Wave Optics Questions and Answers

Physics
Wave OpticsIn young s double slit experiment fringe width is found to be 0 4 mm If the whole apparatus is immersed in water of refractive Index 4 3 without disturbing the geometrical arrangement new fringe width will be Question Type Single Correct Type 1 0 30 mm 2 0 40 mm 3 0 50 mm

Physics
Wave OpticsIn YDSE distance of screen is 2m The fringe width is 1 mm light of wavelength 600 nm is used If a thin plate of glass u 1 5 of thickness 0 06 mm is placed over one of the slits then these will be shift in fringe pattern will be Question Type Single Correct Type 10 cm 2 5 cm 3 10 cm

Physics
Wave OpticsIn a Young s double slit experiment the slit separation is 0 4 mm and the distance between the screen and the slit is 120 cm If the 3rd dark fringe formed at 0 5 cm from the central bright fringe Find the wavelength of the light in cm a 6 6 107 cm b 3 3x10 5 cm c 4 5 10 cm

Physics
Wave OpticsQ4 The frequency of a light ray is 6 1014 Hz Its frequency when it propagates in a medium of refractive index 1 5 will be a 1 67 x 10 4 Hz b 9 10 10 4 Hz c 6 10 4 Hz d 4 10 4 Hz

Physics
Wave OpticsIn a double slit experiment the two slits are 1 mm apart and the screen is placed 1 m away A monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is used What will be the width of each slit for obtaining ten maxima of double slit within the central maxima of single slit pattern AIPMT 2015 1 0 2 mm 3 0 5 mm 2 0 1 mm 4 0 02 mm

Physics
Wave OpticsQuestion 5 A parallel beam of light strikes a piece of transparent glass having cross section as shown in the figure below Correct shape of the emergent wavefront will be figures are schematic and not drawn to scale b Air Light Glass R Air

Physics
Wave OpticsIn the Young s double silt experiment the intensity of light at a point on the screen where the path difference is is K being the wave length of light used The intensity at a point where the path difference is 2 4 will be AIPMT 2014 1 K 2 K 4 3 K 2 4 Zero

Physics
Wave OpticsFind out the minimum distance of a point on the screen such that the intensity at the point is equal the intensity of one of the slit

Physics
Wave OpticsA parallel beam of light of wavelength is incident normally on a narrow slit A diffraction pattern formed on a screen placed perpendicular to the direction of the incident beam At the second minimum of the diffraction pattern the phase difference between the rays coming from the two edges of slit is a 2 b 3T c 4T d

Physics
Wave Optics7 A telescope has an objective of focal length 50 cm and eyepiece of focal length 5 cm The least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm The telescope is focused for distinct vision on a scale 200 cm away from the objective calculate i the separation between the objective and the eyepiece ii the magnification produced Ans 72 91 cm 1 3

Physics
Wave OpticsA concave mirror of radius 40 cm lies on a horizontal table and water is filled in it up to a height of 5 00 cm A small dust particle floats on the water surface at a point P vertically above the point of contact of the mirror with the table The image of the dust particle as seen from a a cm Find point directly above it is 8 4 the value of a Use the refractive index of water is 1 33

Physics
Wave OpticsA transverse wave described by equation y 0 02sin x 30t where x and t are in meters and seconds respectively is travelling along a wire of area of cross section 1 mm2 and density 8000 kg m What is the tension in the string Question Type Single Correct Type 1 20 N 2 7 2 N 3 30 N

Physics
Wave OpticsIn three to five sentences explain why two slightly separated coherent sources of circular waves result in an alternating pattern of bright and dark bands on a screen held some reasonable distance away Assume the two sources are coherently in phase e g both are at a peak at a particular instant at the same frequency

Physics
Wave OpticsAbove figure shows a beam expander made with two co axial converging lenses of focal length f and f and separation d f f Parallel light rays incident on lens 1 will form image I at the focus of lens 1 This image will act as object for lens 2 Second lens is placed that I is at its focus so that its image will be at infinity and the rays refracting from it will be parallel rays In this way the device can expand a laser beam while keeping the light rays in the beam parallel to the central axis through the lens Suppose uniform laser beam of width W 2 5mm and Intensity I 9 0kw m enter a beam expander for which f 12 5cm and f 30 0cm 1 What is the width of final beam W ii What is the value of d for the above beam expander iii If f is increased then what adjustment is required in the beam expander

