Gaseous and liquid states Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states1 Triple point of water exists at 1 T 0 0098 C P 4 7 mm of Hg 2 T 0 98 C P 470 mm of Hg 3 T 25 C P 760 mm of Hg 4 T 298 C P 760 mm of Hg

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe work done which is to be required to increase the area of soap film of 10 cm x 6 cm to 10 cm x 11 cm is x 10 4 J The surface tension of the soap film is 2 3 x 10 3 Nm 1 4 3 x 10 1 Nm 1 1 3 x 10 4 Nm 1 3 3x 10 2 Nm 1

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThree grams of helium diffuses from a container in 1 min The mass of sulphur dioxide diffusing from th same container over the same time interval will be 1 3 g 2 6 g

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA flask filled with CCl4 vapour was weighed at a temperature and pressure The flask was then filled with oxygen at the same temperature and pressure The mass of CCI vapour would be about 1 the same as that of the oxygen 2 one fifth as heavy as oxygen 3 five times as heavy as oxygen 4 twice as heavy as oxygen NIST

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA gaseous mixture contains three gases A B and C with a total number of moles of 10 and total pressure of 10 atm The partial pressures of A and B are 3 atm and 1 atm respectively and if C has molecular weight of 2 Then the amount of C present in the mixture will be 1 8 g 3 3g 2 12 g 4 6 g

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states5 Find the temperature at which the numerical values P of K and K will be equal to each other for the reaction N g H g NH3 g Ans In case of the given reaction An 1 or C numerical values of Kp and Kc be x then for the above reaction Kp x atm and K x mol L x L mol Therefore K K RT x atm 1 T 3 x L mol 1 x 1 If the 12 18 K The numerical values of K and K for the given reaction p C 1 0 0821 L atm mol K T

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA bubble of air is present in underwater at temperature 15 C and the pressure 1 5 bar If the bubble rises to the surface where the temperature is 25 C and the pressure is 1 0 bar what will happen to the volume of the bubble 1 Volume will become greater by a factor of 2 5 2 Volume will become greater by a factor of 1 6 3 Volume will become greater by a factor of 1 1 4 Volume will become smaller by a factor of 0 70

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesorder first B For the following reaction taking place at 400 K 2CO g CO2 g C s the total pressure is found to be 0 24 atm when the reaction is 100 complete Then the initial pressure of CO would have been

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesAt 20 C 0 258 mol A g and 0 592 mol B g are mixed in a closed vessel of 5 L capacity to conduct the following reaction A g 2B g C g If 0 035 mol C g remains in the equilibrium mixture then determine the partial pressure of each constituent at equilibrium
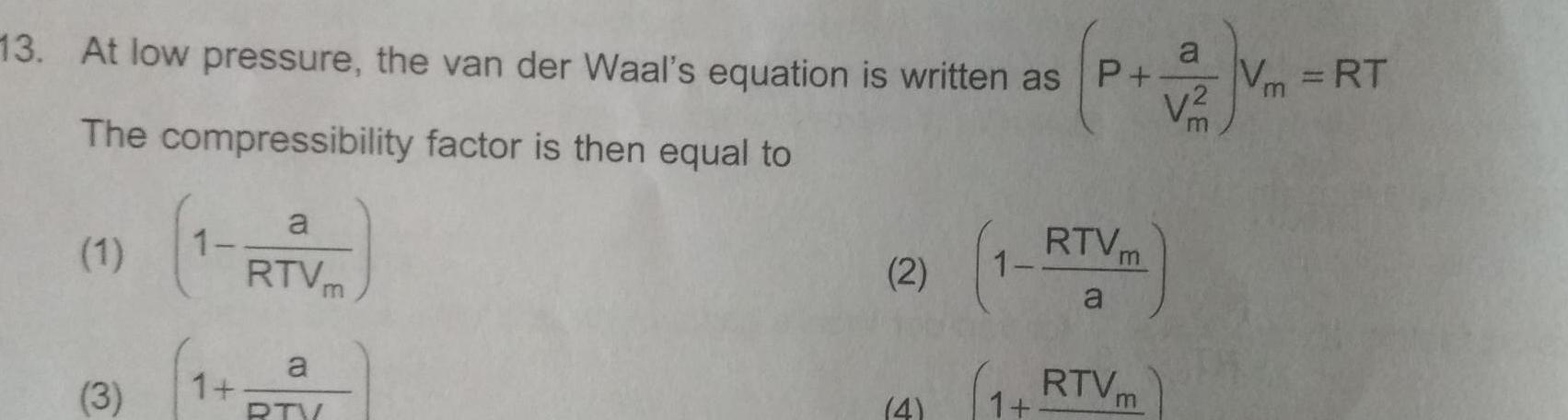
Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states13 At low pressure the van der Waal s equation is written as P V m The compressibility factor is then equal to 1 3 1 a RTV a RTV m 2 4 RTVm a 1 RTVm a V Vm RT

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states1 Air contains 23 oxygen and 77 nitrogen by weight The percentage of O by volume is 2 1 28 1 2 20 7 3 21 8 1

