Waves Questions and Answers

Physics
WavesFour different independent i y a sinot 2 waves are represented by ii y a sin2wt TC iv Y4 a sin ot iii y a coswt With which of two waves interference is possible 1 i ii 2 i iv 3 iii iv 4 Not possible with any combination 3 ce doubled 1 Will 2 Will 3 Wi 4 W 16 In You maxi that 1 2

Physics
Waves28 A certain string will resonante to several frequencies the lowest of which is 200 cps What are the next three higher frequencies to which it resonantes 1 400 600 800 3 100 150 200 2 300 400 500 4 200 250 300

Physics
Waves190 Waves 22 If the tension and diameter of a sonometer wire of fundamental frequency n is doubled and density is halved then its fundamental frequency will become 1 2 2 2n

Physics
Waves5 The driver of a car travelling with speed 30 m s towards a hill sounds a hom of frequency 600 Hz If the velocity of sound in air is 330 m s the frequency of reflected sound as heard by driver is 1 500 Hz 2 550 Hz 4 720 Hz 3 555 5 Hz

Physics
Wavesy asin 2n pt Then the ratio of maximum particle velocity to wave velocity is 1 3 na 5 2na 5 2 2 5ma 2na 4 5

Physics
Waves13 A uniform wire of length L diameter D and density p is stretched under a tension T The correct relation between its fundamental frequency f the length L and the diamete D is a fo c fo 18 12 b foc d fo 1 LVD 1 LD

Physics
WavesQ1 The equation of a wave travelling along a very long string is given by y 6 0 sin 0 02T X 4 0 TT t in C G S unit calculate a amplitude b wave length c frequency d speed of wave e maximum transverse speed of particle Also state the direction of propagation of the wave 21

Physics
Waves010 A damped harmonic oscillator has the amplitude of 20 cm It reduces to 2 cm after 100 oscillations each of period 4 6 s Calculate the logarithmic decrement and damping constant Compute the number of oscillations in which the amplitude drops by 50

Physics
WavesA train moving at a speed of 220 ms towards a 31 fareft feere areg oft 3220 ms7 1000 Hz stationary object emits a sound of frequency 1000Hz Some of the sound reaching the object gets reflected back to the train as echo The frequency of the echo as detected by the driver of the train is speed of sound in air is 330 ms 2 3000 Hz 4 4000 Hz 1 5000 Hz 3 3500 Hz 4 zahllont af at a fe af gift vaffany 1 5000 Hz 3 3500 Hz 330 ms 2 3000 Hz 4 4000 Hz

Physics
Waves3 5 s day 4 20 min day A man standing between two cliffs hears the first 9 echo of a sound after 1 5 sec and the second echo 2 5 sec after the intial sound If the speed of sound be 330 m s the distance between the two cliffs should be 1 1650 m 3 825 m 2 990 m 4 660 m 3 5 s day youth a varfsei 1 5 sa facafay 2 5 aff 330 m s at a art 1 1650 m 3 825 m 4 20 min day e si ich fazafa 2 990 m 4 660 m

Physics
WavesA wire of length t having tension T and radius 33 r vibrates with fundamental frequency f Another wire of the same metal with length 20 having tension 2T and radius 2r will vibrate with fundamental frequency 1 f 2 2f 3 2 2 on a year for at 1 3 2T site are frucht ar 20 1 f 2 2f 3 4 X und 4 2r

Physics
Waves3 The equation of a travelling wave is y a sin 2x 3 Then the ratio of maximum particle velocity to wave velocity is 1 5 3 2 a 2 2 5m 4 2 28 y a sin 2x a fer en annan und 1 3 2 2 2 5 a 4 2

Physics
WavesA block with mass m is located at position x 0 on a horizontal table A spring with spring constant k and relaxed length zero is connected to it and has its other end anchored at position x f as shown in the fig The AX where A is a constant Assume that the block is small enough so that it touches the table at essentially coefficient of friction both static and kinetic between the block and the table depends on position according to only one value of x A A A The block is released from rest at x 0 The condition on A for which the stopping point is to the right to x anchor point is Assume that the block can some how pass through the anchor mg k 3mg k Quiere Ax 3k mg m x 0 x

Physics
WavesQuestion No 3 A block with mass m is located at position x 0 on a horizontal table A spring with spring constant k and relaxed length zero is connected to it and has its other end anchored at position x f as shown in the fig The coefficient of friction both static and kinetic between the block and the table depends on position according to AX where A is a constant Assume that the block is small enough so that it touches the table at essentially only one value of x O O 3k A mg peeleel Ax If the stopping point is to the right of the anchor the condition on A for which the block start moving leftward after it instantaneously comes to rest is Assume that the block can some how pass through the anchor O k A 3mg 4k A mg m x 0 x