Physics
Wave Optics4 Light of wavelength 6000 A falls normally on a thin wedge shaped film of refractive index 1 35 forming fringes which are 2 mm a part Find the angle of the wedge in second of arc

Physics
Wave Optics10 A practically very small source S of light is kept in front of a plane mirror But due to imperfect manufacturing there is a small spherical bulge radius of curvature 80 mm The situation is as shown in the figure You can assume that principal axis of bulge is perpendicular to the plane mirror Find the separation between the images formed A 10 025 mm B 20 025 mm C 40 025 mm D 80 025 mm S 20 mm 1mm

Physics
Wave OpticsA ray of light travels through air and strikes the surface of a liquid at an angle of 38 then refracts in the liquid at an angle of 24 2 What is the index of refraction for the material 1 5 O 1 7 2 0 1 3

Physics
Wave OpticsIf the wavelength of a wave in a medium is doubled increased by a factor of 2 wha will happen to the frequency a The frequency will also increase by a factor of 2 Ob The frequency will remain the same c The frequency will decrease by a factor of 2 d The frequency will decrease by a factor of 4

Physics
Wave OpticsThe wavelength of sound emerging from a moving source is observed to decrease from its stat value in a certain direction from the source Then the source A must be moving in that direction B must be moving in the opposite direction C must be moving at an acute angle with this direction D must be moving at an obtuse angle with this direction
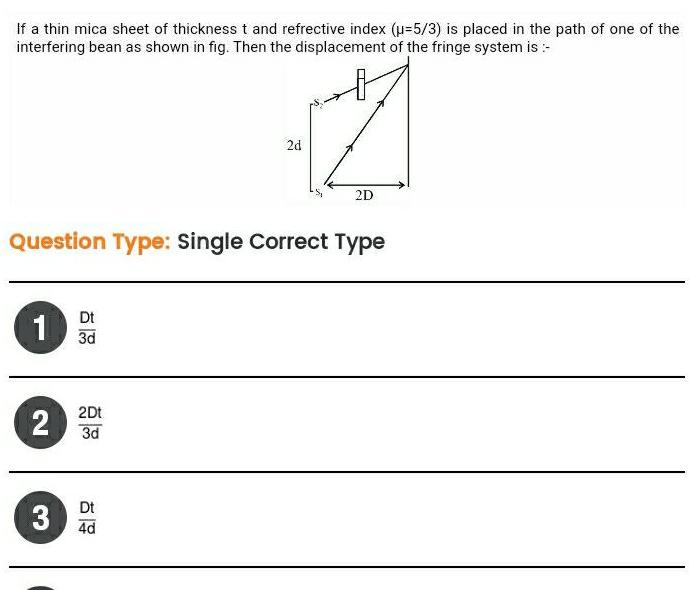
Physics
Wave OpticsIf a thin mica sheet of thickness t and refrective index u 5 3 is placed in the path of one of the interfering bean as shown in fig Then the displacement of the fringe system is 1 Question Type Single Correct Type 2 Dt 3d 2Dt 3d 2d Dt 3 4d 7 2D

Physics
Wave OpticsQ 4 A monochromatic light of wavelength is incident normally on a narrow slit of width a to produce a diffraction pattern on the screen placed at a distance D from the slit With the help of a relevant diagram deduce the conditions for maxima and minima on the screen Use these conditions to show that angular width of central maxima is twice the angular width of secondary maxima U Foreign II 2017

Physics
Wave OpticsTwo coherent sources are separated by a distance d 2X are placed at the centre of a large circular screen arranged symmetrically as shown R is radius of circular screen R d Light of wavelength is used in the experiment How many bright fringes will be observed on screen from A to B first quadrant Y axis S S 2186 B Circular screen 2 3 4 X axis