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states5 Helium atom is two times heavier than a hydrogen molecule At 298 K the average kinetic energy of a Helium atom is 1 two times that of hydrogen molecule 2 same as that of a hydrogen molecule 3 four times that of a hydrogen molecule 4 half that of a hydrogen molecule

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe total number of valence electrons in 4 2 c N ion is NA is the Avogadro s number 2 4 2 NA 4 3 2 N 1 2 1 NA 3 1 6 N

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesProblem 5 Calculate the number of molecules present in 350 cm of NH3 gas at 273 K an 2 atmosphere pressure

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA container contains O and N in equal molar concentration at same temperature what is the corre statement about the average molar kinetic energy of the two gases 1 Depends upon volume 2 KEN KE0 KE 02 4 KEN KEN 3 KEN KE02 1 2

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesCalculate the total pressure in a 10 litre cylinder which contains 0 4 g of helium 1 6 g of oxygen and 1 4 g of nitrogen at 27 C Also calculate the partial pressure of helium gas in the cylinder As sume ideal behaviour of gases Given R 0 082 li tre atm K 1 mol 1

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe absolute value of enthalpy of a system cannot be determined experimentally According to the definition

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states40 of a mixture of 0 2 mole of N and 0 6 mole of H react to give NH3 according to the equation N g 3H g 2NH3 g at given temperature and pressure Then the ratio of the final volume to the initial volumes of gases are as a 4 5 c 7 10 b 5 4 d 8 5

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states50 A closed bulb contains 0 01 mole of an inert gas He and NH4Cl s The initial pressure inside the bulb of helium at 27 C was 114 mm of Hg The bulb is now heated to 327 C when all the NH4Cl was decomposed and the final pressure becomes 908 mm of Hg Assuming ideal gas behaviour calculate a Partial pressure of HCl in mixture Amount of NH4Cl taken initially b

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesTwo flasks A B of equal capacity of volume contain NH and SO gas respectively under similar conditions Which flask has more number of moles 1 A 2 B 3 Both have same moles

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesVapour pressure of one molal aqueous solution of AgNO3 at the normal boiling point of water assuming 100 ionisation is 1 787 05 torr 2 733 56 torr 3 720 12 torr 4 700 torr pole in le no

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesB 8 Calculate the radius of He atoms if its Vander Waal s constant b is 24 ml mol 1 cubic centimeter Note 1 ml A 1 355 A B 1 314 A C 1 255 A D 0 355 A

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesIn a 13 L vessel initially following reaction occur C s S g CS g by 12 g C 64 g S 76 g CS at 1027 C temperature then total pressure is 1 200R 2 158R 3 100R 4 79R

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states3 Two gases P and Q having ratio of rate of diffusion is 1 2 and the ratio of their masses present in the mixture is 1 3 then the ratio of their mole fraction would be 1 2 5 3 5 9 2 1 6 1 3 4 1 12 1 3

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA 4 56 Pure O diffuses through an aperture in 224 second whereas mixture of O and another gas containing 80 O diffuses from the same in 234 second The molecular mass of gas will be A 51 5 B 48 6 C 55 D 46 6 onde of 200 cm long tube HCI gas through inlet X and NH

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesB 3 Calculate the volume occupied by 2 0 mole of N at 200 K and 8 21 atm pressure PcVc RTC 8 3 and 2 4 P V T

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesMaximum deviation from ideal gas is expectec from NEET 2013 1 N g 2 CH g 3 NH 9 4 H g

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states252 The heat of combustion of CH is 400 KJ mol Calculate the heat released when 40 g of H O is formed upon combustion 1 444 4 KJ 2 888 8 KJ 3 444 4 KJ 4 888 8 KJ

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states5 Initial temperature of an ideal gas is 75 C At what temperature the sample of neon gas would be heated to double its pressure if the initial volume of gas is reduced by 15 a 319 C b 592 C c 128 C d 60 C

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states1 In which case is number of molecules of water maximum 2018 a 18 mL of water b 0 18 g of water c 10 mol of water
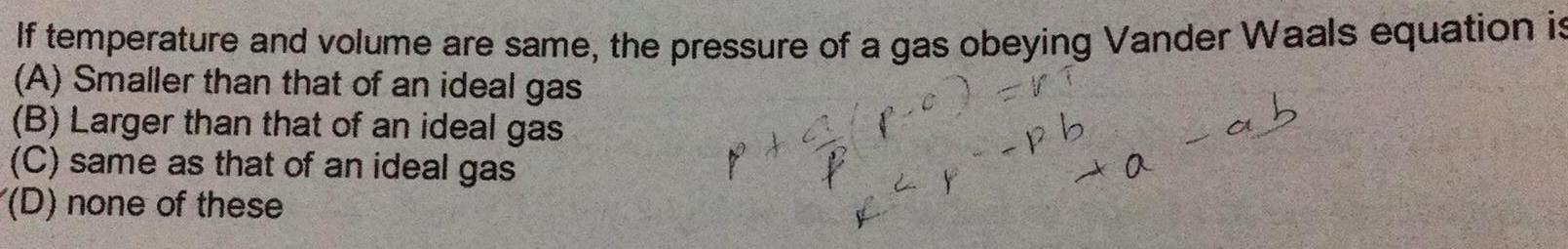
Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesIf temperature and volume are same the pressure of a gas obeying Vander Waals equation is A Smaller than that of an ideal gas B Larger than that of an ideal gas P C ab C same as that of an ideal gas D none of these P 4 P pb a

