Center of mass and momentum Questions and Answers

Physics
Center of mass and momentum28 A rocket has a mass of 20000 kg of which 16000 kg is fuel The rocket engine can exhaust fuel at the rate of 200 kg s with an exhaust velocity of 3000 m s relative to the rocket Find the net force acting o the rocket 10 second after blast off Take g 10 m s 1 4 2 10 N 2 6 10 N 3 1 8 10 N 4 zero

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA particle of mass m and velocity u collides elastically with another particle of the same mass at rest in laboratory frame The scattering angle in the centre of mass frame is found to be 90 Find the velocities of the scattered particles in the centre of mass frame and the laboratory frame

Physics
Center of mass and momentumFour particles of masses 1kg 2kg 3kg and 4kg are at the vertices of a rectangle of sides a and bas shown Ifa 1m and b 2m What is the location of their centre of mass 4kg 1 kg b 3 kg a 2kg 1 0 5m 1 4m X 2 1 4m 0 5m 3 0 14m 0 05m 4 None

Physics
Center of mass and momentumM I of a thin rod of mass M and length about an axis through its centre is Me 12 Its M I about an axis passing through one end and parallel to the length 2 M 1 zero 3 MC 4 MC

Physics
Center of mass and momentum5 Rolling ball A semi cylindrical piece of radius R is cut out from a tile The tile is standing on a smooth frictionless horizontal surface see figure The tile s mass is M A small ball of radius r and mass m is pushed down from the point A to move along the cylindrical sur face How much has the tile moved by the moment when the ball reaches the point B Author Hans Daniel Kaimre regional round 2016 G 8 A B

Physics
Center of mass and momentuma other 4 20 The plane of a dip circle is set in the geographical meridian and the apparent dip angle is 0 It is then set in a vertical plane aration perpendicular to the geographical meridian the apparent dip tancer becomes 0 The angle of declination a at that place is given as A tan a tan 0 tan 0 B tan a tan 0 tan 0 C tan a tan 0 tan 0 D tan a tan 0 tan 0 1

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo particles of equal masses are moving with equal speeds at an angle 60 de Broglie wavelength of these particles is 2 Find de Brooglie wavelength of the particles in the frame of centre of mass of particles Ala D 4 B 2 2 C 3

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA ball is thrown with a velocity of 6m s vertically downwards from a height H 3 2m above a horizontal floor If it rebounds back to same height then coefficient of restitution e is g 10m s A 0 5 C 0 7 B 0 6 D 0 8 e N

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA ball is allowed to slide a distance 1 from rest down a smooth inclined plane having inclination of 30 with the horizontal The ball impringes on a fixed smooth horizontal with the coefficient of restitution of at the foot of the inclined plane The range of the ball on the horizontal plane is 3 2 ych iz ct fau 30 yg fag 3ad da fagmaz A 3 1 3 fhuat fu da 2 92 grudzYa Quic a 3 2 B A 1 C and fa fa fau uz chua 1 fu am a Z 31 4 Correct Answer

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA uniform chain of mass 4 kg and length 2 m is kept on table such that 3 4th of the chain hangs freely from the edge of the table How much work has to be done in pulling the entire chain on the table AAJ KA TOPPER 1 7 2 J 2 120 J 3 1200 J 4 3 6 J

Physics
Center of mass and momentumQuestion 15 An isolated particle of mass m is moving in a horizontal plane x y along the x axis at acertain height above the ground It suddenly explodes into two fragments of masses m 4 and 3m 4 An instant later the smaller fragment is at y 15 cm The larger fragment at this instant is at a y 5 cm b y 20 cm c y 5 cm d y 20 cm

Physics
Center of mass and momentumIllustrated below is a uniform solid cubical block of mass M and side a Mark the correct statements D a M C A RI C A The moment of inertia about axis A passing through the centre of mass is A Ma B B The moment of inertia about axis B which bisects one of the cube faces is Ig Ma The moment of inertial about axis C along one of the cube edges is Ic Ma The moment of inertia about avis passing through body diagonally opposite vertices is Mg

