Atomic Structure Questions and Answers

Physics
Atomic Structure2 If radiations ranging from ultraviolet to infrared are passed through hydrogen gas at room temperature then the absorption lines will be observed in the 1 Lyman series 2 Balmer series 3 Paschen series 4 All of these

Physics
Atomic Structure32 An electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition from h N to n N The frequency of the electron in the final state is eight times that in initial state The possible values of N and are 1 N 6 2 2 N 8 N 1 3 N 8 N 2 36 4 1 9 36

Physics
Atomic Structuren If the potential energy of electron in Bohr s atomic model of hydrogen is taken as zero in its first orbit then the P E of electron in the 2nd orbit of same hydrogen atom will be 1 6 8 eV 2 20 4 eV 4 27 2 eV

Physics
Atomic Structure56 The wavelength of radiation emitted when an electron jumps from the third to second orbit of hydrogen atom is The wavelength of radiation emitted for the electron jumps from the fourth to second orbit of hydrogen atom will be 2 3 27 20 201 27 42 5 52

Physics
Atomic StructureAn electromagnetic wave of intensity 30 W m2 is incident on a surface of area 2 m If the surface is per absorbing then the amount of momentum transferred to the surface in 10s will be 2 x 10 6 kg m s 2 x 106 kg m s 4 x 10 9 kg m s 10 8 kg m s

Physics
Atomic Structure1 In the fusion reaction H H He ont The masses of deutrons helium and neutron expressed in amu are 2 015 3 017 and 1 009 respectively If 1 kg of deuterium undergoes complete fusion Find the amount of total energy release 1 amu 931 MeV C A 6 x 10 3 J C 9 x 10 3 J B 5 6 x 10 3 J D 0 9 x 10 3 J

Physics
Atomic StructureA and B are two radioactive substances whose 12 half lives are 1 and 2 years respectively Initially 10 gm of A and 1 gm of B is taken The time approximate after which they will have same quantity remaining is A 6 62 years C 2 years B 1 year D 100 years

Physics
Atomic StructureThe orbital velocity of electron in the ground state is v If the electron is excited to energy state 0 54eV its orbital velocity will be 3 3 Saf sa 0 54eV A V B v 3 C v 5 D v 7 Coe

Physics
Atomic StructureIf the visible region of the spectrum is taken to be wavelengths longer than 400 nm and shorter than 700 nm the number of lines in the hydrogen spectrum which lie in the visible region is A 2 B 3 C 4 D

Physics
Atomic StructureThe range of frequency allotted for FM radio is FM fay ang at A 88 to 108 kHz B 88 to 108 MHz C 88 to 108 GHz D 88 to 108 GHz Your Answer B

Physics
Atomic StructureLet V1 be the frequency of first line of Lyman series and V2 be the frequency of first line of Balmer series then the frequency of second line of Lyman series is 1 V V 2 V V 3 V V1 V V2 4

Physics
Atomic StructureH 30 6 eV 2 13 6 eV 3 13 6 eV 4 In Bohr series of lines of hydrogen spectrum the third line from the red end corresponds to which one of the followi inter orbit jumps of the electron for Bohr orbits is an atom of hydrogen 1 3 2 2 5 2 3 4 1 4 2 5 ll of mass 60 moving with a velocity of 10 metres per second is approxima

Physics
Atomic Structure1 1 1 eV 2 2 63 eV 3 Work function a metal is 5 26 x 10 18 then its threshold wavelength will be 1 736 7 2 760 7 3 301 4 344 4 A radio station is transmitting the waves of wavelength 300 m Radiation capacity of the transmitter is

Physics
Atomic StructureJ J Thomson s cathode ray tube experiment demonstrated that cathode rays are streams of negatively charged jons 2 all the mass of an atom is essentially in the nucleus 3 the e m of electrons is much greater then the e m of protons 4 the e m ratio of the cathode ray particles changes when a different gas is placed in the discharge aves

Physics
Atomic StructureGold crystallises 1 197 N O 3 3 NA in ccp structure The total number of voids present in 197g of gold will be Au 197 4X NAX97 2 2 N 197X 4 4 197 NA relation for r

Physics
Atomic StructureDetermine the bandwidth of each of the amplifiers in Figure 12 43 Both op amps have an open loop gain of 100 dB and a unity gain bandwidth fr of 3 MHz Vin a www our Rf 220 kn R 3 3 k Vino b R www 1 0 kn R www 47 k Vout

