Atomic Structure Questions and Answers

Physics
Atomic StructureAn astronaut is approaching the moon He sends out a radio signal of frequency 5 x 10 Hz and finds out that the freque shift in echo received is 10 Hz Find his speed in m s of approach ptions

Physics
Atomic StructureAn imaginary particle has a charge equal to that of an electron and mass 50 times the mass of the electron It moves in a circular orbit around a nucleus of charge e Considering mass of the nucleus to be infinite radius of first Bohr s orbit and energy of this shell will be A B C D 26 45 x 10 10 m 0 272 eV 1 058 x 10 12 m 0 272 eV 26 45 x 10 10 m 0 68 keV 1 058 x 10 12 m 0 68 keV K

Physics
Atomic StructureIf the series limit wavelength of the Lyman series of hydrogen atom is 912 then the series limit wavelength of the Balmer series of the hydrogen atom is A B D 912 1824 3648 456

Physics
Atomic StructureA hypothetical element positronium consists of an electron moving in space around a nucleus consisting a positron Using the Bohr s atomic model determine the first Bohr radius Positron is a subatomic particle similar to electron in all respect except possessing a positive charge
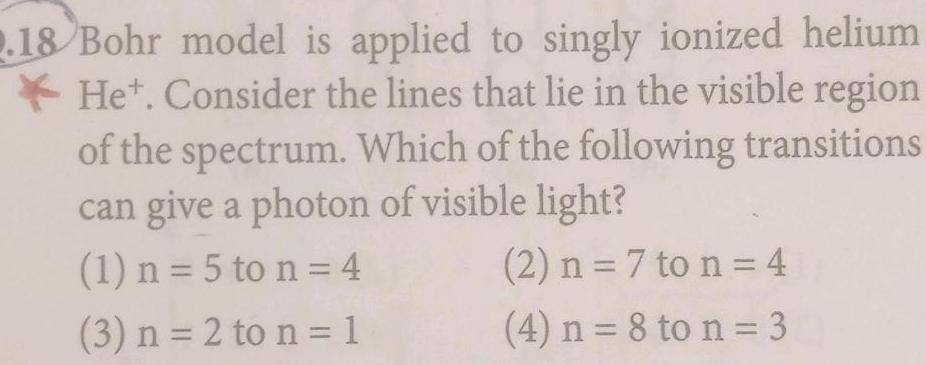
Physics
Atomic Structure2 18 Bohr model is applied to singly ionized helium Het Consider the lines that lie in the visible region of the spectrum Which of the following transitions can give a photon of visible light 1 n 5 to n 4 2 n 7 to n 4 3 n 2 to n 1 4 n 8 to n 3

Physics
Atomic StructureThe graph between wave number and angular frequency w is oil Wave no Angular o frequency w What Wave no 1 Angular frequency Angular frequency w n Wave no 1 Wave no

Physics
Atomic StructureThe energy of an excited hydrogen atom is 3 4 eV The angular momentum of the electron is Take h 6 63 x 10 4 J s a 1 05 x 10 4 Js c 3 16 x 10 34 Js b 2 11 x 10 34 Js d 4 22 x 10 34 Js

Physics
Atomic StructureSolveLancer Test The energy of an electron in nth orbit in a hydrogen atom is E By what factor the energy E will be related to the original energy E when the electron transits in 2n th orbit SolveLancer Test 3 a 4 42L12

Physics
Atomic Structuresubstance with the FCC lattice has density of 6200 kg m3 The molecular weight of that substance is 0 2 amu The atomic packing fraction of lattice will be OPTIONS TT 6

Physics
Atomic Structure1 Decreases Remains same newton metre of a relativistic charged particle increases it s specific charge 2 Increases 4 First decreases then increases Smallest unit of charge is

Physics
Atomic Structure7 17 An electron tube was sealed off during manufacture at a pressure of 1 2 x 10 mm of mercury at 27 C Its volume is 100 cm The number of molecules that remain in the tube is a 2 10 6 c 3 86 x 10 1 b 3 10 5 d 5 10

Physics
Atomic Structure7 3 17 An electron tube was sealed off during manufacture at a pressure of 1 2 x 10 mm of mercury at 27 C Its volume is 100 cm The number of molecules that remain in the tube is a 2 10 6 c 3 86 x 1011 b 3 x 10 5 d 5 10