Physics
Center of mass and momentum21 1 19 A body of mass 1 kg initially at rest explodes and breaks into three fragments of masses in the ratio 1 1 3 The two pieces of equal masses fly off perpendicular to each other with speed v each What is the momentum of heavier fragment 14 3V0 2 5 3 3v 2 2 a po 2071 Jee 4 5 10 2 5 1 5 2

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo train A B are running in same direction on parallel rails such that A is faster than B packets of equal weight are transferred between them What will happen due to this 1 A will be accelerated but B will be retarted 2 B will be accelerated but A will be retarted 3 There will be no change in A but B will be accelerated 4 There will be no change in B but A will be

Physics
Center of mass and momentum3 Three identical spheres each of mass 1 kg are placed touching one another with their centres in a straight line Their centres are marked as A B C respectively The distance of centre of mass of the system from A is AB AC a b AB BC

Physics
Center of mass and momentum17 Santi 50 kg and Banti 60 kg are sitting at the two extremes of a 4 m long boat 40 kg standing still in water To iscuss a mechanics problem they come to the middle of the moat Neglecting friction with water how far does the boat move on the water during the process a 5 5 cm b 11 2 cm c 13 3 cm d 15 1 cm 50 kg S 40 kg 4 m B 60 kg

Physics
Center of mass and momentum9 3 50 W If two bulbs of power 60 W and 100 W respectively each rated 110 V are connected in series with the supply of 220 V then 1 60 W bulb will fuse 3 Both bulbs will fuse 2 100 W bulb will fuse 4 Bulbs will not fuse Two electric bulbs whose resistances are in the ratio 1 2 are connected in series to a constant voltage source The power dissipated in them are in the ratio

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo particles are inter connected by an ideal spring see figure The spring is compressed and system is projected in air under gravity If the acceleration of m is find acceleration of m 1 bo 3 Question Type Single Correct Type 2 a m m g ma m2 m m g m g m a tod g

Physics
Center of mass and momentumThe rebound coefficient between a tennis ball and a racket is defined as v v where v is the incoming speed of the ball and v he speed of the ball after rebound while the racket is at rest A tennis ball falls from height H to a racket at rest and bounces back to 0 A tennis player is using the racket to hit an incoming tennis ball traveling at 150 km hr and the racket is moving at 100 km hr What is he speed of the ball after being hit Assume the mass of the racket that of the ball

Physics
Center of mass and momentumMarks ve Marks 1 If wrong option is selected A of mass 3kg moving with a speed 2m s collides elastically with a stationary block B of mass 4kg The location of block B is at origin at the time Assume the collision with the wall to be elastic in nature and the size of the blocks is negligible The x coordinate of block B when it collides with for the second time is m 0 If none of the option is selected 2m m 2m s AC B x 0 x 12m

Physics
Center of mass and momentumWhich of the following option s is are correct A Centre of gravity for triangular lamina is situated at point of intersection of medians B Centre of gravity for circular ring is situated at the centre of ring C Centre of gravity for hollow cone is situated at a height from the base on its axis 4 D Centre of gravity for rectangular lamina is situated at the point of intersection of the diagonals The correct option is

Physics
Center of mass and momentumhe force F acting on a particle of mass m is show force time graph The change in momentum of th article over the time interval from t 0 tot 6s is N 5 0 20 N s 10 Ns N I t s

Physics
Center of mass and momentum15 A sphere of radius R carries charge density p such that p kr where k is positive constant and ris distance from centre Find the magnitude of electric field at distance R 2 from centre KR 1 200 3 KR 580 2 KR 10 KR 4 40

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA block of the mass of 1 kg is moving on the x axis A force F acting on the block is shown The velocity of the block at time t 2 s is 3 m s What is the speed of the block at time t 4 s 5 F N 0 5 A B 2 8 ms 3 4 5 1 2 1 2 ms 1 3 ms 1 t sec

