Work, power & energy Questions and Answers

Physics
Work, power & energyA point like mass moves horizontally between two walls on a frictionless surfaces with initia kinetic energy E With every collision with the walls the mass loses 50 of its kinetic energy to thermal energy How many collisions with the walls are necessary before the speed of the 1 mass is reduced by a factor of 8 means it becomes th of initial speed 8

Physics
Work, power & energy6 One man takes 1 minute to raise a box to a heigh 1 of 1 metre and another man takes minute to d so The energy of the two is a different b same c energy of the first is more d energy of the second is more 2

Physics
Work, power & energy20 Two strips of metal are riveted together at their ends by four rivets each of diameter 6 0 mm What is the maximum tension that can be exerted by the riveted strip if the shearing stress on the rivet is not to exceed 6 9 x 107 Pa Assume that each rivet is to carry one quarter of the load CESE

Physics
Work, power & energyAt t 0 two blocks of 2 kg and 3 kg are moving on a smooth fixed surface with given velocity as shown in the figure Assure the lower block is long enough u 0 3 2kg 3kg smooth 10m s RO 5m s Find out the work done by kinetic friction force on 2 kg block till the relative motion is ceased A 51 Joule B 51 Joule C 100 Joule D 100 Joule Find out the work done by kinetic friction force on 3 kg block till the relative motion is ceased A 51 Joule B 51 Joule C 36 Joule D 37 5 Joule

Physics
Work, power & energyJee 3 1 21 Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume Area of cross section of one wire is A and other wire is 3A If wire of cross section area A is stretched by force F then force on another wire for same extension is ALL 12 A AL L 1 F 2 4F 3 6F ford 4 9F 22 A wire of length area of cross section A and 2 LL 42 ALL f 25 W 9F 3 F 4 The bu is subj decrea 1 p B

Physics
Work, power & energyIn the situation below block A having mass m and block B having mass 3 m are held at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface with a massless spring compressed between them After the blocks are released from rest what is the ratio of the magnitude of B s momentum to the magnitude of A s momentum mm 3m O 9 1 O 3 1 O 1 1 O 1 3

Physics
Work, power & energy1 1 1 2 2 3 4 A small steel ball falls through a syrup at constant speed of 10 cm s If the steel ball is pulled upwards with a forc equal to twice its effective weight how fast will it move upwards 1 10 cm s 2 20 cm s 3 5 cm s 4 5 cm s

Physics
Work, power & energyAs a ball rolls down the inclined plane the 5 power of gravitational force P and frictional force P thereafter A P increases with time and Pf remains constant with time B P as well as P remain constant with time C P as well as P increase with time D P remains constant and P with time decreases Go Uch Hardlich Pa f A P g dri B Pa C Pa g D Pf g

Physics
Work, power & energyA box of mass m 2 00 kg is released at the top of an inclined plane as sheen in the figure The box starts out at height h 0 500 m above the top of the table the table height is H 1 5 m and the angle of the inclined plane is 35 degrees a Calculate the speed of the mass at the bottom of the inclined plane b Calculate the distance R the object travels 0 500 1 S 1

Physics
Work, power & energyQ 44 Shown below are two circular fixed rings of radii R and 2R on which three identical beads are free to move Beads 2 and 3 are initially stationary while bead 1 is moving with velocity u and spring is initially relaxed 1 collides with 2 with coefficient of restitution Determine maximum extension of spring in subsequent motion 2R 200 R m 3 m 2 m