Physics
Atomic Structure18 53 Based on equation E 2 178 107 J Z 2 n certain conclusions are written Which of them is not correct a Equation can be used to calculate the change in energy when the electron changes orbit b For n 1 the electron has a more negative energy than it does for n 6 which means that the electron is more loosely bound in the smallest allowed orbit c The negative sign in equation simply means that the energy of electron bound to the nucleus is lower than it would be if the electrons were at the infinite distance from the nucleus d Larger the value of n the larger is the orbit NEET

Physics
Atomic Structure38 If the kinetic energy of a free electron doubles it s de Broglie wavelength changes by the factor a 2 12 b 1 c 2 HAS d 2

Physics
Atomic StructureCalculate the de Broglie wavelength of Rb atom at a temperature of T 100 K Assume kinetic energy at temperature T is given by 3kgT 2 where kg 1 38x1023 J K and I amu 1 6605x10 27 kg 4 marks PART C 2 x 10 20 marks

Physics
Atomic Structurealternate dark and bright bands 47 In an absorption an absorption spectrum dark lir corresponds to same wavelengths which w found in emission line spectrum of gas Ab statement is 1 correct for all gases 2 correct only for hydrogen like atoms 3 incorrect for all gases 4 incorrect except for hydrogen

Physics
Atomic StructureA stationary hydrogen atom in the first excited state emits a photon If the mass of the hydrogen atom is m and its ionization energy is E then the recoil velocity acquired by the atom is speed of light c 3E A 2 5 c 2m B C Correct Answer 3 3E 4mc 3E 4m c C c C

Physics
Atomic StructureIn the potential energy curve for the formation of H molecule as a function of internuclear distance of H atoms what happens at the minimum in the curve 1 Net force of attraction equals the force of repulsion 2 Most stable state of H is achieved 3 System acquires minimum energy 4 All of these

Physics
Atomic StructureA particle of mass M moves in a circular orbit in such a way that the potential energy is U ar where a is a constant an r is the distance of particle from the origin Assuming the Bohr s quantization rule to be valid find the radius of nth allowed orbit O O r n h 8 aM nh 8 aM 1 4 nh 8 aM 2 1 2 n h 14

Physics
Atomic StructureThe frequency of ka X ray from an element A of atomic number 20 is The frequency of ka X ray from an element B is 4f Then find the atomic number of element B Answer 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09

Physics
Atomic StructureA small sphere of mass m made of a material of density d falls from a height h on to the free surface of a liquid of density 3d in a large tank If g is the acceleration due to gravity the maximum depth the sphere reaches in the liquid is neglect viscous forces A Bh C 2h D h 2 h 4

Physics
Atomic StructureIf the kinetic energy of an electron gets tripled then the new de Broglie wavelength associated with it will be times of initial value 3 times of initial value times of initial value 3 times of initial value

Physics
Atomic StructureWhich among the following can emit radiation Excited electron in H atom Excited nucleus Excited electron in Li ion Both 1 and 3

Physics
Atomic Structure1 A grenade of mass 5M initially at rest explodes into two pieces of mass 3M and 2M and the masses travel in opposite direction with velocity 2V and 3V respectively Calculate the ratio of de Broglie wavelength of 3M to that of 2M a 2 3 b 3 2 c 9 4 d 1 O A O O B O C

Physics
Atomic StructureA particle of mass m moves in circular orbits with potential energy V r Fr where F is a positiv constant and r is its distance from the origin Its energies are calculated using the Bohr model If the radius of the particle s orbit is denoted by R and its speed and energy are denoted by v and E respectively then for the nth orbit here h is the Planck s constant A R x n 3 and vx n 3 1 3 C E 4x m B R x n 3 and v x n 3 1 3 D E 2

Physics
Atomic StructureV3 V is the frequency of series limit of Lyman series v is the frequency of the first line of Lyman series and v3 is the frequency of the series limit of Balmer series then O V V V3 V V V3 1 V V 1 1 V V3 V 1 1 V

Physics
Atomic StructureFive grams of KCIO yield 3 041 g of KCl and 1 36 L of oxygen at standard temperature and pressure Show that these figures support the law of conservation of mass within limits of 0 4 error

Physics
Atomic StructureIn hydrogen spectrum La line arises due to transition of electron from the orbit n 3 to the orbit n 2 In the spectrum of singly ionized helium there is a line having the same wavelength as that of the La line of hydrogen This is due to the transition of the electron from the orbit to 25 5gwoo Lap obsono 3085 Dobos Ke 30 s de Dojaos O sono dopo 55850 Options 1 n 3 n 2 2n 4 n 2 n 5 n 3 3 4 on 3558 5008 n 25558 Dogs Bosno sto es Lop dong dong50 n 6 n 4 558 5008