Physics
Center of mass and momentumThreads of length h h h are fastened to the vertices of a homogeneous triangular plate of weight W The other ends of the threads are fastened to a common point as shown in the figure assume all the threads are taut and the plate is in equilibrium and in Horizontal plane The incorrect statement among the following is h A Tension in the threads are proportional to their lengths B Vector sum of tensions in the strings at the plate and weight of the plate is zero C Tensions in the threads are inversely proportional to their lengths D The contra of mace of the plata is at its controid and it should halow the point of cucpancion

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA particle of mass 4kg moving with a speed of 10m s collides with a train moving in an opposite direction with a speed of 20m s If coefficient of calculate the final speed of the restitution e e 2 2 particle in m s 1 5 3 20 2 15 4 35

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA rod of length R and mass M is free to rotate about a horizontal axis passing through hinge P as in figure First it is taken aside such that it becomes horizontal and then released At the lowest point the rod hits the block B of mass m and stops Find the ratio of masses such that the block B completes the circle Neglect any friction 10 m B
Physics
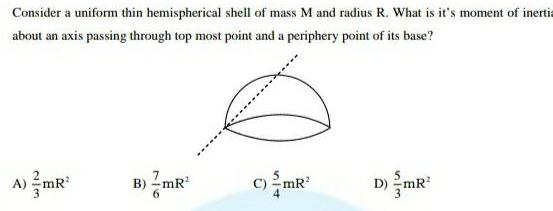
Center of mass and momentumConsider a uniform thin hemispherical shell of mass M and radius R What is it s moment of inertia about an axis passing through top most point and a periphery point of its base A MR B mR C 2 mR D MR

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA uniform disc of radius R and mass M is spun to an angular velocity wo in its plane about its centre and then placed on a rough horizontal surface such that the plane of the disc is parallel to the horizontal plane If the co efficient of friction between the disc and the surface is how long will it take for the disc to come to stop RITond n dom

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA rod of length L is hinged from one end It is brought to the horizontal position and released The angular velocity of the rod when it is in the vertical position is A 2g L B 3g L D g L C g 2L

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA ball is hanging from a thread of length 5m A bullet of mass 100 gm travelling horizontally with a speed of 100 m s strikes the ball elastically and deflects from its path by an angle of 37 in the horizontal plane It s speed after the collision is 50 m s What is the tension in the thread in N immediately after the collision Options

Physics
Center of mass and momentumQ5 A plane electromagnetic wave of wave intensity 6 W m strikes a small mirror of area 39 cm held perpendicular to the approaching wave The momentum transferred in kg ms by the wave to the mirror each second will be a 1 2 x 10 10 b 2 4 x 10 9 c 3 6 x 10 9 d 4 8 x 10 7

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA thermometer of mass m is filled with mercury of mass m2 and placed in a gravity free space without touching anything As temperature rises mercury expands and ascend in thermometer If height ascend by mercury in thermometer is h then by what height COM of mercury thermometer system descend

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA child is standing at one end of a long trolley moving with a speed v on a smooth horizontal track If the child starts running towards the other end of the trolley with a speed u the centre of mass of the system trolley child will move with a speed A zero Your Answer B v u v u

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA 5 75 kg steel ball has an initial velocity of 6 34 300 meters per econd The ball collides with and imbeds itself in a 3 85 kg block of clay traveling at 2 50 140 meters per second a Calculate the initial momentum of each object and write the re sult in rectangular form b Calculate the momentum of the combined mass after collision and write the result in polar form Calculate the final velocity after collision and write the result in polar form 30 140

Physics
Center of mass and momentum16 A cylindrical pipe of radius R and mass M is placed vertically on a horizontal floor Two identical spheres each of radius r and mass m are inserted in the cylinder as shown in the figure Radius of the spheres is more than 0 5R At what minimum value of m M will the arrangement topple There is no friction between the spheres and between a sphere and inner wall of the cylinder