Physics
Waves19 A metallic wire of lenght Larea of cross section A and youngs modulus Y is extended to lenght I by suspending a rigid body of mass M from one end keeping the other end fixed by a hook in the ceiling If the wire is further extended by pulling the body and then releasing the body then it will execute S H M with angular frequency given by LA Ger en af de and are och ten After and gut fat or Tara L 1 gensent fi effecx fox 3 fuld at a fost foren den and 2YA YA 2 fort and ad as an accrual ff at YL 3 VAM 4 2YL AM

Physics
Waves12 A student performed the experiment to measure the speed of sound in air using resonance air column method Two resonances in the air column were obtained by lowering the water level The resonance with the shorter air column is the first resonance and that with the longer air column is the second resonance Then 1 The intensity of the sound heard at the first resonance was more than that at the second resonance 2 The prongs of the tuning fork were kept in a horizontal plane above the resonance tube The amplitude of vibration of the ends of the prongs is typically around 1 cm 4 The length of the air column at the first resonance was somewhat shorter than 1 4th of the wavelength of the sound in air dy to and correction

Physics
WavesIf the ratio of amplitudes of wave in two different strings is 2 1 and frequency ratio of wave is 1 2 then ratio of power transmitted through the strings are 1 4 1 2 1 4 3 16 1 4 1 1

Physics
WavesExample 4 A triangular wave pulse moving at 2 cm s on a rope approached an end at which it is free to slide on a vertical pole 2 cm s 1 cm P 2 cm 1 cm 1 cm

Physics
WavesThe thickness at the centre of a plano convex lens is 3 mm and the mat diameter is 6 cm If the speed of light in the material of the lens is mathongo mat 2 x 108 ms The focal length of the lens is mathongo mathongo 1 0 30 cm 2 15 cm 3 1 5 cm 4 30 cm mathongo mathongo mathongo mat mathongo mathonge mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongomathongo mas mathongo mathonco mathango mathongo mat

Physics
WavesThe graph shows variation of source voltage V and steady state current I drawn by a series RLC circuit Identify correct statement s 400 0 400 ImA S 05 10 15 20 A Current lags the voltage B Resistance in circuit is 250 30 VIV t ms C If capacitive reactance is 74 S2 then inductive reactance will be 324 D Average power dissipated in circuit will be 20 3w

Physics
WavesTwo uniform strings A and B formed of steel are made to vibrate under the same tension If the first overtone of A is equal to the second overtone of B and the radius of A is twice that of B Then the ratio of the length of the strings is Both strings are fixed at both ends 01 2 01 3 hr min 01 4

Physics
Wavesamplitude m wave IS represented by expression Vm 5 1 0 6 cos 6280f sin 211 x 10 t volts The minimum and maximum amplitudes of the amplitude modulated wave are respectively 1 5 V 8 V 2 2 An 3 3 V 5 V 5 2 V 8 V 2 4 3V 5V 2

Physics
WavesThe vibrations of a string of length 40 cm fixed at both ends are represented by the equation y 4 sin cos 96mt where x and y are in cm and it is in seconds Maximum displacement of a point at x 5 cm is 1 4 cm 3 5 cm 2 2 cm 4 Zero

Physics
Waves1 between interface with velocity Line PQ and RS are the interface of medium 1 and medium 2 respectively A car is running in 3v towards right as shown in figure y is the speed of sound in air A man A is moving with velocity v 3 towards left and man B with velocity v 2 towards right in their respective medium The speed of sound in medium 1 is 5v and in medium 2 it is 7v Car is emitting a sound of frequency fo Then 4 Q SU Man A 2A MA is A is MB Medium 1 4 S P R A If A and B are the wavelength received by man A and man B respectively then the ratio of 35 7 S 3v 4 B B If A and B are the wavelength received by man A and man B respectively then the ratio of 7 Medium 2 When two coop bubble 11 11 11 If fA and fs are the frequency received by man A and man B then the ratio of fA 28 is fB 195 D If f and f are the frequency received by man A and man B then the ratio of A is 35 fB 7

Physics
WavesPhysics Question Palette Question No 30 A simple harmonic oscillator of angular frequency 50 Hz is attached to the ends of a chord that has a mass density of 0 1 kg m under tension of 10 N What power must oscillator provide to the chord to generate sinusoidal wave with an amplitude of 2 cm

