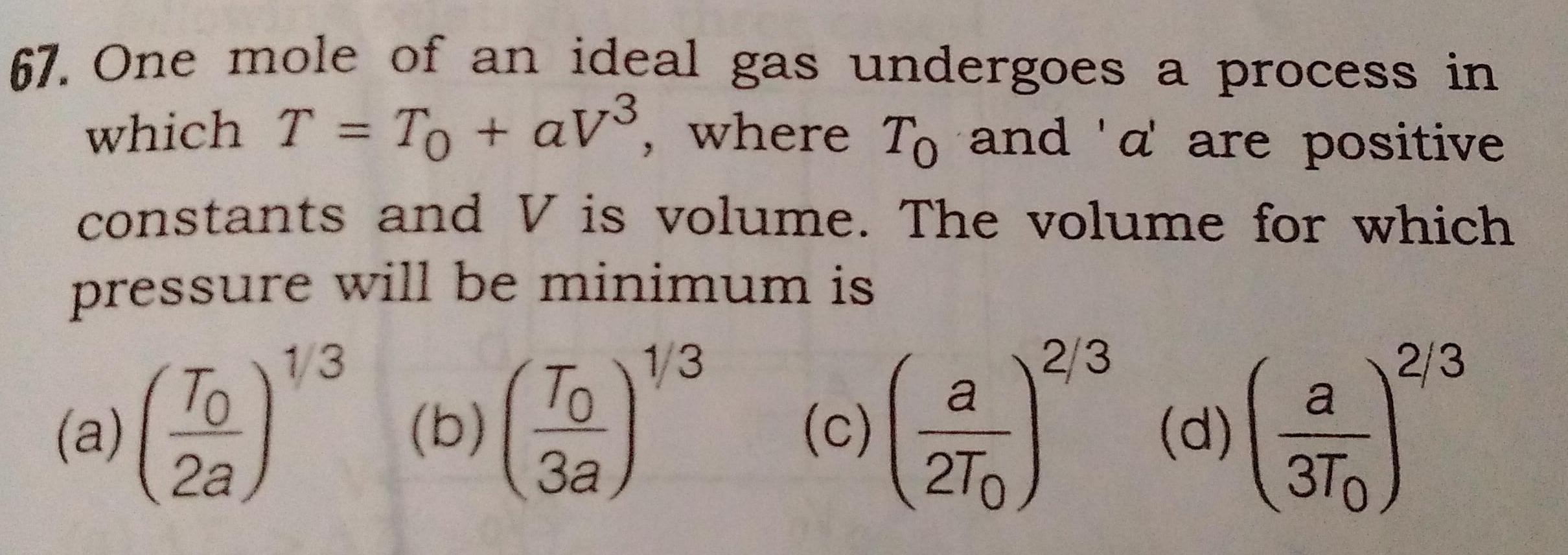
Physics
Thermodynamics67 One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process in which T To aV where To and a are positive constants and V is volume The volume for which pressure will be minimum is 1 3 a To 2a b 1 3 To 3a c a 2T 2 3 d a 3T0 2 3

Physics
Thermodynamics1 A sample of ideal gas y 1 4 is heated at constant pressure If an amount of 100 J heat is supplied to the gas the work done by the gas is a 42 12 J b 56 28 J28 57J d 36 23J

Physics
ThermodynamicsQ5 A closed rigid container of volume 0 5 m3 is placed on a hot plate Initially the container holds a two phase mixture of saturated liquid water and saturated water vapor at p1 1 bar with a quality of 0 5 After heating the pressure in the container is p2 1 5 bar Indicate the initial and final states on a T v diagram and determine a the temperature in degree Celcius at each state b the mass of vapor present at each state in kg c If heating continues determine the pressure in bar when the container

Physics
ThermodynamicsP volume V and temperature T of a certain T Here a is a 33 Pressure material are related by P V constant The work done by the material when temperature changes from To to 2To while pressure remains constant is 3 a 673 b 2uT c 2aT 9 378 6 T3

