General Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
GeneralRe AIPMT 2015 20 The rate constant of the reaction A B is 0 6 x 10 M sec If the concentration of A is 5 M then concentration of B after 20 min is 1 0 36 M 2 0 72 M 4 3 60 M 3 1 08 M

Physical Chemistry
GeneralTD0068 53 For a reaction at 25 C enthalpy change AH and entropy change AS are 11 7 x 10 Jmol and 105 J mol K respectively The reaction is 1 Spontaneous 2 Non spontaneous 3 At equilibrium 4 Can t say anything

Physical Chemistry
General4 Either greater or less than 50 kCal CK0108 9 An exothermic reaction X Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol If energy change AH during the reaction is 20 kJ then the activation energy for the reverse reaction is 1 10 kJ 3 50 kJ 2 20 kJ 4 30 kJ CK0109 10

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAIPMT Pre 2012 13 In a zero order reaction for every 10 rise of temperature the rate is doubled If the temperature is increased from 10 C to 100 C the rate of the reaction will become 1 64 times 3 256 times 2 128 times 4 512 times CK0135 19

Physical Chemistry
General14 The dissociation equilibrium of a gas AB2 can be represented as 2AB2 g 2AB g B g The degree of dissociation is x and is small compared to 1 The expression relating the degree of dissociation x with equilibrium constant K and total pressure P is CBSE PMT 2008 a 2K P 1 3 b 2Kp P 2 c Kp P d 2Kp P

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAH for transition of carbon from diamond form to graphite form is 453 5 Cal This suggests that 1 Graphite is chemically different from diamond 2 Graphite is as stable as diamond 3 Graphite is more stable than diamond 4 Diamond is more stable than graphite

Physical Chemistry
General10 M is a metal that forms an oxide M 0 MO M O AH 120 kcal When a sample of metal M reacts with one mole oxygen what will be the AH in that case 1 240 kcal 2 240 kcal 3 480 kcal 4 480 kcal TC012

Physical Chemistry
General01 Given enthalpy of formation of CO g and Cao s are 94 0 kJ and 152 kJ respectively and the enthalpy of the reaction CaCO s CaO s CO g is 42 kJ The enthalpy of formation of CaCO s is 1 42 KJ 3 202 KJ 2 202 KJ 4 288KJ
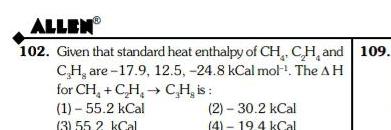
Physical Chemistry
GeneralALLEN 102 Given that standard heat enthalpy of CH CH and 109 CH are 17 9 12 5 24 8 kCal mol The AH for CH C H 1 55 2 kCal 3 55 2 kCal CH is 2 30 2 kCal 4 19 4 kCal

Physical Chemistry
GeneralH gas 2 Decrease in 50 mL 4 Decrease in 200 mL 4NO g 6H O 1 a and 1 mole of O are cion e consumed e produced roduced be consumed ntaining C H and N gave C 40 H 13 33 formula would be 2 CH N 4 C H N acid mol weight 200 00 ml of the aqueous C 1 7 gm N les gram 9 2 2 gm H 3 16 gm NO 4 16 gm O 41 In Haber process 30 litres of dihydrogen and 30 litres of dinitrogen were taken for reaction which yielded only 50 of the expected product What will be the composition of gaseous mixture under the aforesaid condition in the end 1 20 litres ammonia 20 litres nitrogen 20 litres hydrogen 2 10 litres ammonia 25 litres nitrogen 15 litres hydrogen 3 20 litres ammonia 10 litres nitrogen 30 litres hydrogen COL 4 20 litres ammonia 25 litres nitrogen 15 litres hydrogen 42 The maximum number of molecules is present in 1 15 L of water at STP 100x NA 18 OTD Naz Cac PE P

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA Reaction first order with respect to reactant A has a rate constant 6 0 x 10 2 min If we start with A 0 5 mol L when would A reach the value 0 05 mol L 1 48 4 min 3 38 4 min 2 28 9 min 4 18 6 min