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states2 When 3 2 g sulphur is vaporised at 450 C and 723 mm Hg pressure the vapours occupy a volume of 780 mL What is the molecular formula of S vapours a S c S6 d Sg b S4 22

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesCHOLARSDEN 51 Two glass bulbs A and B are connected by very small tube having a stop cock Bulb A has a volume of 100 ml and contained the gas while bulb B was empty and had a volume of 150 ml on opening the stop cock the pressure of the gas in bulb A will fall down to A 80 B 60 C 40 D 20 the barometric pressure is 750 mmHg The partial pressure of oxygen

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states0 10 1 0x10 2 kg of hydrogen and 6 4x10 2 kg of oxygen are contained in a 10x10 3 m flask at 473 K Calculate the total pressure of the mixture If a spark ignities the mixture What will be the final pressure

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesExample 19 7 One end of a copper rod of length 1 m and area of cross section 4 0 104 m is maintained at 100 C At the other end of the rod ice is kept at 0 C Neglecting the loss of heat from the surroundings find the mass of ice melted in 1 h Given kcu 401 W m K and L 3 35 x 105 J kg

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesf Explain emulsions and their types ultiple choice questions The change of liquid to gas is a Freezing b Sublimation c Fusion d Vapori

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states30 The volume of O liberated from 0 96 g of H O at STP is 1 224 6 mL 3 390 0 mL 2 316 2 mL 4 112 5 mL

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe pressure exerted by 12g of an ideal gas at temperature C in a vessel of volume V lit is one atm When the temperature is increased by 10 degree at the same volume t pressure increases by 10 Calculate the temperature t and volume V Molecular weight the gas 120 IIT 199

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesD N g 3H If a mixture containing 3 moles of hydrogen and 1 mole of nitrogen is converted completely into ammonia the ratio of initial and final volumes at the same temperature and pressure would be A 1 2 B 2 1 C 1 3 D 3 1 constant for the synthesis 81

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesOne mole of an ideal gas at 273 15 K undergoes expansion from an initial volume of 2 24 I to 22 4 against a constant pressure of 1 atm Calculate the work done 20 Also calculate ALL AH and AS

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states4 1 A flask filled with CCI was weighed at a temperature and pressure The flask was then filled with oxygen at the same temperature and pressure The mass of CCl4 vapour would be about 1 Same as that of oxygen 2 1 5th as heavy as oxygen 3 5 times as heavy as oxygen Twice as heavy as oxygen 47 148

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesa 2 A balloon contains 14 0 L of air at 760 torr What will be the volume of the balloon when i taken to a depth of 10 ft in a swimming pool Assume that the temperature of the air an water are equal density Hg 13 6 g mL a 11 0 b 11 3 c 10 d 10 8

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesWhich one of the following set of phenomenon would increase on raising the temperature a diffusion evaporation compression of gases b evaporation compression of gases c evaporation diffusion expansion of gases d evaporation solubility diffusion compression of gases

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states13 Equal volumes of two monoatomic gases A and B at same temperature and pressure are mixed The ratio of specific heats C C of the mixture will be AIPMT Mains 2012 2 1 50 1 0 83 3 33 1 1 67

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states2 Difference of C and C for diatomic gas is Cp and C are molar heat capacities at constant pressure and volume respectively 1 2R 3 R 2 R 2 4 4R dt 58 2R 2 B

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA bubble of gas released at the bottom of a lake increases to four times its original volun when it reaches the surface Assuming that atmospheric pressure is equivalent to the presst exerted by a column of water 10 m high what is the depth of the lake a 20 m c 30 m d 40 m b 10 m

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesInitially in a container 1 g of gas A has 4 atm pressure at constant temperature If 2 g of gas B is added in same container at same temperature then pressure becomes 6 atm what will be the ratio of molecular weight of A and B 1 M 4MB A 3 M 2M S 2 M 2MB A 4 MB 4MA D

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesthis IIT 1993 7 The average velocity of gas molecules is 400 m sec Calculate its rms velocity at the same temperature DUT 20031

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states53 At a certain temperature and total pressure of K nots 1 atm A vapours contains 20 by volume of A atoms A g 2A g The Kp of reaction is 1 5 x 10 3 5 x 10 3 2 2 x 10 3 4 4 x 10 4

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesMeasuring Zeta potential is useful in determining which property of colloidal solution Viscosity 1 2 3 4 Solubility Stability of the colloidal particles Size of the colloidal particles