Work, power & energy Questions and Answers

Physics
Work, power & energyIn Searle s apparatus we have two wires During experiment we study the extension in one wire The use of second wire is A to support the apparatus because it is heavy and may not break single wire B to compensate the changes in length caused by changes in temperature of atmosphere during experimentation C to keep the apparatus in level so that extension is measured accurately D all the three above

Physics
Work, power & energyProblem 93 A car of mass 4m holds a block of mass m which is attached to the former by means of a spring of spring constant k as shown in the diagram All surfaces are The system is at rest A bullet horizontal velocity vo and frictionless and the wheels are massless of mass m is fired at the first block with a sticks to it Find a the velocity of the car at the moment when the spring undergoes maximum compressio b the maximum compression of the spring Pla www A 11 1 of macr kg approaches a spring of stiffness k 80 k 10 m s in

Physics
Work, power & energyA body of mass 4 9 kg hangs from a spring and oscillates with a period 0 5 s On the removal of the body the spring is shortened by Take g 10 ms 10 1 6 3 m 2 0 63 m 3 6 25 cm 4 63 cm A simple pendulum of frequency n falls E

Physics
Work, power & energyA body of mass 0 1 kg travelling with a velocity of 5 m s collides head on with another body of mass 0 2 kg travelling in the same direction with a velocity of 1 2 m s If the two bodies stick together after collision their common velocity is A 0 967 m s B 1 233 m s D 2 524 m s C 2 467 m s

Physics
Work, power & energyWhen a spring is compressed or 1 point stretched beyond its natural position by applying some force work is done on it Its elastic potential energy O O O increases decreases disappears
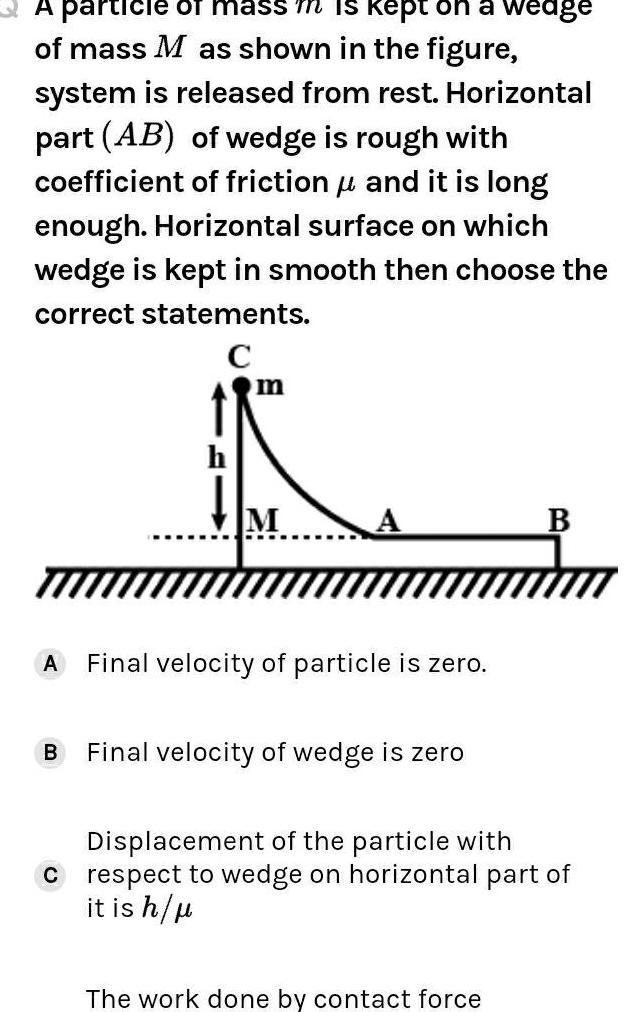
Physics
Work, power & energyA particle of mass m is kept on a wedge of mass M as shown in the figure system is released from rest Horizontal part AB of wedge is rough with coefficient of friction and it is long enough Horizontal surface on which wedge is kept in smooth then choose the fl correct statements C m B M A Final velocity of particle is zero Final velocity of wedge is zero B Displacement of the particle with C respect to wedge on horizontal part of it is h The work done by contact force