Physical Chemistry
Generalme reaction CK0052 period of centration 4 Cannot be calculated CK0059 3 160 56 The reaction L M is started with 10 g L After 30 minute and 90 minute 5 g L and 1 25 g L are left respectively The order of reaction is 1 0 2 2 3 1 4 3 CK0061 TCHEWLENGR MODULE 12 CHEMICAL KINETICS

Physical Chemistry
Generalg is less is higher ower than 87 Which of the following values of heat of formation indicates that the product is least stable 1 94 kCal 2 231 6 kCal 3 21 4 kCal 4 64 8 kCal TC0096

Physical Chemistry
General5 H g 2NO g 2 NH3 g 2 H O g Express your answer using four significant figures VO AXO AG Submit Part D Request Answer AG will increase with increasing temperature SWED kJ

Physical Chemistry
General13 The half life period and initial concentration for a reaction are as follows Initial concentration 1 order of reaction is 1 2 2 1 350 425 3 540 275 158 941 4 4

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species X and Y for the reaction X Y as a function of time the point of intersection of the two curves reperesents Concentration Y Time 1 2 4 3 4 Data are insufficient to predict

Physical Chemistry
Generalthat of water TC0090 82 Which plot represents for an exothermic reaction R 1 H 3 H Progress in reaction R Progress in 2 H RP Progress in reaction 4 HR P Progress in

Physical Chemistry
General92 From the reaction P White P Red AH 18 4 kJ it follows that 1 Red P is readily formed from white P 2 White P is readily formed from red P 3 White P can not be converted to red p 4 White P can be converted into red P and red P is more stable

Physical Chemistry
General1 2 2 3 0 4 14 The activation energy for the reaction C 02 H O H O 0 H O 1 20 is 18 K cal mol at 300 K calculate the fraction of molecules of reactonts having energy equal to or greater than activation energy Anti log 13 02 9 36 10 4 1 9 36 x 10 14 2 1 2 10 12 4 5 2 x 10 15 3 4 2 10 16 Which of the following is falso about catalud

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe standard heats of formation of CH CO C and H O0 are 76 2 394 8 and 241 6 KJ moll respectively Heat evolved by burning 1m methane measured under normal condition will be 1 801 8 KJ KJ 3 890 KJ KJ ideal gas expand isothermally a 2 35794 6 4 3570

Physical Chemistry
General1 Spontaneous 3 At equilibrium 54 If A H 0 and AS spontaneously when 1 AH 0 3 AH TAS 2 Non spontaneous 4 Can t say anything TD0069 0 the reaction proceed 2 AH TAS 4 None

Physical Chemistry
General5 42 The decomposition te e t CK0044 of N O occurs as O and follows first order 2N O 4NO kinetics hence 1 The reaction is bimolecular 2 The recation is unimolcular 3 t 2 a a 4 a

Physical Chemistry
General4 None TD0083 75 If the equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10 then the value of AG will be R 8JK mol T 300 K 1 5 527 kJ mol 3 55 27 kJ mol 2 5 527 kJ mol 4 55 27 kJ mol

Physical Chemistry
GeneralTROPY SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS For which reaction from the following AS will be maximum 1 Ca s 1 2O g CaO s 2 CaCO s CaOs CO g 3 C s O g CO g 4 N g O g 2NO g TD0047 MENGMODULE 1STHERMODYNAMICS102 EXE P65

Physical Chemistry
GeneralFor the reaction 2A B CA B C the rate law has been determined to be Rate K A B C If the value of the K is 2 0 x 10 6 mol 2 L S 1 for the reaction Initial rate of the reaction with A 0 2 mol L 1 B 0 1 mol L 1 C 0 5 mol L is 1 2 x 10 9 Ms M 1 2 4 10 9 Ms 9 M 1

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA chemical reaction 2A4B C in gaseous phase shows an increase in concentration of B by 5x10 M in 10 second The rate of reaction and rate of appearance of B are respectively 1 5 x 10 4 MS and 1 25 x 10 Ms 5 x 10 4 Ms 1 2 1 25 x 104 Ms and and 3 1 25 x 10 4 Ms 1 4 2 5 x 10 4 MS 1 2 5 x 10 4 Ms and 1 25 x 104 Ms