Physics
Work, power & energyIf specific resistance of a potentiometer wire is 10 70 m and current flow through it is 0 1 A cross sectional area of wire is 10 6 m then potential gradient will be 1 10 2 volt m 2 10 4 volt m 3 10 6 volt m 4 10 8 volt m
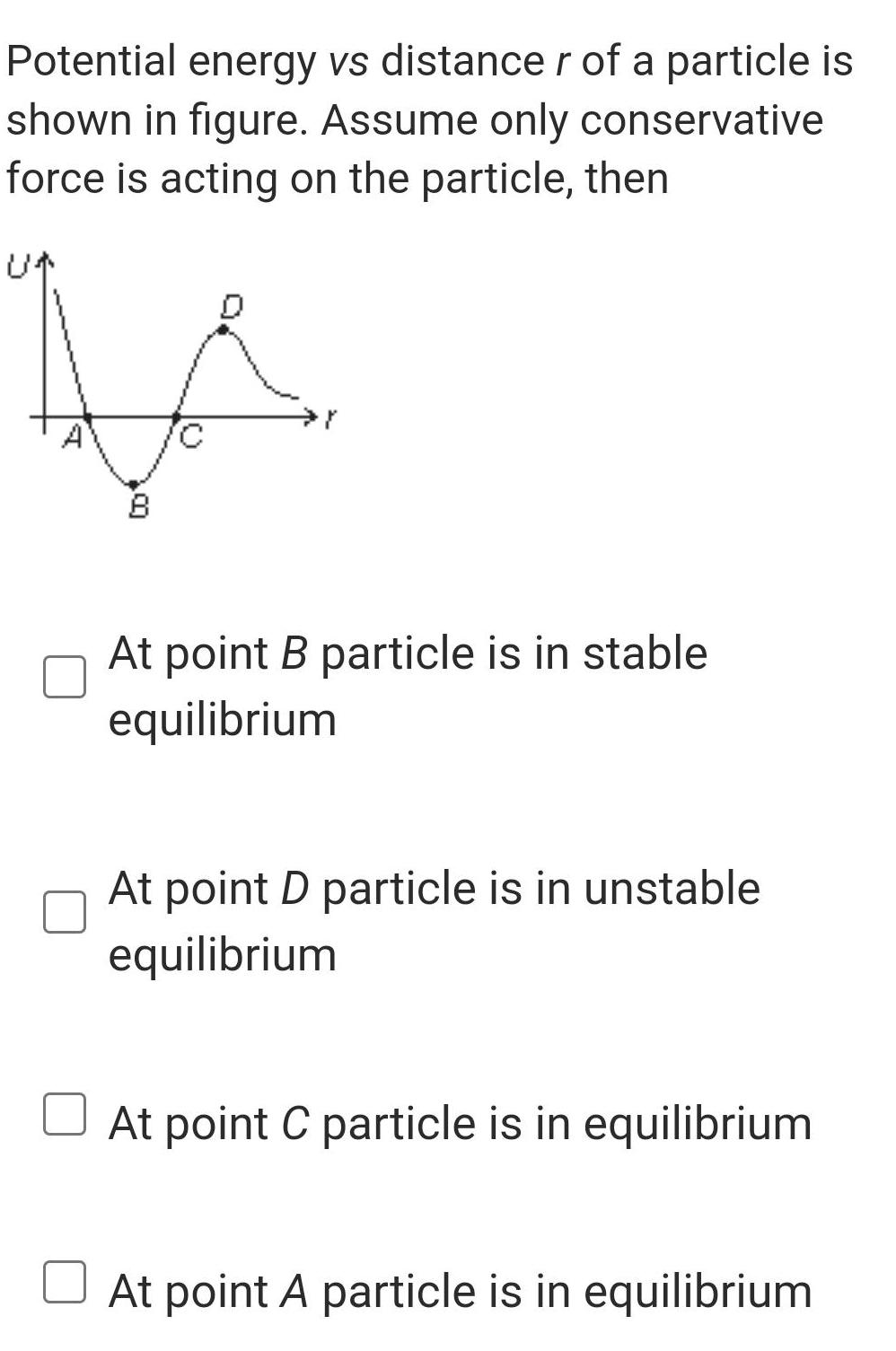
Physics
Work, power & energyPotential energy vs distance r of a particle is shown in figure Assume only conservative force is acting on the particle then I At point B particle is in stable equilibrium At point D particle is in unstable equilibrium At point C particle is in equilibrium At point A particle is in equilibrium
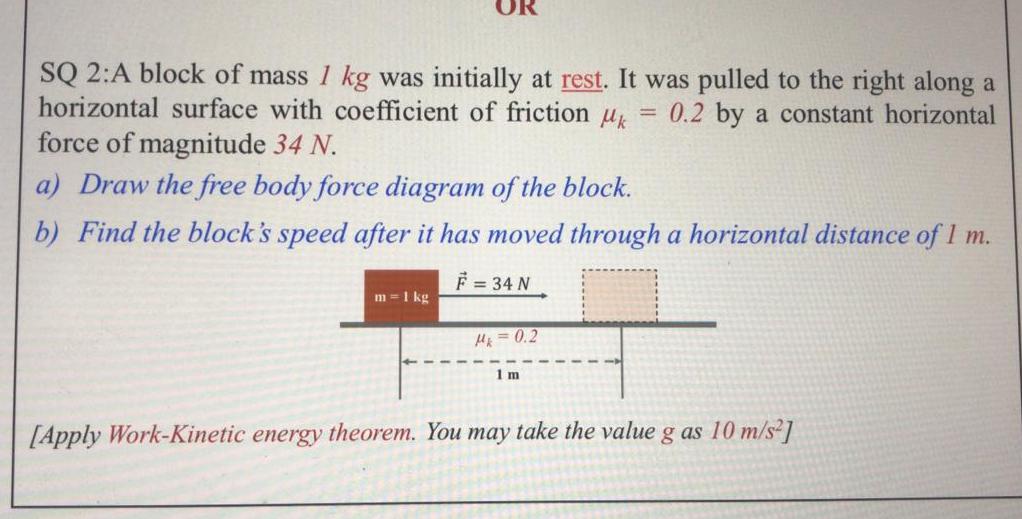
Physics
Work, power & energySQ 2 A block of mass 1 kg was initially at rest It was pulled to the right along a horizontal surface with coefficient of friction k 0 2 by a constant horizontal force of magnitude 34 N a Draw the free body force diagram of the block b Find the block s speed after it has moved through a horizontal distance of 1 m F 34 N m 1 kg Mk 0 2 1 m Apply Work Kinetic energy theorem You may take the value g as 10 m s2

