Gaseous and liquid states Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesOne mole of an ideal monoatomic gas expands isothermally against constant external pressure of 1 atm from initial volume of 1L to a state where its final pressure becomes equal to external pressure If initial temperature of gas is 300 K then total entropy change of system in the above process is R 0 082 L atm mol 1 K 1 8 3 J mo1 K 1 1 0 2 Rin 24 6 3 Rin 2490 4 RIn 24 6

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesd N O CO C3H8 36 The root mean square speed of an unknown gas at 27 C is x cm s The temperature at which its rms speed will be 3x cm s is a 2700 K c 2700 C 7 For H O b 270 K d 900 C
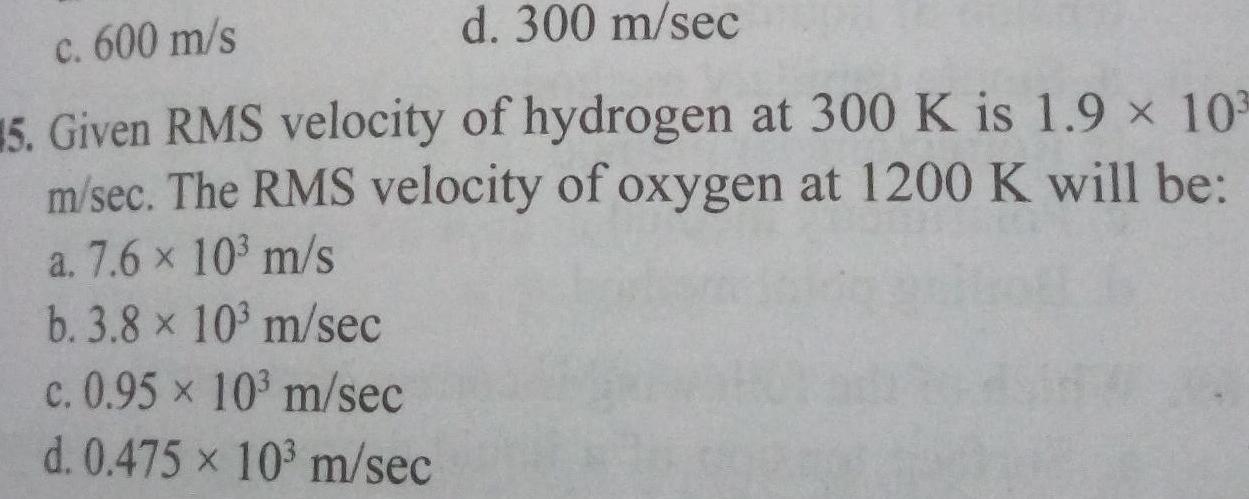
Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesd 300 m sec c 600 m s 15 Given RMS velocity of hydrogen at 300 K is 1 9 103 m sec The RMS velocity of oxygen at 1200 K will be a 7 6 10 m s b 3 8 x 10 m sec c 0 95 x 10 m sec d 0 475 x 10 m sec

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states5 0 30 g of gas was found to occupy a volume of 82 0 ml at 27 C and 3 atm pressure The molecular mass of a gas is a 60 c 90 b 30 d Unpredictable

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states14 2 g of hydrogen diffuse from a container in 10 min How many gram of oxygen would diffuse through the same container in the same time under similar conditions a 0 5 g c 6 g b 4 g d 8 g

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesc 67 2 L d 33 6 L 4 The volume of a gas at 0 C is 273 mL The volume of the gas at 27 C and at same pressure would be a 573 mL b 300 mL c 546 mL d 327 mL

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesa 1 5M b M s c 3M d M 3 37 The approximate temperature at which 1 mol L of a sample of pure ideal gas exhibits a pressure of 101 325 K Pa is a 12 2 K b 122 K c 244 K d 300 K

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states23 A constant pressure air thermometer gave a reading of 47 5 units of volume when immersed in ice cold water and 67 units in a boiling liquid The boiling point of the liquid will be 2 125 C 4 190 C 1 135 C 3 112 C

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states2 1 Which of the following expression is true regarding g laws W weight M molar mass a C T M W T M W T M W T M W M W T M W 2 b T d T M W T

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesWhen chromium metal is added to nitric acid the following reaction takes place Cr s 6 HNO aq Cr NO3 3 aq 3 H O 1 3 NO g Calculate the volume of NO gas in L collected over water at 40 0 C when 48 7 g of chromium is added to excess nitric acid if the total pressure is 675 0 torr The vapor pressure of water at 40 0 C is 55 3 torr 1 st 4 7

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA metal oxide has the formula M 03 This oxide reacts with hydrogen to produce M and H O according to the reaction unbalanced M O3 H M H O If 32 g of M 03 required 1 2 g of hydrogen for complete reduction The atomic mass of metal M is in gm mol