Physics
Atomic StructureWhich of the following transitions of He ion will give rise to spectral line which has same wavelength as some spectral line in hydrogen atom Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 4 n 4 to n 2 n 6 to n 5 n 6 to n 3 None of these

Physics
Atomic StructureThe de Broglie wavelength of an electron in first orbit of hydrogen atom is equal to Only one correct answer A Diameter of the orbit B C Perimeter of the orbit Half the perimeter of the orbit

Physics
Atomic StructureIn the figure shown the wavelength and frequency of photons in transition a b and c for hydrogen atoms are a Ab Ac and va V and vc respectively then Only one correct answer A B C Vb Va Vc Vc Va Vb Ve do des dave ne

Physics
Atomic Structure42 A particle of mass m is projected from ground with velocity v making an angle e with vertical Then the debroglie wavelength of particle at the highest point is 1 oc 2 h mv sin 0

Physics
Atomic Structurem SolveLancer Test Choose the correct option When an element X undergoes 5 p decays and a decay the daughter nucleus is given by SolveLancer Test n a b c d a b 17 n 44 mz n 5 mx n 4Z n 4 m
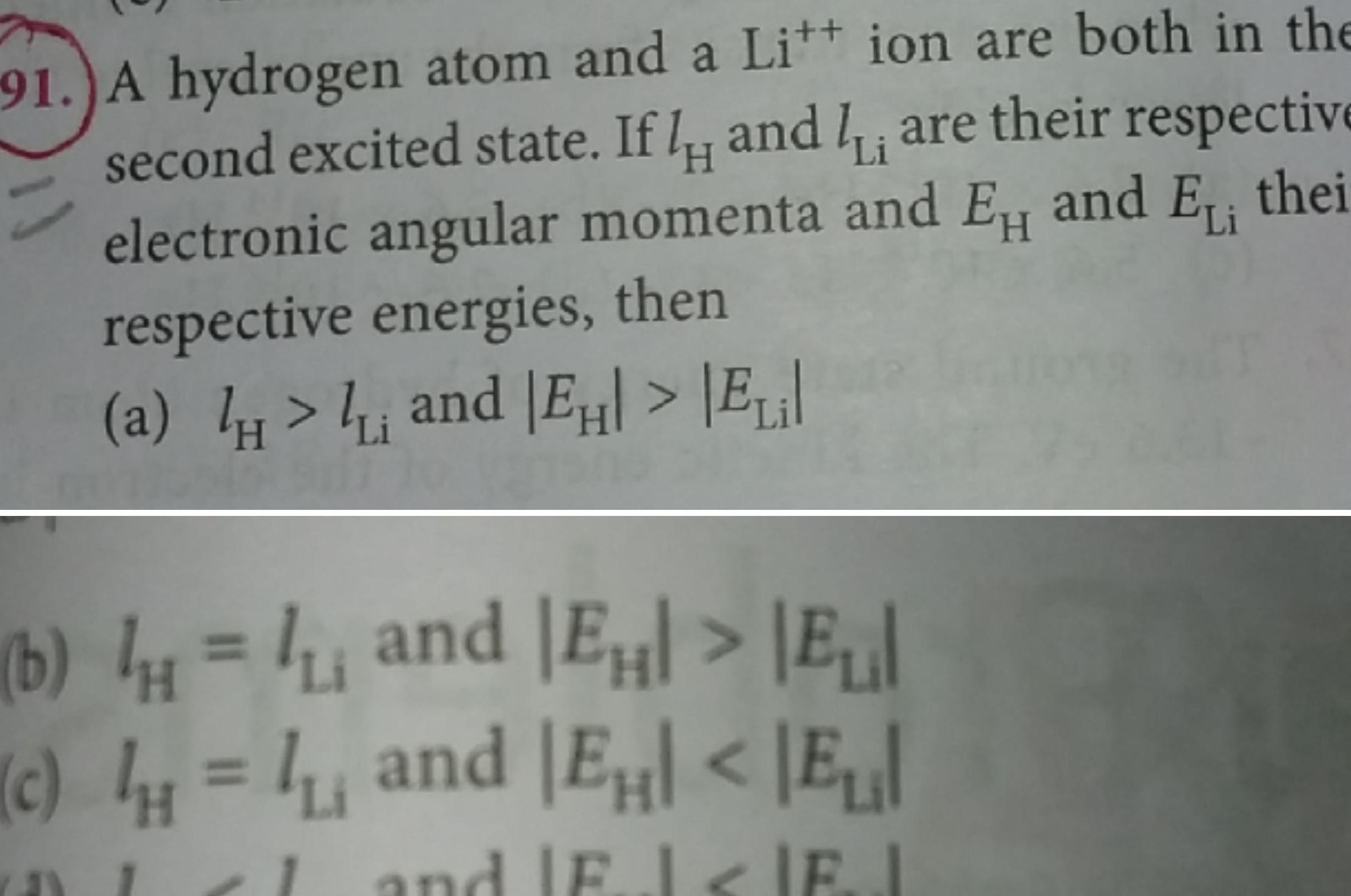
Physics
Atomic Structure91 A hydrogen atom and a Litt ion are both in the second excited state If I and I are their respective electronic angular momenta and EH and EL thei respective energies then a and E Eil Li H b and E E and EH E c and Fl IEJ