Physics
Thermodynamics81 The following graph shows two isotherms for a fixed mass of an ideal gas The ratio of r m s speed of the molecules at temperature T and T is a 2 2 c 102 x 105 Pa 3 2 01 2 3 V m b 2 d 1 4 T2 T st

Physics
ThermodynamicsIn a mechanical refrigerator the low temperature coils are at a temperature of 23 C and the compressed gas in the condenser has a temperature of 27 C The theoretical coefficient of performance is LO 5 8 6 6 5

Physics
Thermodynamics19 Pressure versus density graph of an p ideal gas is shown in figure a during the process AB work done by the gas is positive b during the process AB work done by the gas is negative F c during the process BC internal energy of the gas is increasing d None of the above B D

Physics
ThermodynamicsA Carnot engine working between 300 K and 600 K has work output of 800 J cycle What is amount of heat energy supplied to the engine from source per cycle 1800 J cycle 1000 J cycle 2000 J cycle 1600 J cycle

Physics
Thermodynamics10 An ideal gas y 15 is expanded adiabatically How many times has the gas to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules 2 0 times a 4 times b 16 c 8 times d 2 times b 16 times

Physics
Thermodynamics8 An ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA as shown in the figure The ratio of heat absorbed during AB to the work done on the gas during BC is a 5 2ln 2 21 b Vo 5 3 To B 2To T 5 4 ln 2 d 56

Physics
Thermodynamicsgas 2 If 2 moles of an ideal monoatomic at temperature To is mixed with 4 moles of another ideal monoatomic gas at temperature 2 To then the temperature of the mixture is 5 a 3 b To 65 c To 3 5 d To 4

Physics
ThermodynamicsA Goodyear blimp typically contains 5610 m of helium He at an absolute pressure of 1 10 x 10 Pa The temperature of the hell is 286 K What is the mass in kg of the helium in the blimp Number Units

Physics
Thermodynamics244 In which of the figure no heat exchange between the gas and the surroundings will take place if the gas is taken along curve curves are isothermal and adiabatic 1 A Pressure AC 2 B B D Volume 3 C 4 D

Physics
Thermodynamicsdiatomic gas is trapped by two insulting massless pistons with the help of an ideal spring The natural length of the spring is equal to the length of the cylinder Initial state of the gases are as shown in the figure n P V vaccum wwww n P V The value of energy stored in the spring is Po Vo CORRECT ANSWER The value of energy stored in the spring is 2Po Vo INCORRECT Now the gases are heated slowly such that their temperature becomes three times to their initial

Physics
ThermodynamicsIf the temperature of the sun becomes twice its present temperature then Radiated energy would be predominantly in infrared Radiated energy would be predominantly in ultraviolet Radiated energy would be predominantly in X ray region Radiated energy would become twice the present radiated energy

Physics
ThermodynamicsQuestion 21 A gaseous mixture initially at 300 K and 2 105 N m pressure contains 6 gm o H and 8 gm of He The mixture is expanded four times its initial volume through a isobaric heating process Then it is isochorically cooled until its temperature again become 300 K Afte that the gas mixture is isothermally compressed to its original volume Work done by complete cycle is Po Vo are initial pressure and volume respectively OntionsE

Physics
ThermodynamicsA volume V of a gas at a temperature T and a pressure p is enclosed in a sphere It is connected to another sphere of volume V 2 by a tube and stopcock The second sphere is initially evacuated and the stopcock is closed If the stopcock is opened the temperature of the gas in the second sphere becomes T The first sphere is maintained at a temperature T What is the final pressure D within the apparatus A 2pT 2T T B 2pT T 2T C pT 2T T D 2pT T T

Physics
ThermodynamicsTwo adiabatic process involving an ideal gas are plotted on a P V diagram A and B are two points on these curves as shown in the diagram Which of the following statements is are true P4 O Heat is given to system in the process AB Heat is rejected by system in the process AB B A V Whether heat is rejected or absorbed by the system during the process AB does not depend on the magnitude of the slope of line AB Whether heat is rejected or absorbed by the system during the process AB does not depend on the position of the points A and B on the P V diagram