Physics
Work, power & energyP79 A heavy body of mass m hangs on a flexible thread in a railway carriage which moves at speed to on a train safety test track as shown in the figure The carriage is brought to rest by a strong but uniform braking Can the pendulum travel through 180 so that the tant thread ronghon 10

Physics
Work, power & energyA ladder 2 5 m long and of weight 150 N has its centre of gravity 1 m from its bottom A weight of 40 N is attached to the top end The work required to raise the ladder from the horizontal position to the vertical position is A 190 J C 285 J L B 250 J D 475 J

Physics
Work, power & energyD A B C energy is conserved Four possible forms of the potential energy of the particle are given unit mass is moving along the x axis under the influence column I a and U are constants Match the potential energies in column I to the correspond statement s in column II Column I plumn I U x U 1 2 DI a U x 2 2 a U x U x 0 0 0 1 10 x 2 2 a U x 0 20 exp U x a 3 a 1 x P Q R P Q s E X a Q pa R RIS S PR Column II The force acting on the particle is zero at x a The force acting on the particle is zero at x 0 The force acting on the particle is zero at x a The particle experiences an attractive force towards x 0 in the region x a U The particle with total energy about the point ya can oscillate

Physics
Work, power & energyA mass M is supported by a massless string wound round uniform cylinder of mass M and radius R On releasing the mass from rest it will fall with acceleration M 1 g 2 g 2 3 g 3 4 2 g 3 3 vo M 10 A solid ball of radius r rolls inside a hemispherical shell of radius R It is released from rest from point A as shown in fig The angular velocity of centre of the ball in position B about the centre of the shell is g 2 5 R 1 1 2 3 4 10 g 7 R r 28 5 Rr 5g 2 R 1 9 12 A heavy ball is thrown on a rough horizontal surface in such a way that it slides with a speed vo initially without rolling It will roll without sliding when its speed falls to 1 vo In the fig the plank is being pulled to the right with a constant speed v If the cylinder does not slip then 11 The speed of a homogeneous solid sphere after rolling down an inclined plane of vertical height h from rest without sliding is 10 1 gh V 2 gh 3 6 4 gh 1 the speed of the centre of mass of the cylinder is 2 v 2 the speed of the centre of mass of the cylinder is v 3 the angular velocity of the cylinder is v R 4 the angular velocity of the cylinder is zero 13 R The minimum value of F for which the cube a begins to topple about an edge is mig 20 3

Physics
Work, power & energyThe given plot shows the variation of U the potential energy of interaction between two particles with the distance separating them r B D E C 1 B and D are equilibrium points 2 C is a point of stable equlibrium 3 The force of interaction between the two particles is attractive between points C and D and repulsive between points D and E on the curve 4 The force of interaction between the particles is attractive between noints E and F on the curve

Physics
Work, power & energyA person standing near the edge of the top of a building throws two balls A and B The ball A is thrown vertically downward and the ball B is thrown vertically upward with the same speed The ball A hits the ground with a speed and the ball B hits the ground with a speed up We have VA C VA UB B A VA UB B UA UB D the relation between A and B depends on height of the building above the ground

Physics
Work, power & energyVelocity time graph of a particle of mass 2 kg moving in a straight line is a shown in figure Work done by all the forces on the particle from t 0 to t 2 sec is v m s 20 1 400 J 2 400 J 3 200 J 1 s

Physics
Work, power & energy12 Force acting on a particle is 21 31 N Work done by this force is zero when a particle is moved on the line 3y kx 5 Here value of k is a 2 b 4 c 6 d 8

Physics
Work, power & energyBlocks of mass 20kg and 5kg are connected by a light string as shown Coefficient of friction between block A and fixed inclined is 0 1 Find the minimum distance in m between the two blocks 30 20kg 0 1 Fixed 5kg B 10m 2