Physics
Waves7 Electromagnetic wave of intensity 1800 W m falls on a completely absorbing spherical surface having radius R as shown in the figure R 3 cm Force exerted by beam on the sphere is 1 108 10 10 N 2 54 x 10 10 N 3 216 10 10 N 4 Zero

Physics
Waves38 Three waves of equal frequency having amplitudes 12 4 and 8 unit meet at a point with successive phase difference of Amplitude of resulting wave will be 1 24 unit 3 4 2 unit 2 12 2 unit 4 20 unit

Physics
WavesD pick the right answer O ME the polarisation of the propagation medium the frequency dependence of the properties of the propagation medium the losses in the propagation medium the magnetisation of the propagation medium Question 9 In a uniform plane wave the electric field pick the right answer is parallel to the Poynting vector is along the direction of propagation is transverse to the propagation direction www

Physics
Wavesseparation between the plates 6 A prism of refractive index u and refractin angle A is placed in the minimum deviation position If the angle of minimum deviation is then the value of A in term of u is 1 sin 2 sin 3 2 cos 4 cos F 2

Physics
WavesConsider the superposition of N harmonic waves of equal amplitude and frequency If N is a very large number determine the resultant intensity in terms of the intensity Io of each component wave for the conditions when the component wave have identical phases

Physics
Waves3 581 nm waves 5 The light y 10 sin cot kx interfere The ratio of maximum to minimum average intensity of light in interference pattern is 2 1 3 4 575 2 nm having displacements and y 2sin ot kx 67 95 3

Physics
WavesTX At certain instant the shape of a simple train of ple wave is y 12 sin x and y are in cm The velocity of the wave 50 propagation is 100cm s in a positive direction away from the origin Find the equation giving the shape of the wave 0 25s later

Physics
WavesThe tension length diameter and density of a string B are double than of another string A Which of th following overtones of B is same as the fundamental frequency of A String is fixed from both ends A 1st B 2nd 3rd D 4th

Physics
WavesA proton accelerated through a potential difference V has a certain de Broglie wavelength In order to have the same de Broglie wavelength an a particle must be accelerated through a potential difference 8 V V 8 4V

Physics
WavesRefer to figure 2 The ball then lands in a fast moving river barely floating in water The ball now travels down stream with a velocity of 10 0 m s when suddenly the river goes from 10 0 wide to just 2 00 m It also travels through a change in density from 1000 0 kgm blue to 950 0 kgm yellow How fast is the ball traveling at the end of the river Was there any wor done on the ball and if so how much 10 0 m Figure 2 The ball is floats along the river at 10 0 m s The ball has a radius of 0 300 m

Physics
WavesA travelling sound wave is described by the equation y 2 sin 4t 5x where y is measured in centimeter t in seconds and a in meters a Find the ratio of amplitude and wavelength of wave b Find the ratio of maximum velocity of particular to wave velocity

Physics
WavesTest 4 Code A 7 In a sinusoidal wave the time required for a particular point to move from maximum displacement to zero displacement is 0 2 s The frequency of the wave is 1 1 5 Hz 3 1 4 Hz 2 1 25 Hz 4 1 47 Hz

Physics
WavesThe audible frequency for a normal human being is 20Hz to 20kHz Fuind the corresponding wavelengths if the speed of sound in air 320m s b Find the phase difference between two position separated by 20cm at a particular instant

Physics
Waves22 A sonometer wire supports a 4 kg load and vibrates in fundamental mode with a tuning fork of frequency 416 Hz The length of the wire between the bridges is now doubled In order to maintain fundamental mode the load should be changed to 1 2 kg 2 8 kg 3 16 kg 4 4 kg

Physics
WavesMarks 31 In the given arrangement shown in figure a mass M is suspended with the help of string which passes over a light pulley The string is connected to a vibrator having constant frequency The vibrator gives transverse oscillation to string When the value of M is either 16 Kg or 25 Kg standing waves are observed however no standing waves are observed with any mass between these values The largest mass for which standing waves could be observed is n x 10 Kg Find the value of n String is very light Virbrator

Physics
Wavesmoving 0 with re The served ms 5 Re 20 A source of unknown frequency gives 4 beats s when sounded with a source of known frequency 250 Hz The second harmonic of the source of unknown frequency gives five beats per second when sounded with a source of frequency 513 Hz The unknown frequency is 2013 a 260 Hz b 254 Hz c 246 Hz d 240 Hz 21 A wave travelling in the ve x direction having di