Physics
Wave OpticsAnna looks at white light through a slit in a spectroscope and sees a rainbow of colors Which of these is the best explanation for why she sees many colors O The colors in the white light refract different amounts The frequency of the white light is changing when it passes through the slit The colors in the white light diffract different amounts The amplitude of the white light is changing when it passes through the slit

Physics
Wave Optics2 What is the critical angle for the light rays hitting cornea from the inside of the eye for them not being able to leave the eye assume the medium in the eye has refractive index 1 38 1 48 7 2 45 2 3 46 4 19 1

Physics
Wave OpticsIn the figure shown if a parallel beam of white light is incident on the plane of the slits then the distance of the nearest white spot on the screen from O is d A Find the value of A assume d D d A 3 C 6 d2d 3 B 5 D 4 10

Physics
Wave Opticslet be the In a Young s double slit experiment fringe width and let I be the intensity at the central bright fringe At a distance x from the central bright fringe the intensity will be B 1 cos A Io cos C I cos B HF B D cos B

Physics
Wave OpticsTwo identical loudspeakers are placed on a line at distance 4 m and 6m from a microphone lying on the line joining them The output of each speaker at the microphone is 2 mW If the two speakers are connected in series and excited by the same oscillator and they vibrate in phase with each other the resultant output at the microphone will be frequency of oscillator 660 Hz and speed of sound 330 m s A zero B 2 mW C 4 mW D 8 mW

Physics
Wave Optics9 The first diffraction minimum due to a single slit diffraction is at angle 0 30 for a light of wavelenth 5000A The width of the slit is 1 5 x 10 5cm 2 1 x 10 cm 3 2 5 x 10 4cm 4 1 25 x 10 5cm 007 S 8

Physics
Wave OpticsFigure shows the displacement time graph of a particle executing SHM with a time period T Four points 1 2 3 and 4 are marked on the graph where the displacement is half that of the amplitude A 2 0 A 2 A Ap 2 T a Identify the points of same displacement but with opposite direction of motion Find the time difference between them 2 b Identify the points where the particles move in the same direction Find the time difference between them T 4 Sol a Points 1 and 2 have same displacements x 4 2 with equal but opposite velocities Similarly points 3 and 4 have same displacements x A 2 with equal but opposite velocities The phase difference between 1 and 2 and 3 and 4 is t 3 Therefore the time difference is T 27

Physics
Wave OpticsRed light 1 600 nm falls on a single slit an forms a diffraction pattern on a white marke board 1 50 meters away If the second dark band is located 4 5 cm from the central brigh fringe find the width of the slit in micrometers

Physics
Wave OpticsThe radius of the objective lens of a telescope is 5 cm and wavelength of light is 5000A The telescope is situated at a distance of 1 km from two objects The minimum distance between the two objects which can be resolved by the telescope is approximately 1 0 6 m 3 6 mm 8 2 6 m het to bon nirt A 08 4 6 cm

Physics
Wave Optics1 A transverse wave is travelling along a horizontal string The first picture shows the shape of the string at an instant of time This picture is superimposed on a coordinate system to help you make any necessary measurements The second picture is a graph of the vertical displacement of one point along the string as a function of time How far does this wave travel along the string in one second KA NAA 6 10 12 14 16 18 seconds centimeters A 0 3 cm B 3 0 cm C 9 0 cm D 27 cm

Physics
Wave OpticsAs shown mono energetic x rays with a wavelength of 0 35 nm are diffracted by a crystal The angle relative to normal incidence to the crystal is 8 0 The first diffraction maximum is observed when 0 77 What is the lattice spacing d O 0 12 nm 0 18 nm 1 6 nm 0 38 nm 0 78 nm d 0 36 nm

Physics
Wave OpticsA beam of bright red light of wavelength 654 nm passes through a diffraction grating Enclosing the space beyond the grating is a large semicylindrical screen centered on the grating with its axis parallel to the slits in the grating Fifteen bright spots appear on the screen Find the minimum possible values for the slit separation in the diffraction grating

Physics
Wave Optics4 In Young s double slit experiment the wavelength of red light is 7800 and that of blue light is 5200 A The value of n for which nth bright band due to red light coincides with n 1 bright band due to blue light is a 1 c 3 6 2 d 4