Physics
Work, power & energyA system of two paint buckets connected by a lightweight rope is released from rest with the 12 0 kg bucket 2 50 m above the floor as shown in the Figure Use the principle of conservation of energy to find the speed with which this bucket strikes the floor Ignore friction and the mass of the pulley a 4 43 m s c 4 95 m s e None b 5 42 m s d 4 04 m s 12 0 T 2 5 m 6 0 kg

Physics
Work, power & energyA household watches T V for about 2 0 hours total per day Their T V uses 400 Watts when it is plugged in What is the cost of 1 month 30 days of using the T V if the power company charges 0 30 per kW hr a 0 30 b 3 60 c 7200 d 7 20

Physics
Work, power & energyPotential energy and kinetic energy of a two particle system under imaginary force field are shown by curves KE and PE respectively in figure This system is bound at 1 only point A 2 only point D 3 only point is st 30 de sd A B and C 4 All points A B C and D d ARXAMD 8 Energy SIGA 91190 KE B Distance PEO snil D

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle describes a horizontal circle in a conical funnel whose inner surface is smooth with speed of 0 5 m s What is the height of the plane of circle from vertex of the funnel Question Type Single Correct Type 1 0 25cm 2 2cm 3 4cm 4 2 5cm

Physics
Work, power & energy1 A 10 kilogram ball rolls down a stair case from a 20 m second floor and reached the ground after 1 sec a Solve for kinetic energy at 2 sec Su A v 4t at V 0 10x1 v 10 m s at I see when it reaches ground 10 m s 2 x 15 x 100 500 Joule b Solve for potential energy Potential energy mgh m 10 kg 9 h 10 m s 20 m mgh 10x10x26 After 2 sec velocity so K E 2 2 x mu c Solve for total mechanical energy when the time is 0 sec V 2660 Jouk

Physics
Work, power & energyd zero mB c zero mB 17 The work done in moving a dipole from its most stable to most unstable position in a 0 09 T uniform magnetic field is dipole moment of this dipole 0 5 A m a 0 071 b 0 08 J c 0 09 d 0 1J ular coil of 25 turns and radius of 12 cm is a 4 c 4 33 A circu current horizon make a magnit to prev

Physics
Work, power & energyIn the figure shown the hollow tube of mass M is free to move without friction in the horizontal direction supported by two fixed vertical ring attached to the roof The system is released from rest Find the velocity of the tube when the block B has fallen through a height h Neglect any friction and mass of the string m M B

Physics
Work, power & energy4 Calculate the work done in twisting a steel wire of diameter 2mm and length 50 through 45 Rigidity modulus of the steel is 8 x 10 N m SECTION D

Physics
Work, power & energy21 A body of mass 2 kg is moved from a point A to a point B by an external agent in a conservative force field If the velocity of the body at the points A and B are 5 m s and 3 m s respectively and the work done by the external agent is 10 J then the change in potential energy between points A and B is a 6 J c 16 J b 36 J d None of these

Physics
Work, power & energy13 An object of mass m slides down a hill of height h of certain arbitrary shape and after travelling a horizontal path stops because of friction The friction coefficient is different for different segments for the entire path but is independent of the velocity and direction of motion The work that a force must perform to return the object to its initial position along the same path is a mgh b 2 mgh d mgh c 4 mgh

Physics
Work, power & energy1 Kinetic energy of a particle moving in a straight line varies with time t as K 4t2 The force acting on the particle 1 is constant 2 is increasing 3 is decreasing orgas

Physics
Work, power & energyA given object takes n times as much time to slide down a 45 rough incline as it takes to slide down a perfectly smooth 450 incline The coefficient of kinetic friction between the object and the incline is given by

Physics
Work, power & energy22 15 J energy is paid by a person to pull an object of mass 3 kg from depth h in empty well 40 energy is wasted due to friction When this object reach to the edge of well suddenly rope breaks and object goes to bottom of well if its velocity at bottom is 3 ms find the death of well A 6 m B 2 m C I m D 0 45 m 23 Two balls A and B Pagem the 4se heip Ratio 12 eir mass are 1 4 when potential