Physical Chemistry
General0 A 1 250 g sample of octane CH is burned in excess of oxygen in a bomb calorimeter The temperture of the calorimeter rises from 294 05 K to 300 78 K If heat capacity of the calorimeter is 8 93 KJ K enthalpy of combustion of the sample of octane is 1 6285 KJ mol 3 2800 KJ mol 2 5481 1 KJ mol 1 4 3680 KJ mol

Physical Chemistry
General3 For the reduction of NO ion in an aqueous solution E is 0 96 V Values of E for some metal ions are given below V aq 2e V s E 1 19V Fe aq 3e Fe s E 0 04 V Au aq 3e Au s E 1 40 V Hg2 aq 2e Hg 1 E 0 86 V The pair s of metal that is are oxidized by NO in aqueous solution is are A V and Hg B Hg and Fe C Fe and Au D Fe and V

Physical Chemistry
General21 Choose which of column Il condition are applicable for Column l items Column II Column I A When P 0 PS B Single phase of substance C Vapour state q D Liquid state t o p Boyle s temperature q Temperature Tc Pressure Pc r Temperature Tc Pressure Pc s Z 1 t Z 1

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich of the following orbital diagram violates Hund s rule 2s 16 2s 1 2s 14 2s 12 2p 111 2p 111 2p 11 2p 111

Physical Chemistry
General50 If S for H Cl and HCl are 0 13 0 22 and 0 19 kJ K mol respectively The total standard entropy for the reaction in H Cl 2HCl is 1 30 JK mol 3 60 JK mol Ses 2 40 JK mol 4 20 JK mol TDO054

Physical Chemistry
General17 If work done by the system is 300 joule when 100 cal heat is supplied to it The change in internal energy during the process is 1 200 Joule 2 400 Joule 3 720 Joule 4 120 Joule

Physical Chemistry
General4 Rate K CXC C CK0013 14 A chemical reaction involves two reacting species The rate of reaction is directly proportional to square of the concentration of one of them and inversely proportional to the concentration of the other The order of reaction is 1 1 3 Zero 2 2 4 Unpredictable CK0014 The 1 r 3 r 19 Calc A n 0

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIf one molecule of h20 contains 4 unbound ed electrons then why each pair of electrons cannot bound with one H in one molecule of water Therefore it should bound with tw o h ion Why this cannot happen Ht II Hx O 111 H xH

Physical Chemistry
GeneralFor a gaseous reaction A g 3B g 3C g 3D g AE is 17 kCal at 27 C assuming R 2 Cal K mol the value of AH for the above reaction is 1 15 8 Kcal 3 20 0 Kcal 2 18 2 Kcal 4 16 4 Kcal

Physical Chemistry
General18 A system has internal energy equal to E 450 J of heat is taken out of it and 600 J of work is done on 2 it The final energy of the system will be 1 E 150 2 E 1050 3 E 150 4 None of these

Physical Chemistry
General6 Consider the following sets of quantum numbers n I m S 0 0 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 i 3 0 ii 2 2 iii 4 3 iv 1 0 1 v 3 2 3 Which of the following sets of quantum number not possible a i ii iii and iv b ii iv and v c i and iii d ii iii and iv 200

Physical Chemistry
General21 Under which of the following conditions is the relation AH AE PAV valid for a system 1 Constant pressure 2 Constant temperature 3 Constant temperature and pressure 4 Constant temperature pressure and composition TH0023

Physical Chemistry
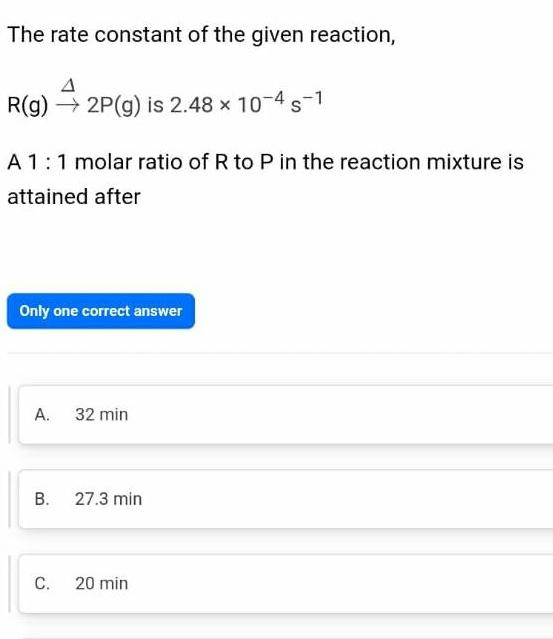
GeneralThe rate constant of the given reaction R g 2P g is 2 48 10 4 s 1 A 1 1 molar ratio of R to P in the reaction mixture is attained after Only one correct answer A 32 min B C 27 3 min 20 min