Physics
ThermodynamicsA carnot engine with sink s temperature at 17 C has 50 efficiency By how much should its source temperature be changed to increases its efficiency to 60 Question Type Single Correct Type 1 225 K 2 128 K 3 58 K

Physics
ThermodynamicsWhen M gram of ice at 10 C specific heat 0 5 cal g C is added to M gram of water at 50 C finally no ice is left and the water is at 0 C The value of latent heat of ice in cal g is 50M 2 5 b a M 50M M 50 c 2019 Main 12 April L 5M 2 5 M 50M 2 M

Physics
ThermodynamicsIn the diagrams i to iv of variation of volume with changing pressure is shown A gas is taken along the path ABCDA The change in internal energy of the gas will be i iii A VA B C B P ii iv A A B B 1 Positive in all cases i to iv 2 Positive in cases i ii and iii but zero in case iv 3 Negative in cases i ii and iii but zero in case iv

Physics
ThermodynamicsA 9 0 g ice cube at 10 C is in a rigid sealed container from which all the air has been evacuated The following values for H O may be helpful J kg C Cice 2090 Cwater 4190 J kg C CP steam 1557 CV steam 2080 J kg C J kg C L 333 000 L 22 6 x 105 ka Part A How much heat is required to change this ice cube into steam at 240 C Express your answer using two significant figures Submit VAZO Request Answer J

Physics
ThermodynamicsA cylindrical tube of uniform cross sectional area A is fitted with two air tight frictionless pistons The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire Initially the pressure of the gas is Po and temperature is To atmospheric pressure is also Po Now the temperature of the gas is increased to 2To the tension in the wire will be 1 2 PA 2 PA wire

Physics
Thermodynamicsm When a force Facts at a point p at position from the origin O torque of this force about O is defined ast fxF It is a vector quantity having its direction perpendicular to both r and F according to the rule of cross product When a rigid body is rotating about a fixed axis and a force is applied on it at some point then we are concerned with the component of torque of this force about the axis of rotation not with the net torque When there are more than one force then net torque is given by the vector sum of the torque due to individual force Find the torque of a force F i 23 3k about a point O The position vector of point of application of force from O is F 21 3 k m A 7i 5j k 2i 6j 3k B 3i 5j 4k D none C If the axis of rotation of the body is along the y axis Then what is the component of the torque along the axis in the previous question A 7 Unit C I Unit B 5 unit D zero If F be a force acting on a particle having the position vector F and 7 be the torque of this about the origin then A 7 0 and F 0 C 7 0 and F t 0 B 7 70 and F 7 0 D F 0 and F F 0 force

Physics
ThermodynamicsA sample of an ideal gas is taken through a cycle a shown in figure It absorbs 50J of energy during the process AB no heat during BC rejects 70J during CA 40J of work is done on the gas during BC Internal energy of gas at A is 1500J the internal energy at C would be P 1 1590 J 2 1620 J 3 1540 J 4 1570 J B A V
Physics
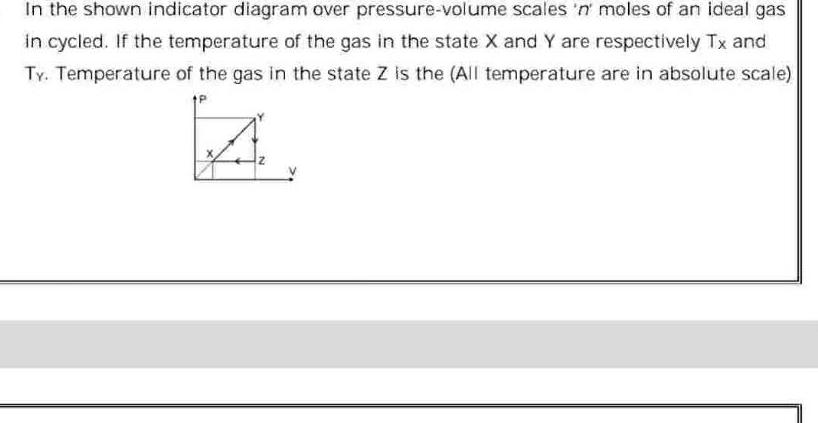
ThermodynamicsIn the shown indicator diagram over pressure volume scales n moles of an ideal gas in cycled If the temperature of the gas in the state X and Y are respectively Tx and Ty Temperature of the gas in the state Z is the All temperature are in absolute scale