Physics
Atomic Structurellion that proved the existence of De Broglie s matter waves The radius of hydrogen atom is 5 3 x 10 1 m Use uncertainty principle to estimate the minimum energy an electron can have in this atom

Physics
Atomic StructureIn the given figure the energy levels of hydrogen atom have been shown along with some transitions marked A B C D and E The transitions A B and C respectively represent 1 2 n 5 n 4 n 3 3 n 2 A n 1 B Continuum C D E eV 0 eV 0 54 eV 0 85 eV 1 51 eV question Type Single Correct Type 3 4 eV 13 6 eV The ionization potential of hydrogen second member of Balmer series and third member of Paschen series The first member of the Lyman series third member of Balmer series and second member of Paschen series The series limit of Lyman series third member of Balmer series and second member of Paschen series

Physics
Atomic StructureAn electron m 9 109 10 31 kg is confined in a one dimensional well of width L 10 nm Choose the correct options Marks 2 determine uncertainty in velocity OPTIONS 5791 m s 9010 m s 2888 m s infinite square 8900 m s

Physics
Atomic StructureThe wavelength of emission of radiation is 3000 and the coefficient of spontaneous emission is 10 power12 s Given k 8 6x 10 5eV K or 1 38 X 10 power 23 J K Choose the correct options Marks 2 The coefficient for absorption is OPTIONS

Physics
Atomic StructureTitle An electron m confined in a one dimensional well of width L 10 nm Choose the correct options Marks 2 determine uncertainty in momentum OPTIONS 9 109 10 31 kg is 0 7 10 26 kgm s 2 527 10 23 kgm s 0 52 10 20kgm s infinite square

Physics
Atomic StructureIn a hydrogen like atom an electron is orbiting in a orbit having quantum numbern Its frequency of revolution is found to be 13 6 x 10 5 Hz Energy required tofree the electron from the atom from the above orbit is 54 4 eV In timesecond the electron jumps back to orbit having quantum number be the average torque acted on the electron during the above process then t in Nm is Find the value of n Given 2 1 x 10 34 J s frequency of revolution of electron in the ground state of H atom Y C 6 6 10 15 H ionization energy of H atom Fa 13 6 ev

Physics
Atomic StructureQ 48 In a photoelectric experiment a monochromatic light is incident on the metal plate A It was observed that with V 5 volt the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons striking plate B was 1 eV The polarity of the applied potential difference was as shown in figure a With polarity of the applied potential difference reversed as shown in figure b and frequency of incident light doubled it was observed that in saturation state the kinetic energy of electrons striking plate B ranged between 5 eV to 20 eV Find the work function of metal used in plate A i T of e er e to B V 5 v a V 5 v F b

Physics
Atomic StructureWhich of the following statement is correct A B At sunset or sunrise the sun s rays have to pass through a small distance in the atmosphere At sunset or sunrise the suns rays have to pass through a larger distance in the atmosphere C Rayleigh scattering which is proportional to 1 Most of the blue and other shorter wavelengths are not removed by scattering D

Physics
Atomic StructureA doubly ionised Li atom is excited from its ground state n 1 to n 3 state The wavelengths of the spectral lines are given by 232 231 and 221 The ratio 32 31 and 221 31 are respectively a 8 1 0 67 c 6 4 1 2 b d 8 1 1 2 6 4 0 67 Two wires A and B of the same material having radii in the ratio 1 2 and carry currents in the ratio 4 1 The ratio of

Physics
Atomic Structure3 In each situation of Column I a physical quantity related to orbiting electron in hydrogen like atom is given The terms Z and n given in Column II have usual meaning in Bohr s theory Match the quantities in Column I with the terms they depend on in Column II B C D Column I Frequency of orbiting electron P Q Angular momentum of orbiting electron Magnetic moment of R orbiting electron The average current due S to orbiting of electron Column II is directly proportional to Z is directly proportional to n is inversely proportional to n is independent of 2

Physics
Atomic StructureThe electric potential between a proton and an electron given by V V In where ro is a constant Assumit ro Bohr s model to be applicable write variation of r w n n being the principal quantum number 1 rno n In 3 r n 2 x 2 rn 1 n 4 rn 1 n