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIn the reaction sequence HOH C CHOH CH OH C H5O 3 Al A Product B will be Only one correct answer A B A D H2C CH CHO H C CH CH OH C C Mixture of H C CH COOH and H C CH CH OH a B Cu 0 Oqu KHSO A CUTT au
Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe rate constant of the given reaction R g 2P g is 2 48 x 10 4 1 A 1 1 molar ratio of R to P in the reaction mixture is attained after Only one correct answer A 32 min B C 27 3 min 20 min

Physical Chemistry
GeneralJoule TH0018 to E 450 J of work is done on will be 1050 of these TH0019 25 1 AH AE 3 AH AE 2 AH AE 4 None of the above TH0026 For the reaction Ag O s 2Ag s 1 2O g which one of the following is true 2 AH 2AE 4 AH AE 1 AH AE 3 AH AE TH0027

Physical Chemistry
General24 Which of the following statements is correct for the reaction 250 g O g 2SO g at constant temperature and pressure 1 AH AE 3 AH AE 2 AH AE 4 None of the above

Physical Chemistry
General2 157 A pulse on a string is shown in the figure Q 157 farangurvey from P P is particle of the string Then state which of the following is incorrect positive 1 If P is stationary point then pulse consists of two waves travelling in opposite direction 2 If P is moving upwards then puise is travelling in positive direction 3 If P is moving downwards then pulse is travelling in negative direction 4 none of these positive 1 ufe P fere fag att f fara fram 2 fa si fara f 4 3 uf Pf t we 1

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhen a certain conductance cell was filled with KCl solution conductivity 3 0 1m and it had a resistance of 1000 at 300 K when the same cell is filled with 0 01 M K SO4 it has a resistance of 300 Q Calculate molar conductivity of K SO4 solution in terms of Q 1 m mol 1 Question Type Single Correct Type 1 10 5 2 3 105 10 1

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIn aqueous solution the ionization constants for carbonic acid are K 4 2 x 107 and K 4 8 x 10 11 Select the correct statement for a saturated 0 034 M solution of the carbonic acid 1 The concentration of m n p and q are integers such that n q 0 and qm pr 0 034 M 2 The concentration of CO2 is greater than that of HCO3 3 The concentration of H and HCO3 are approximately equal 4 The concentration of H is double that of CO2 MAINS 201

Physical Chemistry
GeneralK In the reversible reaction 2NO2 N O4 the rate of K disappearance of NO2 is equal to Only one correct answer A NO 2K K B 2K NO 2 2K2 N204 C D 2K NO 2 K2 N 04 K NO 2 K N204

Physical Chemistry
General5 Given van der Waal s constant for NH3 H O and CO are 4 17 0 244 1 36 and 3 59 L atm mol respectively which one of the following gases is most easily liquefied 1 NH3 2 H 3 0 4 CO

Physical Chemistry
General1 AIPMT Pre 2011 Two gases A and B having the same volume diffuse through a porous partition in 20 and 10 seconds respectively The molecular mass of A is 49u Molecular mass of B will be

Physical Chemistry
GeneralQ 180 In photo emissive cell with exciting Q 180 are for wavelength the fastest electron has speed v If the exciting wavelength is changed to 32 4 the speed of the fastest emitted electron will be 1 v 3 4 1 2 2 v 4 3 2 3 less than v 4 3 2 4 greater than v 4 3 28 afe afore a 3 4 and at vefa za awa 1 v 3 4 0 v 4 3 9 flagg REER IN ier In rututa V 2 3 v 4 3 4 v 4 3 sf res