Physics
Work, power & energy1 a The displacement of a particle which moves along the x axis is given by x 2 3t e 05t Find the maximum value of velocity attained and the time taken for attaining the maximum velocity b Each of the two uniform hinged bars has a mass m and length I and is supported and loaded as shown For a given force P determine the angle 8 for equilibrium using the principle of virtual work mg X mg

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle is moving with a constant speed along a straight line path A force is not required to 1 Increase its speed 2 Decrease its momentum 3 Change the direction 4 Keep it moving with uniform velocity

Physics
Work, power & energyIf energy E momentum p and force F are chosen as fundamental units The dimensions of mass in new system is a E p c E p b E p d none of these

Physics
Work, power & energyWork done Force in the direction of motion distance through which body moves here Force is a vector quantity then wh y work is sclaler quantity Work done is negetice when the force acts opposite to the direction of motio n and work done is positive when the fo rce is in the direction of motion The above line concludes that work do ne requires direction therefore it shoul

Physics
Work, power & energy154 A constant horizontal force F 0 10 N is applied to a small bar of mass m 50 g resting on a horizontal plane Find the work performed by the friction force for whole time of motion if friction coefficient depends on the distance x covered as k yx where y is a constant

Physics
Work, power & energy34 180 Mark for Review A block of mass 10 kg moving in x direction with a constant speed of 10 ms is subjected to a retarding force F 0 1 x J m during its travel from x 20 m to 30 m Its final KE will be 250 J 475 J 02 52 hr min 450 J

Physics
Work, power & energy7 A bead is connected with a fixed cylinder of radius R by an inextensible massless string fR in a smooth horizontal plane If the bead is pushed with a velocity 2 of length v perpendicular to the string The bead moves in a horizontal curve and consequently collapses on the surface of cylinder after a time t Then RI Top View A Work done by the string on the bead is mv B The average speed of the bead is v during the time t C During motion before hitting tension in the string will increase continuously D Kinetic energy of the bead increases gradually

Physics
Work, power & energyThis section contains 20 SINGLE CORRECT TYPF questions Fach question has 4 choices Read More Hollow hemisphere is fixed and has radius R 8r where r is radius of small solid sphere released at top as shown Sphere rolls without slipping When sphere reaches bottom velocity of top most point of sphere is O 10 gr O 20 gr x