Physics
Atomic StructureLet us consider what happens in the case of Si or Ge crystal containing Natoms For Si the outermost orbit is the third orbit n 3 while for Ge it is the fourth orbit n 4 The number of electrons in the outermost orbit is 4 2s and 2p electrons Hence the total number of outer electrons in the crystal is 4N The maximum possible number of electrons in the outer orbit is 8 2s 6p electrons So for the 4Nvalence electrons there are 8N available energy states These 8N discrete energy levels can either form a continuous band or they may be grouped in different bands depending upon the distance between the atoms in the crystal see box on Band Theory of Solids At the distance between the atoms in the crystal lattices of Si and Ge the energy band of these 8N states is split apart into two which are separated by an energy gap E Fig 14 1 The lower band which is

Physics
Atomic StructureRadiation coming from transitions n 2 to n 1 c hydrogen atoms fall on He ions in n 1 and n 2 states The possible transition of helium ions as they absor energy from the radiation is a n 2 n 3 8 April 2019 L b n 1 n 4

Physics
Atomic StructureNa has an ionization energy of 5 14eV Cl has an electron affinity of 3 61eV NaCl crystal has a lattice constant of 0 563nm and a Madelung constant of 1 748 Calculate the binding and cohesion energy per ion pair The repulsion of ions doesn t have to be accounted for

Physics
Atomic Structurec In a singly ionized Helium atom the electron is in the third orbit A photon of energy 10 04eV knocks out the electron Calculate the stopping potential of the electron Ionisation potential of H atom is 13 6 eV 5

Physics
Atomic Structure5 Calculate value of spherical harmonics for 1 2 and m 0 and report the values in a table for 0 0 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 and 360 Draw the Marks 5 00 polar plot for the above values

Physics
Atomic StructureIn hydrogen atom in its ground state the first Bohr orbit has a radius r When the ator is raised to one of its excited states the electron s orbital velocity becomes one third The radius of the orbit excited states is A 2r B 3r C D 9r 4r

Physics
Atomic StructureElectromagnetic radiations of Antensity 1 W m strikes on the surface of a substance which reflect 80 incident radiation back into same medium The radiation pressure on the surface of substance is Only One Carved Anwar A 4 10 N m B 2 5 107 N m 8 x 10 8 N m

Physics
Atomic Structurespectrum To which part of electromagnetic radiation with 21 cm wavelength emitted by atomic hydrogen in interstellar space belongs Microwaves Radiowaves min se Gamma rays

Physics
Atomic StructureThese rays lie in upper frequency range of electromagnetic spectrum The rays are produced in nuclear reactions and used in medicine to destroy cancer cells The rays are X rays Gamma rays Microwaves Infrared raus

Physics
Atomic Structurea State and explain Heisenberg s uncertainty principle Describe gamma ray microscope experiment b The lifetime of an atom in its excited state is 10 8 s Calculate the minimum uncertainty in determining the energy of the excited state c Applying Heisenberg s uncertainty principle show that i electron cannot stay inside a nucleus ii minimum energy of a harmonic oscillator gan never be zero and iii there exist a finite width of the spectral lines

Physics
Atomic Structure12 The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0 C to 50 C when no work is done is R is the universal gas constant a 750R b 250R c 500R d 175R

Physics
Atomic Structure27 If radius of the A1 nucleus is taken to be RAI then the radius of 125 Te nucleus is nearly 53 13 53 53 13 r 3 13 O ERA RAI Ral

Physics
Atomic StructureThe nuclear radius of a nucleus with nucleon number 16 is 3 10 15 metre Then the nuclear radius of a nucleus with nucleon number 128 is Question Type Single Correct Type 13 x 10 15 m 2 1 5 10 15 m 36 10 15 m A 45 x 10 15 m

Physics
Atomic Structure19 20 3 13 6 eV 4 12 1 V 3 13 6 eV 4 12 1 eV The element which has a Ka x rays line of 19 ara faut Kax 1 8 A 8 wavelength 1 8 A is R 1 1 x 10 m b 1 5 33 0 39 R 1 1 x 10 m b 1 and 5 33 0 39 1 Co Z 27 2 Iron Z 26 3 Mn Z 25 4 Ni Z 28 30 1 Co Z 27 3 Mn Z 25 Proffers 2 Iron Z 26 4 Ni Z 28 Aferit