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states50 ml of gas A diffuses through a membrane in the same time as for the diffusion of 40 ml of a gas B under identical conditions of temperature and pressure If the molecular weight of A is 64 the molecular weight of B is

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA real gas becomes ideal at Low temperature and high pressure Low temperature and low pressure High temperature and high pressure High temperature and low pressure

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statessystem yielded a steady state error of 0 20 for unit step input A unit integrator is cascaded to this system and unit ramp input is applied to this modified system What is the value of steady state error for this modified system a 0 10 c 0 20 b 0 15 d 0 25 ten perm

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesFor a fixed mass of a gas consider the following graph for an ideal gas P P2 P4 P3 P P T C Correct relation between P P2 P3 and P4 is P P P3 P4 P P2 P4 P3 P P4 P3 P1 P2

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesIn the van der Waals gas equation the term which indicates the volume occupied by the gas molecules is V nb an V nb P hr min an V

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesConsider the following statements a For ideal gas Z 1 at all temperature and pressure b 0 is more compressible than H c The temperature at which a real gas obeys ideal gas law over an appreciable range of pressure is called critical temperature The correct statements are a and b only b and c only a and c only a b and c

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe combustion of octane C8H18 proceeds according to the reaction shown 2C8H18 1 25O2 g 16CO2 g 18H2O l If 4 90 102 mol of octane combusts what volume of carbon dioxide is produced at 16 0 C and 0 995 atm

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA closed cylinder contains 20 g helium gas and 64 g oxygen gas exerting a pressure of 10 atm Partial pressure of oxygen in the cylinder is 3 21 atm 2 86 atm 4 45 atm

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesIn preparation for a demonstration your professor brings a 1 50 L bottle of sulfur dioxide into the lecture hall before class to allow the gas to reach room temperature If the pressure gauge reads 198 psi and the lecture hall is 20 C how many moles of sulfur dioxide are in the bottle In order to solve this problem you will first need to calculate the pressure of the gas Hint The gauge reads zero when 14 7 psi of gas remains mol

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesWhich reaction is suitable for preparing a Chloroacetic acid 2 Stephen s reaction 1 Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction 3 Perkin s reaction 4 None of these A mixture of methane and Ethene in a molar ratio of x y has an average molecular mass of The mean molar mass when they are mixed in the molar ratio of y x will be 1 20 2 25 3 24 4 15

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states6 Estim of oxygen nitrogen water vapour and other constituents in a room of capacity 25 0 m at a temperature of 27 C and 1 atm pressure Solution Volume of the room V 25 0 m Temperature of the room T 27 C 300 K Pressure in the room P 1 atm 1 x 1 013 x 105 Pa The ideal gas equation relating pressure P Volume V and absolute temperature T can be written as PV KBNT Where KB is Boltzmann constant 1 38 x 10 23 m kg s K 1 N is the number of air molecules in the room Therefore N PV KBT 1 013 x 105 x 25 1 38 x 10 23 x 300 We get 6 11 x 1026 molecules Hence the total number of air molecules in the given room is 6 11 x 1026

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe vapour pressure of pure liquid solvent A is 0 80 atm When a nonvolatile substance B is added to the solvent its vapour pressure drops to 0 60 atm What is the mole fraction of component B in the solution

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states3 i Based on the Barometric distribution law estimate the height at which partial pressure of oxygen is half of its sea level value at 25 C assume with changing height temperature does not change

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe vapour pressure of pure benzene at 30 C is 640 mm of Hg and the vapour pressure of a solution of a solute in CH at the same temperature is 624 mm of Hg Calculate molality of solution LS0010

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe adsorption of a gas is described by the Langmuir isotherm with the equilibrium constant K 0 9 kPa at 25 C The pressure in kPa at which the fractional surface coverage is 0 95 is 2 34 x x Find the value of x to nearest integer our Answer Rate this questic

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesIf density of a gaseous mixture of dinitrogen tetroxide N O and nitrogen dioxide NO 127 C and 1 atm pressure R 0 08 atm lit mole K Partial pressure of N O is A 0 62 atm B 0 47 atm LIC 0 74 atm D 0 26 atm p

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesUsing the data in Appendix 4 what is the standard change in entropy in J K for the reaction 2Ag s Br 1 2AgBr s Don t include units in the answer

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA common laboratory preparation for O gas involves the thermal decomposition of potassium nitrate 2KNO3 s 2KNO2 s O2 g What volume of O at 18 C and 1 29 atm pressure can be produced from the decomposition of 37 9 g of KNO3 What volume of O at 17 C and 1 15 atm pressure can be produced from the decomposition of 21 1 g of KNO33

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states28 A solution of protein extracted from crabs was prepared by dissolving 0 75 g in 125 cm of an aqueous solution At 4 C an osmotic pressure rise of 2 6 mm of the solution was observed Then molar mass of protein 3 is Assume density of solution is 1 00 g cm a 9 4 x105 b 5 4 x 105 d 9 4 1010 c 5 4 1010