Physics
Work, power & energyLEN Target JEE Main Advanced 2021 SAMPLE PAPER 1 Paper 1 A uniform rod of mass m and length L is held at one of its ends such that the other end is vertically above it Now holding the lower end we release the rod so that it rotates in a vertical plane When it reaches the lowermost position we release the end which has been held in our hands It is seen that the end which was held in our hands strikes the ground first with rod being vertical at that time What could be the possible height of the point above the ground where we had held the rod Take n 10 neglect friction 11L B 31L C 8L A D 64L

Physics
Work, power & energy7 A body is moved from rest along a straight line by a machine delivering constant power The ratio of displacement and velocity s v varies with time t as t a c S V CDC 96 S V CAT b d S V S V

Physics
Work, power & energy0 72 mgH mgH 0 28 mgH A uniform rectangular parallelopiped of mass m and with sides l 2l and 4l is placed in turn on each c its three sides on a horizontal surface What is the potential energy of the parallelopiped in each of thes positions What position will be the most stable

Physics
Work, power & energy7 As shown in figure a sphere of simple pendulum having mass m releases from position A becomes steady after a collision with a sphere having mass m 2m at mid position of its path of motion Hence a sphere of m mass attains kinetic energy of 4 J then m A 2 kg B 3 2 kg C 6 3 kg D 8 2 kg 60 m 1m m A

Physics
Work, power & energyWhen a body moves with an increasing speed alo a horizontal circle then 1 No work is done on body 2 Work done on the body is positive 3 Work done on the body is negative 4 Work done may be positive or zero

Physics
Work, power & energyTwo masses of equal mass m 2 points 0 1 mg are connected by a spring of constant 25 N m Compute the two normal mode frequencies 2 marks E k O 500 Hz 500 Hz O 500 Hz 866 Hz O 1000 Hz 8000 Hz 25 Hz 75 Hz m

Physics
Work, power & energy3 2850 J 5 The standard Gibb s energy change for a gaseous reaction at 27C is X Kcal If equilibrium constant for a reaction is 100 and R is 2 cal K mol Then X is 1 2 7636 2 2 7636 3 807 BAT 4 807

Physics
Work, power & energyA satellite of mass m is circulating around the earth with constant angular velocity If radius of the orbit is R and mass of the earth M the ratio of angular momentum of the satellite about the centre of the earth and its kinetic energy will be 1 3 2 R MV GM 2 1 Ro 2 4 2 Ro GM Ro

Physics
Work, power & energyTwo bodies having masses m and m are velocities v and v collide and form a composite system it m v m v 0 the m m velocity of composite system iwll be 1 V V 2 V V 3 V V2 2 4 zero

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle is moving on the circular path of the radius R with centripetal acceleration a k Rt Then the correct relation showing power P delivered by net force versus time t is 5 P 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 1 2 3 A h 3 3
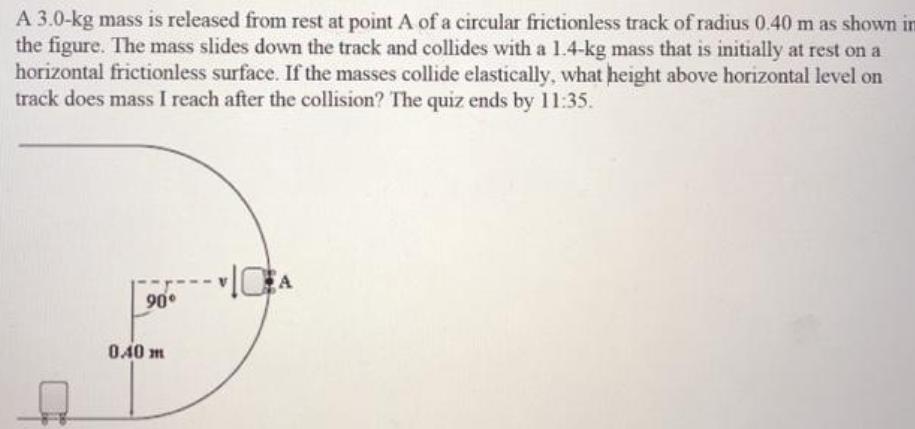
Physics
Work, power & energyA 3 0 kg mass is released from rest at point A of a circular frictionless track of radius 0 40 m as shown im the figure The mass slides down the track and collides with a 1 4 kg mass that is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface If the masses collide elastically what height above horizontal level on track does mass I reach after the collision The quiz ends by 11 35 90 0 40 m