Physics
Atomic StructureGiven this information what equation would I use to find frequency I already know hkw to concert MT to Joules but I dont know which equation id use because V h c guves error bc the 10 34 in the denominator Target Earth Composition Rock Ice Iron Diameter 1 km Results impact into Velocity 20 KMIS Energy Released 59554 MT mauritanian impact into 19518 MT Sudan impact into 1951 T Frequency

Physics
Atomic StructureAn electromagnetic wave of intensity 30 W m is incident or a surface of area 2 m If the surface is perfectly absorbing then the amount of momentum transferred to the surface in 10 s will be O 2x 10 6 kg m s O 2x 106 kg m s O 4 x 10 9 kg m s O 10 8 kg m s

Physics
Atomic StructureSolveLancer Test On what factors the impact parameter depend on when angle of scattering is 90 SolveLancer Test a Nuclear charge of the atom on which bombarding is taking place b Kinetic energy of the bombarding alpha particles c Both a and b d None of the above

Physics
Atomic StructureExample 7 The average life time of an electron in an excited state of H atom is about 10 8 s How many revolutions does an electron in n 2 state make before its transition to n 1 state The Rydberg constant for H atom is 1 097 x 107 m

Physics
Atomic StructureConsider the electronic energy level diagram of H atom Photons associated with shortest and longest wavelengths would be emitted from the atom by the transitions labeled To C B OD and C respectively C and A respectively OC and D respectively A and C respectively A n n 4 n 3 n 2 n 1

Physics
Atomic StructureI just have a small query regarding the transition of electrons from one orbit to the other I understood that electrons releases energy when it goes to an upper orbit but does it absorbs energy when it goes to the lower orbit

Physics
Atomic StructureWhich of the following statements does not form a part of Bohr s model of a hydrogen atom 1 The energy of the electrons in the orbit is quantized 2 The electron in the orbit nearest the nucleus has the lowest energy 3 Electrons revolve in different orbits around the nucleus 4 The position and velocity of the electrons in the orbit cannot be

Physics
Atomic Structure7 What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table are called Ogroups O periods sections families 8 What are the vertical columns of the Periodic Table are called spectra periods Ogroups O energy levels 3 pc 3 pc

Physics
Atomic StructureA helium ion of mass 4m and charge 2e is accelerated from rest through a potential difference in vacuum Its final speed will be 2e V m o for O m O ev

Physics
Atomic StructureThe statement outlines the Standard Model and its description of all visible matter The atomic nucleus consists of the sub atomic particles called protons and neutrons which contain up and down quarks A third sub atomic particle called an electron is a type of quark Which of the following correctly identifies an error in the statement Protons and neutrons contain top and bottom quarks Protons and neutrons only contain down quarks The electron is a type of lepton The electron is a type of anti quark

Physics
Atomic Structure9 Which atom contains exactly 18 protons O Sulfur O Hydrogen O Gold O Argon Back Next This form was created inside of West Canada Valley

Physics
Atomic Structurea The average mass of all the isotopes of the element b A measure of the density of that element c The mass of the most common isotope of that element d The number of protons and electrons in the atoms of the element 8 An element and an atom are different but related because a A particular element is made up of many different types of atoms b A molecule is the same as an atom c An element is made up of all the same type of atom d An element is smaller than an atom 9 The periodic table shows that a carbon atom has six protons This means that a carbon atom also has a Six electrons b Six neutrons c More protons than electrons d An atomic mass that equals six 10 The atomic number of nitrogen is 7 The atomic mass is 14 01 This means that a All nitrogen atoms have exactly 7 neutrons b A small percentage of nitrogen atoms have fewer than 7 neutrons c A small percentage of nitrogen atoms have more than 7 neutrons d Some nitrogen atoms have fewer than 7 electrons 11 Electrons are in regions around the nucleus called energy levels The first energy level a Is furthest from the nucleus b is closest to the nucleus c Holds the most electrons d Needs more than two electrons to fill it up 12 Neon has 10 protons and 10 electrons The electrons fill the energy levels in Neon like this a 2 in the first 2 in the second and 6 in the third b 4 in the first 4 in the second and 2 in the third c 2 in the first in the second and in the third

Physics
Atomic StructureAn electron is approaching the speed of light due to an applied force on it Which of the following is true about the electron a Its charge will increase b Its speed will increase infinitely c Its length will increase d Its mass will increase