Physics
Waves2 Two tuning fork when sounded together gives 4 beats per second Frequency of fork A is 248 Hz Now tuning fork Bis waxed due to which beat frequency is increased to 7 beats per second Find the original frequency of B 1 244 Hz 2 252 Hz 3 241 Hz 4 255 Hz 3 For a heat engine the temperature of the source is

Physics
WavesA transverse wave is passing through a string shown in figure Mass density of the string is 1 kg m and cross section area of string is 0 01 m Equation of wave in string is y 2 sin 20t 10x The hanging mass is in kg O O O 40 0 2 0 004 None of these m
Physics
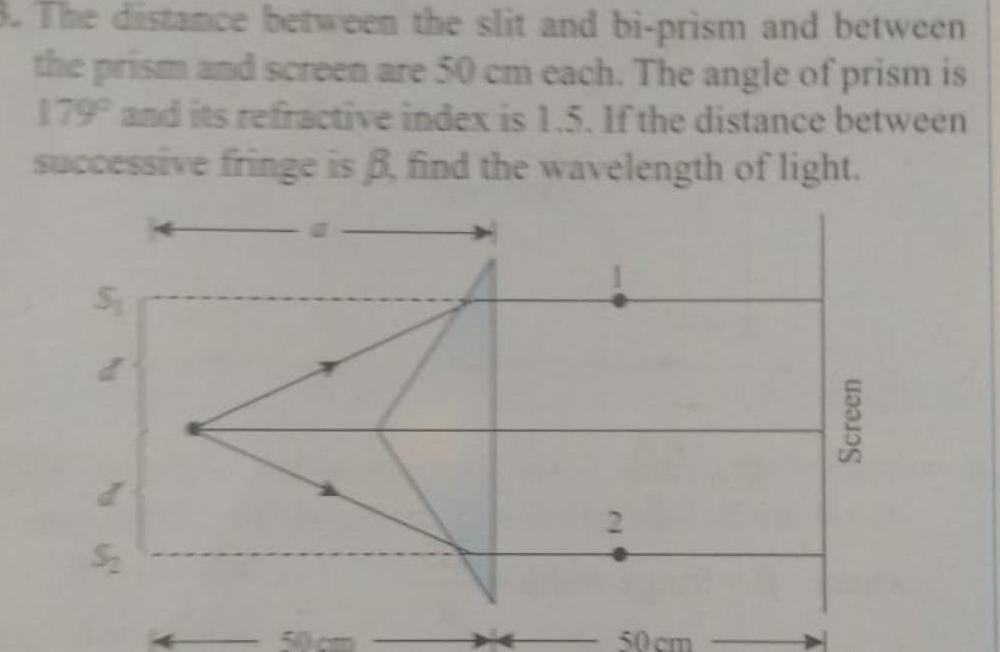
WavesThe distance between the slit and bi prism and between the prism and screen are 50 cm each The angle of prism is 179 and its refractive index is 1 5 If the distance between successive fringe is B find the wavelength of light 29 50 cm Screen

Physics
WavesFundamental frequency of a stretched sonometer wire is f When its tension is increased by 96 and length decreased by 35 its fundamental frequency becomes n f When its tension is decreased by n 11 36 and its length is increased by 30 its fundamental frequency becomesn f The value of is 7 found to be Find n

Physics
WavesIn fresnel s biprism experiment a mica sheet of refractive index 1 5 and thickness 6 x 10 6 m is placed in the path of one of interfering beams as a result of which the central fringe gets shifted through five fringe widths Then calculate the wavelength of light A 4000 B 5000 C 6000 D 7000

Physics
Waves8 Phase difference at the central point changes by 1 3 when a thick film having refractive index 1 5 and thickness 0 4 m is placed in front of upper slit of a YDSE set up If the wavelength in nm of the light used is 600 k find k

Physics
Waves5 Two beams of light having intensities I and 41 interfere to produce a fringe pattern on a screen The phase difference between the beams is 2 at point A and at point B Then the difference between the resultant intensities at A and B is x I Find value of x

Physics
WavesA source of sound S and a detector D are placed at some distance from one another A big cardboard is placed near the detector and perpendicular to the line SD as shown in figure 16 E1 It is gradually moved away and it is found that the intensity changes from a maximum to a minimum as the board is moved through a distance of 20 cm Find the frequency of the sound emitted Velocity of sound in air is 336 m s

Physics
WavesA source of frequency f is stationary and an obsercer starts moving towards it at t C with constant small acceleration Then the variation of observed frequency f registered by the observer with time is best represented as