Physics
ThermodynamicsA solar heat engine uses parabolic collector supplying heat to the working fluid at 500 C A second engine employs a plate collector supplying heat to the working fluid at 80 C How many times to the nearest integer is the maximum work available in the first engine compared to that of the second engine assuming heat supplied to be same when the ambient temperature is 27 C Correct answer 4

Physics
Thermodynamics1 8 A piece of ice heat capacity 2100 Jkg C and latent heat 3 36 x 105 J kg of mass m gram is at 5 C at atmospheric pressure It is given 420 J of heat so that the ice starts melting Finally when the ice water mixture is in equilibrium it is found that 1 g of ice has melted Assuming there is no other heat exchange in the process the value of m is 2010

Physics
ThermodynamicsWhich of the following plots is are hyperbolic A P V diagram for an isothermal process B Current density versus area of cross section in a current carrying wire C Velocity of incompressible flow versus area of cross section for steady flow of a fluid thro a pipe D Wavelength corresponding to which emissive power is maximum versus temperature of black body

Physics
Thermodynamics1 An ideal diatomic gas undergoes a thermodynamic process where pressure P as a 3V function of volume V is given by P Pev The average rotational kinetic energy of the gas V molecules at volume V 1 3 P Vo e 2 3PV B o is 2 2 PoVo 4 5P V e6

Physics
ThermodynamicsP V and Pf Vf are initial and final pressures and volumes of a gas in a thermodynamic process respectively If PV constant then the amount of work done is Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 4 minimum for n y minimum for n 1 minimum for n 0 minimu 1 21
Physics
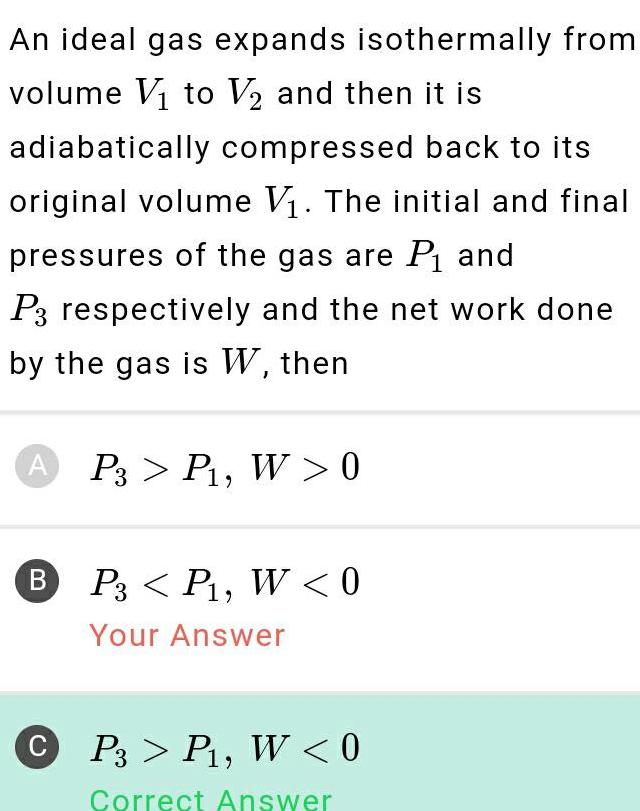
ThermodynamicsAn ideal gas expands isothermally from volume V to V and then it is adiabatically compressed back to its original volume V The initial and final pressures of the gas are P and P3 respectively and the net work done by the gas is W then A P3 P W 0 B P3 P W 0 Your Answer CP3 P W 0 Correct Answer

Physics
ThermodynamicsA metal sphere of radius R at a temperature TO was placed in a medium of lower temperature T1 Find the partial differential equation describing the variation of the temperature T through the sphere with the radial distance r and time t Density of the sphere is p and its specific heat is Cp