Physics
Work, power & energyTwo bodies of masses 1 kg and 5 kg are dropped gently from the top of a towe At a point 20 cm from the ground both the bodies will have the same a www b POWER macam Momentum Kinetic energy Velocity Total energy 2 vel MI MX V thur

Physics
Work, power & energyof system is 1 is conserved in direction SR 2 will change in direction with speed u collides with face at angle 8 with it as nitude of impulse imparted efficient of restitution of 60 A bullet of mass m moving with velocity v strikes a suspended wooden block of mass M If the block rises to height h then the initial velocity v of the bullet must have been 1 2gh 2 3 4 M m m m M m M m M 2gh 2gh 2gh Chapter Conte Vector product Position of ce Motion of cer Torque and momentum Equilibrium Moment o

Physics
Work, power & energyA 15g bullet is shot vertically into an 2kg block The block lifts upward 8 0 mm see figure The bullet penetrates the block and comes to rest in it in a time interval 0 0010 s Assume the force on the bullet is constant during penetration and that air resistance is negligible The intial kinetic energy of the bullet is closest to O a 0 0012 Ob 21 Oc 14 O d 0 16 O e 10

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle of mass 1kg is moving along x a xis under conservative forces only The pote ntial energy U x is given by U x 10 x 3 2 where x is in metre and U x is in joule A tx 5m the particle has kinetic energy of 10 J The total mechanical energy of the particl e remains constant at every position Answ er the following question Q Minimum potential energy of the particle is a 10J b 20J c Zero d

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle of mass 1 kg is moving along x axis under conservative forces only The potential energy U x is given by U 10 x 3 where x is in metre and U X is in joule At x 5 m the particle has kinetic energy of 10 J The total mechanical energy of the particle remains constant at every position Answer the following question Q Maximum speed of the particle is

Physics
Work, power & energySA 2 The plot below shows a graph of a potential energy curve for a particle with mass m If the particle is initially at rest at position ro what will be its speed at position 2ro Assume all forces are conservative U r 30 Vo

Physics
Work, power & energy1 A rod is fixed between a vertical wall and a horizontal surface A smooth ring of mass 1 kg is released from rest which can move along the rod as shown At the release point spring is vertical and relaxed The natural g 10m s length of the spring is 3 1 m Rod makes an angle of 30 with the horizontal Ring again comes to rest when spring makes an angle of 30 with the vertical Fomory B Maximum displacement of ring is 30 5 A Force constant of the spring is 3 1 N m 2 3 1m C Maximum extension in the spring is 3 1 m D Normal reaction on ring due to red when it again comes to rest is 505 DW

Physics
Work, power & energyA force F x y j N where x and y coordinates ar in metres acts upon a body and it moves along the path ABCDA as shown The work done by the force is 0 2 A 0 0 O 20 J 3 2 B 3 0 X

Physics
Work, power & energyTwo particles of masses m m move with initial velocities u and u On collision one of the particles get excited to higher level after absorbing energy If final velocities of particles be v and v then we must have 1 1 m w 1 m x m c m 0 m u 8 m u m u e m v m v 1 1 1 1 m u m u m v m v 1 1 1 1 m u m u e m v m v 2 NH N TR N

Physics
Work, power & energyA force F x i y2j N where x and y coordinates are in metres acts upon a body and it moves along the path ABCDA as shown The work done by the force is 0 2 D A 0 0 O 20 J 20 J O 42 J O Zero 3 2 B 3 0 X

Physics
Work, power & energyPotential energy associated with a conservative force is given by U where A is a constant then force always tends to accelerate the particle towards origin Ax force always tends to accelerate the particle away from origin force always tends to accelerate the particle towards the origin if A is positive force always tends to accelerate the particle away from origin if A is negative

Physics
Work, power & energyA satellite is orbiting around the earth in a circular orbit of radius r A particle of mass m is projected from the satellite in a forward direction with a velocity v 2 3 times the orbital velocity this velocity is given w r t earth During subsequent motion of the particle its minimum distance from the centre of earth is A r 2 Br C 2r co