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states32 The specific heat of a gas is found to be 0 075 calories at constant volume and its formula wt is 40 The atomicity of the gas would be 1 One 2 Two 4 Four 3 Three Wa

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesComplete the following table for an ideal gas V IST P 16 628 10 n Temper

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesNH OH with 25 15 cm mol at the same temperature are 1 275 6 0 91 2 275 6 9 1 3 266 6 9 6 4 30 84 At STP 0 48 g of O diffused through a porous partition in 1200 seconds What volume of will diffuse in the same time and under the same conditions 1 286 5 mL 2 346 7 mL Which of the following compounds is most acidic 3 112 2 mL 4 224 8 mL

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states112 302 CH4 kept in a container A hole was made in the container and gases are allowed to escape After 3 hours the order of partial pressure in the container is Options Pso PcH4 PH PH Pso PCH4 PCH Pso PH

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesArrange the following in correct order of Lewis acidity BF BCI BBr 3 BF BCI BBr 1 BF BBr BCI 2 BF BCI BBr Consider the following structures 4 BBr BF BCI

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesQuestion No 80 Which of the following is incorrect Options A real gas behaves like an ideal gas over a wide range of pressure at Boyle temperature An ideal gas can never be liquefied Below inversion temperature the gas can be heated by adiabatic expansion against vaccuum Inversion temperature is twice of Boyle s temperature

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesHelium atom is two times heavier than a hydrogen molecule At 298 K the average kinetic energy of a helium atom is Options Two times that of a hydrogen molecule Same as that of a hydrogen molecule Four times that of a hydrogen molecule

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states45 When 1 mol of gas is heated at constant volume temperature is raised from 298 to 308 K Hea supplied to the gas is 500 J Then which statement is correct 1 q AU 500 J W 0 2 qAU 500 J w 0 3 q w 500 J AU 0 4 AU 0 q w 500 J

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states2 3 grams of a mixture of NO2 and N O4 have a pressure of 0 82 atm at temperature T K and volume V litres calculate PNO2 Assume V T 1 300 that all the NO2 was converted into N O4 If A 0 52 atm B 0 38 atm C 0 19 atm D 0 41 atm

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states0 Which postulate of the kinetic molecular theory BEST explains why gases can be compressed F Gases are in constant random motion G Gas particles move in a straight line until they collide with other matter H There is empty space between gas particles 3 There is no force of attraction between gas particles

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesA compressed cylinder of gas contains 1 50 10 g of N gas at a pressure of 2 0 x 107 Pa and a temperature of 17 1 C What volume of gas has been released into the atmosphere if the final pressure in the cylinder is 1 80 x 105 Pa Assume ideal behaviour and that the gas temp is unchanged 1 1260 L 2 126 L 3 12600 L 4 45 L

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesF then calculate the value of Z for the vapours One litre gas at 400 K and 300 atm pressure is compressed to a pressure of 600 atm and 200 K The compressibility factor is changed from 1 2 to 1 6 respectively Calculate the final volume of the gas

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states19 From the following bond energies H H bond energy 431 37 kJ mol 1 C C bond energy 606 10 kJ mol C C bond energy 336 49 kJ mol C H bond energy 410 50 kJ mol 1 Enthalpy for the reaction HH C H HH C C H HH HH will be 1 243 6 kJ mol 1 2 120 0 kJ mol 3 553 0 kJ mol HH AIPMT Prelims 2009

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states0 Which of the following pair of gases will diffuse at the same rate through a porous plug a CO NO c NO2 CO2 b NO C H6 d NH3 PH3

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesConsider an ideal gas contained in a vessel If the intermolecular attraction suddenly begins to act which of the following will happen 1 The pressure decreases 2 The pressure increases 3 The pressure remains unchanged 4

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe number of ZnS formula units present in a unit cell of ZnS are 1 2 2 1 3 4 4 8

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statescompressibility factor is changed from 1 2 to 1 6 respectively Calculate the final volume of the gas Reduced temperature for benzene is 0 7277 and its reduced volume is 0 40 Calculate the reduced pressure of benzene

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states7 At what temperature is the rms speed of hydrogen molecules the same as that of oxygen molecules at 1327 C 1 173 K 3 400 K 2 100 K 4 523 K

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesThe internal energy change in the conversion of 1 0 mole of the calcite form of CaCO3 to the aragonite form is 0 21 kJ Calculate the enthalpy change when the pressure is 1 0 bar given that the densities of the solids are 2 71 g cm and 2 93 g cm respectively O 229 72J mol 1 O 249 12 J mol 1 O 289 82 J mol 1 O 209 72 J mol 1

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesFour particles have speed 2 3 4 and 5 cm s respectiv Their R M S speed is 1 3 5 cm s 3 54 cm s 2 27 2 cm s 4 54 4 cm s