Physics
Atomic StructureI Doublet of sodium A II Wavelength corresponding to temperature associated with B the isotropic radiation filling all space Wavelength emitted by atomic hydrogen in interstellar C space Wavelength of radiation arising from two close energy D levels in hydrogen IV A 1 A 11 B III C IV C B 1 A 11 B III B IV C C 1 B II A III D IV A A IV B D an DIDY Visible radiation Microwave Short radiowave X rays 2014

Physics
Atomic StructureAn electron of mass m is moving in nth orbit of hydrogen atom Magnetic field at centre due to motion of electron is ro Bohr radius Hohe 1 8x mr n 3 5 Hohe 2 4 mn r 5 3 Hohe 3 4mn5 3 ro he

Physics
Atomic StructureDetermine the wavelength of the first Lyman line the transition from n 2 to n 1 In what region the electromagnetic spectrum does this line lie 1 1 22 x 10 7 m UV region 2 2 78 x 10 7 UV region 4 2 78 x 10 7 IR region 3 1 22 x 10 7 m IR region Figure shows come operoy levels of on stom If the transition 5 to 5 gives emission of ultraviolet radiation

Physics
Atomic Structureow the marked expression came sir nergy of electron in the hydrogen atom Total Energy of electron in nth orbit e 8 r KE mv 2 and PE 1 e e 4 0 r 2KE PE 2 KE Total energy of the system KE PE e E 2KE KE KE 8

Physics
Atomic StructureSpeed of an electron in hydrogen atom in 1st orbit is 2 x 100 m s The velocity of an electron in 3rd orbit doubly ionized lithium is 1 5 x 10 m s 3 4 x 10 m s 2 6 108 m s 4 2 x 108 m s

Physics
Atomic StructureImagine that the electron in a hydrogen atom is replaced by a muon The mass of muon particle is 207 times that of an electron and charge is equal to the charge of an electron The ionization potential of this hydrogen atom will be 1 13 6eV 2 2815 2eV 3 331 2eV 4 27 2eV

Physics
Atomic StructureThe following diagram indicates the energy levels of a certain atom where the system moves from 4E level to E a photon of wavelength is emitted The wavelength of photon produced during its transition from 7 E level to E is The ratio 3 4E E 9 735 3 will be 20 7

Physics
Atomic Structure3 Energy of atom 4 Speed Radius 25 Consider a hydrogen like atom in Bohr s model It is given that difference between n 1 th Bohr s radius and nth Bohr s radius is equal to n 1 th Bohr s radius then the energy of nth state in eV is Z atomic number 1 0 85 2 2 1 5 Z 3 13 6 2

Physics
Atomic StructureAccording to Bohr s theory the energy of an electron in hydrogen atom in states corresponding to n 1 2 3 4 is repsectively 13 6 eV 3 4 eV 1 51 eV and 0 85 eV In order to obtain emission of HB line of Balmer series the minimum energy that has to be given to a normal hydrogen atom is 1 12 75 eV 2 14 45 eV 3 2 55 eV 4 4 25 eV

Physics
Atomic StructureIn a characteristic X ray spectra of some atom superimposed on continuous X ray spectra Relative intensity 1 P represents Ka line 2 Q represents KB line 3 Q and P represents Ka and KB lines respectively 4 Relative positions of Ka and KB depend on the particular atom

Physics
Atomic Structurer The electric potential between a proton and an electron is given by V V en where ro is a constant Assuming Bohr s model to be applicable the magnetic dipole moment of the electron proportional to n n is principle quantum number x is equal to

Physics
Atomic Structureectron is orbiting in a circular orbit under the influence of a constant transverse magnetic field of strength B Assuming that Bohr s postulate regarding th entum holds good for this electron find the kinetic energy of electron in n th orbit m mass of electron e magnitude of charge of electron CE KE KE nhBe 27 Me nhBe 12 me nhBe