Physics
Wave Optics3 Two polaroid sheets are placed one over the other with their axes inclined to each other at an angle If only 12 5 of the intensity of the light incident on the first sheet emerges out from the second sheet the value of is 0 1 30 2 60 3 45 4 90

Physics
Wave Optics9 Two parallel rays are travelling in a medium of refractive index 4 3 One of the rays passes through a parallel glass slab of thickness t and refractive index 2 3 2 The path difference between the two rays due to the glass slab will be a 4 t 3 c f 8 b 3t 2 d t 6

Physics
Wave Optics7 In a double slit experiment the separation between the slits is d 0 25 cm and the distance of the screen D 100 cm from the slits If the wavelength of light 0 used is 6000 A and Io is the intensity of the central bright fringe the intensity at a distance y 4 10 5 m from the central maximum is x a lo c 3 0 4 b 0 2 d o 3 thin film of thickness and index of refraction 1 33
Physics
Wave Optics10 Light waves travel in vacuum along the y axis Which of the following may represent the wavefront a x constant c z constant b y constant d x y z constant 11 A plate of thickness t made of a material of refractive

Physics
Wave Optics6 In a YDSE with two identical slits when the upper slit is covered with a thin perfectly transparent sheet of mica the intensity at the centre of screen reduces from its initial value Second order minima is observed to be above this point and second order maxima below it Which of the following cannot be a possible value of phase difference caused by the mica sheet a TC 3 10t 3 c b d TC 2 11 3

Physics
Wave OpticsUnpolarised light of intensity 32Wm passes through three polarisers such that the transmission axis of the last polariser is crossed with first If the intensity of the emerging light is 3Wm2 the angle between the axes of the first two polarisers is 2 60 3 30 4 zero 1 150 0
Physics
Wave Opticsth 4 In Young s double slit experiment the wavelength of red light is 7800 and that of blue light is 5200 The value of n for which n bright band due to red light coincides with n 1 th bright band due to blue light is a 1 c 3 6 2 d 4

Physics
Wave Optics10 8 A thin film of thickness t and index of refraction 1 33 coats a glass with index of refraction 1 50 What is the least thickness t that will strongly reflect light with wavelength 600 nm incident normally a 200 nm c 400 nm b 100 nm d 300 nm

Physics
Wave OpticsD A horizontal beam of vertically polarized light of intensity 43 W m is sent through two polarizing sheets The polarizing direction of the first is 60 to the vertical and that of the second is horizontal The intensity of the light transmitted by the pair of sheets is nearly 1 8 1 W m 2 7 3 W m 3 6 4 W m 4 3 8 W m

Physics
Wave Optics2 A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave given as E Eicos kz cot is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at z a Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive the reflected wave will be given as A a E Eo i kz wt b E E i cos kz wt c E E i cos kz wt d E E i sin kz ot 6 The ma wa a C 7 A W el th

Physics
Wave Opticsshown in figure a S1 S2 D 1m If S S 3mm OP 11 mm then a If a 0 36 degree then destructive interfaces at point P b If a 0 36 degree then constructive interfaces at point O c If a 0 then constructive interfaces at O O

Physics
Wave Optics15 A prism having refractive index 1 414 and refracting angle 30 has one of the refracting surfaces silvered A beam of light incident on the other refracting surface will retrace its path if the angle of incidence is a 0 d 45 b 30 c 60

Physics
Wave OpticsAn object moves with velocity V i towards the inclined plane mirror as shown in figure The velocity of the image is YO Iv iv 30 Answer Your Attempt x i Rate this question Correct answer

Physics
Wave Optics2 10 In the figure shown S 0 S 0 30 0 4 Intensity at O due to any one of the slits is Io What is the intensity due to all the three coherent sources S S2 and S3 a 3 S S S3 b lo c 5 0 O d 9

Physics
Wave OpticsIn a young s double slit experiment fringe width equal to 1 mm is observed Then the distance of the nearest bright fringe from the central fringe will be Question Type Single Correct Type 1 1 mm 2 0 5 mm 3 2 mm A 15 mm