Physics
Work, power & energyA crane lifts a car of mass 100 kg to a height 50 m in 10 seconds 9 Work done by crane A 50 kJ 10 1 Power of crane in HP is A 6 7 HP B 50 J OHP B If power delivered is 6700 W The time taken is A 10 seconds C 7 462 seconds C 2J C B D 67 HP 15 seconds data insufficient D D 5 kJ 76 HP

Physics
Work, power & energyIf a spring of stiffness k is cut into two parts A and B of length A B 2 3 then the stiffness of spring A is given by AIEEE 2011 11 May 4 1 3k 2k 2 4 5 5 1 3 k 5k 2

Physics
Work, power & energyA body of mass m is projected vertically with a velocity vo If it passes through the point of projection with speed resistance is 1 Zero 2 the work done by air 2 3mv 4

Physics
Work, power & energyParagraph for Questions 1 and 2 A block and wedge are displaced slowly from A to B as shown in diagram 5 Kg block is at rest w r t wedge A 5kg Work done in J by weight of block is 37 10m B 5kg 37

Physics
Work, power & energyA uniform chain of mass 2 kg and length 90 cm overhangs a smooth table with its two third part lying on the table The kinetic energy of the chain as it completely slips off the table in joule is m s g 10 Answer

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle has energy 100 GeV and momentum components Px 10 Py 5 Pz 20 all in GeV c as measured by the ATLAS detector at CERN What are its energy and momentum as measured by an observer travelling at 0 6c in the z direction c is the speed of light of course E Px Py Pz O a 140 10 5 100 O b 110 0 0 50 O c 110 10 5 50 O d 110 10 5 50 O e 140 0 0 100

Physics
Work, power & energy23 A highly elastic ball moving at a speed of 3 m s approaches a wall moving towards it with a speed of 3 m s After the collision what is the speed in m s of the ball 3 m s 3 m s tlu on another ball at rest The first
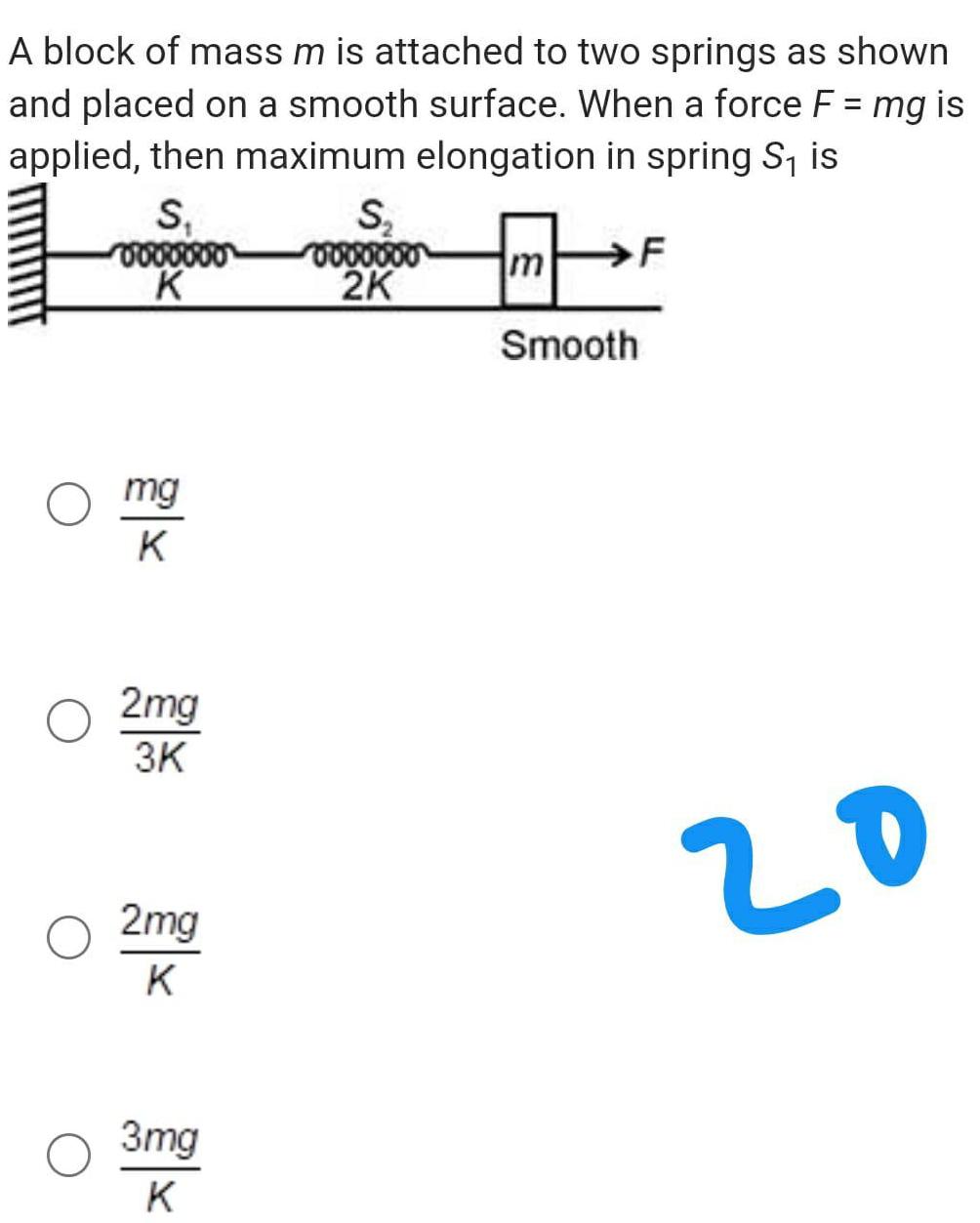
Physics
Work, power & energyA block of mass m is attached to two springs as shown and placed on a smooth surface When a force F mg is applied then maximum elongation in spring S is S vo K mg K 2mg 3K 2mg K 3mg K S 0000000 2K m Smooth 20