Physics
ThermodynamicsThe figure shows a Carnot cycle for an ideal gas on a P V diagram Then where 1 2 and 3 4 are isothermal and 2 3 and 4 1 are adiabatic process Note A and A are the area bounded by curve 4 1 2 3 on V axis respectively P A A A 1 B A A 4P 0 3Po 2P P 0 2 1 A 4 V 2V 0 C 2 A A A 3V 4V 3 4 V D Data is insufficient

Physics
Thermodynamics20 The relation between internal energy pressure and volume U P and V for a certain gas is U a bPV where a and b are positive constants Then equation of process is assume no heat exchange to take place 1 PVa constant 3 PVb constant b 1 2 pv b constant A PVb a constant

Physics
Thermodynamicsmole of an ideal gas contained in a cylinder undergoes a thermodynamic process during which pressure relates to volume as 1 5R 2 6AB 3 P are constants As the volume of the gas is changed from V B to V 2B its change of temperature can be expressed as AB 2 VIOUS 3AB 5R 11 AB 1 A 2 B A B

Physics
ThermodynamicsA piston cylinder device contains 3 lbm of refrigerant 12 at 120 psia and 120 F The refrigerant is cooled at constant pressure until it exists as a compressed liquid at 90 F If the temperature of the surroundings is 70 F determine A the work added to the refrigerant and B heat transfer removed from the system Also determine C the total entropy change of the system

Physics
Thermodynamics7 c 2x 10 s d 0 5 x 11 A vertical closed cylinder is separated into two parts by a frictionless piston of mass mand of negligible thickness The piston is free to move along the length of the cylinder The length of the cylinder above the piston is 4 and that below the piston is 2 such that 2 Each part of the cylinder contains n moles of an ideal gas at equal temperature T If the piston is stationary its mass m will be given by where R is universal gas constant and g is the acceleration due to gravity 2019 Main019 12 Jan II nRT 12 a nRT g c g 442 RT 24 12 1 b d 1 12 RT 312 4

Physics
ThermodynamicsA pressure P absolute temperature T diagram was obtained when a given mass of gas was heated During the heating process from the state 1 to state 2 the volume Question Type Single Correct Type 1 Remained constant 2 Decreased P 3 Increased 2 T

Physics
Thermodynamics13 A gas mixture consists of 3 moles of oxygen and 5 moles of argon at temperature T Considering only translational and rotational modes the total internal energy of the system is a 12 RT b 15 RT c 20 RT 2019 Main 11 Jan I d 4 RT

Physics
Thermodynamics33 The graph shows logarithmic readings of pressure and volume for two ideal gases A and B undergoing adiabatic It can be process conduded that one of the gases A and B is monoatomic and one is diatomic In P B 1 A is diatomic 2 Bis diatomic 3 B is monatomic 1 Both 1 and 3 A In V

Physics
ThermodynamicsA closed system undergoes a process 1 2 for which the values W 2 and Q1 2 are 50 kJ and 20 kJ respectively If the system is returned to state 1 and Q21 is 10 kJ then the work done W 1 is Options 40 kJ 50 kJ 60 kJ

Physics
Thermodynamics5 A thermodynamic system is taken from an original state to an intermediate state by the linear process shown in Fig 12 13 Pressure P N m 600 300 2 0 Volume V m E 5 0 BYJU S Its volume is then reduced to the original value from E to F by an isobaric process Calculate the total work done by the gas from D to F to F

Physics
Thermodynamicsa Two bodies at different temperatures T and T if brought in thermal contact do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature T T 2 b The coolant in a chemical or a nuclear plant i e the liquid used to prevent the different parts of a plant from getting too hot should have high specific heat c Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving d The climate of a harbour town is more temperate than that of a town in a

Physics
Thermodynamics1 A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3 0 litres per minute from 27 C to 77 C If the geyser operates on a gas burner what is the rate of consumption of the fuel if its heat of combustion is 4 0 x 104 J g