Physics
Work, power & energyA smooth sphere of mass M moving with velocity u directly collides elastically with another sphere of mass m at rest After collision their final velocities are V and v respectively The value of v is 1 2M 2 3 4 2 um M 2u 1 20 M

Physics
Work, power & energyA block of mass m initially at rest is dropped from a heighth on to a spring of force constant k The maximum compression in the spring is x then mmmmm 1 mgh kr mg h 2 mg t th 3 mgh k a h 4 mg h x k a h

Physics
Work, power & energyWhich of the following statements is true about a particle moving freely in a three dimensional space where potential energy is 5J a Particle cannot have arbitrary speed b Force equation for free particle is derivable from energy equation c It can have non zero power d Angular momentum is not conserved

Physics
Work, power & energyQuestions 23 and 24 are based on the following physical situation Ends of three light identical rods each of length 1 are connected to a light pivot that enables them to rotate in any direction At the other ends of the rods three particles A B and C of masses m 2m and 3m respectively are affixed Initially the rods are coplanar angle between any two adjacent rod is 120 and the particles are at rest Now the particle C is given a velocity u perpendicular to the rod connected to it and in the plane of the rods as shown in the figure Ignore gravitational interaction between the particles 23 Denoting acceleration vectors of the particles A B and C by a a and ac respectively which of the following conclusion can you make a c 0 c a 2a 3 0 A b 3a 2a c 0 d None of these B 120 1 120 120 u

Physics
Work, power & energysmall putty of mass m 1 kg and speed vo 4 m s strikes a dumbbell placed on a smooth table as shown in figure Putty moving in the plane of the dumbbell The putty sticks to dumbbell ball which is to be treated as particle How much hermal energy is produced in J Consider rod of dumbbell to be massless m 30 m

Physics
Work, power & energyother cases 13 A particle is moved along a path AB BC CD DE EF FA as shown in figure in presence of a force P ayt 2xxj N where x and y are in meter and a on the particle by this force F will be 1 Nm The work done Jouk 1 0 Is entered y B H D F 0 5 CU X

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle is moved along a path AB BC CD DE EF FA as shown in figure in presence of a force F ay 2xxj N where x and y are in meter and a H 1 Nm The work done on the particle by this force F will be Joule 1 0 0 5 y 0 A IF D E 0 5 B 1 0 X

Physics
Work, power & energyFor what minimum value of m will the block of mass m just leave contact with the surface blution Let extension in the spring be then m gx kx 2 Xo due to m kx 2m g but kx mg so 2m g mg m therefore minimum value of m m EN m 2 k ellele m m

Physics
Work, power & energyEngine is used to move a mass of 0 8 kg starting from rest a distance of 2 m in a straight line along a frictionless flat surface Engine exerts a constant force of 5 N Find the average power in W exerted by the engine

Physics
Work, power & energyA waterfall is 100 meters high If one fourth of the potential energy of the falling water gets converted to heat the rise in temperature of water will be 0 059 C 0 159 C 0 90 C

Physics
Work, power & energyExample 6 6 A block of mass m 1 kg moving on a horizontal surface with speed v 2 ms enters a rough patch ranging from x 0 10 m to x 2 01 m The retarding force F on the block in this range is inversely proportional to x over this range k F for 0 1 x 2 01 m 0 for x 0 1m and x 2 01 m where k 0 5 J What is the final kinetic energy and speed u of the block as it crosses this patch V