Physics
Work, power & energyA block A of mass m is at rest and another block B of equal mass moving with velocity Vo collides with A and sticks with it The total work done by friction after collision is BV A smooth 0 1 2mv 2 0 32m 1 2mv 2 rough

Physics
Work, power & energyExample 14 A small mass m starts from rest and slides down the smooth spherical surface of R Assume zero potential energy at the top Find a the change in potential energy the kinetic energy c the speed of the mass as a function of the angle 8 made by the radius through the mass with the vertical

Physics
Work, power & energyThe ratio of lengths of smooth and rough part of an inclined plane is 1 2 A particle starts moving from top and again comes to rest at the bottom point then the co efficient of friction of rough surface is 1 tan 0 2 3 3 tane u 0 1 Smooth TTT 2 Rough v 0 2 tane 4 1 tan e

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle of mass 1 kg is moving along a circle of radius 2 m If centripetal acceleration of particle varies as ac 3t2 where all quantities are in SI units The average power delivered to the particle in first 10 s in watt is

Physics
Work, power & energy2 10 A man is throwing bricks of mass 2 kg onto a floor of height 2m Bricks reaches to floor with speed 2 10 m s Man throws 10 bricks in a minute If power of man is W watt then W is equal to 3 10

Physics
Work, power & energyTwo equal and opposite forces each of magnitude F is applied along a rod of transverse sectional area A The normal stress to a section PQ inclined to transverse section is A Fsine A 20 X B cos 0 of F20 IT MR 0 0 stros F

Physics
Work, power & energyA source and an observer are situated on two perpendicular tracks as shown in the figure The observer is at rest and sources is moving with a speed 50 m s The source emits sound waves of frequency 90 Hz which travel in the medium with velocity 200 m s The frequency in Hz of sound heard by observer when the source crosses the origin O is Source

Physics
Work, power & energyHow internal force can change T OTAL ENERGY OF A SYSTEM som e answer say that when a bomb e xplodes energy is generated total energy changes But as we know t hat mass converts to energy and mass is the form of energy then p lease explain what is the correct a nswer as many answers are itself contradicting Thank you Internal force cannot change 1 Kinetic energy 2 Total momentum of system 3 Total energy of system 4 All of these

Physics
Work, power & energyA ball of mass 100g is dropped from a height of 10 m It loses 10 of its energy every time when it bounces off the floor Then the maximum height attained by it after 3rd bounce is approximately take g 10m s 07 3 m 0 7 1 m O 7 8 m 6 9 m