Physics
Center of mass and momentumIf a semicircular ring of mass M and radius R is tied with string at one end and is free to rotate about hinge on other end Find tension in the string A T mg T mg c T mg D T 2mg E

Physics
Center of mass and momentumQ Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink of uniform line thickness The mass of ink used to draw each of the two inner circles and each of the two line segments is m The mass of the ink used to draw the outer circle is 6m The coordinates of the centres of the different parts are outer circle 0 0 left inner circle a a right inner circle a a vertical line 0 0 and horizontal line 0 a The y coordinate of the centre of mass of the ink in this drawing is y X

Physics
Center of mass and momentumFind the center of mass and inertia tensor for rotations about the center of mass of a prism which base is a rectangle 20 cm for 4 cm and its edges are equilateral triangles sides 4 cm it is made with uniform material so it has a constant density and total mass of M

Physics
Center of mass and momentumThe ballistic pendulum is a simple device to measure projectile velocity v by observing the maximum angle to which the box of sand with embedded projectile swings What is the velocity of the 60 g bullet fired horizontally in to the suspended sand 20 kg sand bag swings 30 2m

Physics
Center of mass and momentumal me Question 1 The centre of mass of a system of particles does not depend upon a position of particles b relative distance between particles c masses of particles d force acting on particle LAIPMT 1997 AIEEE 2004 2 A couple produces pure rotation b pure translation c rotation and translation d no motion AIPMT 1997 3 A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to positive X axis The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is a zero b increasing with x c decreasing with x d remaining constant L distan 1220 b 25 rad s d 25 m s NEET 2017 IIT 2002 14 A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 404 CXID cm What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force 30 N m a 0 25 rad s c 5 m s 5 A closed cylindrical container is partially filled with water As the container rotates in a horizontal plane about a perpendicular bisector its moment of inertia 38CTUB a increases c remains constant d depends on direction of rotation IIT 1998 6 A rigid body rotates with an angular momentum L If its kinetic energy is halved the angular momentum becomes a L c 2L b decreases b 1 2 4 L 2 AFMC 1998 AIPMT 2015 7 A particle undergoes uniform circular motion The angular momentum of the particle remain conserved about a the centre point of the circle b the point on the circumference of the circle is not changing c any point inside the circle d any point outside the circle IIT 2003 8 When a mass is rotating in a plane about a fixed point its angular momentum is directed along a a line perpendicular to the plane of rotation COL b the line making an angle of 45 to the plane of rotation c the radius d tangent to the path AIPMT 2012 9 Two discs of same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA 1000 kg rocket is fired from the surface of earth so that its exhaust speed is 1000 m s relative to rocket If initial acceleration of the rocket is 5 m s then mass of fuel burning per second is Take g 10 m s 1 15 kg s 2 5 kg s rur dm 3 10 kg s 4 20 kg s

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA stationary bomb of mass 10 kg explodes into two pieces of masses 4 kg and 6 kg If the magnitude of velocity of mass 6 kg is 10 m s the magnitude of velocity of mass 4 kg is 2 10 m s io 176x10 4 20 m s 1 6 m s 3 15 m s vu

Physics
Center of mass and momentumIf the linear density of a rod of length L varies as A Bx where A and B are constant The separation of the centre of mass from one end of the rod is L 3A 2BL L 3A 2BL A B 2BL 3A 3 2A BL C LB 3 A D 5LB 3A

Physics
Center of mass and momentumElon Mask the astronaut has a total mass of 57 1 kg While in space he throws a 3 23 kg tool away from him at a speed of 3 93 m s relative to his space ship What will Elon Mask s speed be relative to the space ship after throwing his tool Express your answer in two decimal places with units of m s

Physics
Center of mass and momentum5 Three girls Shivangi Radhika and Saili sat o one side of see saw at distances of 1m 1 2m an 1 5m from the fulcrum that is situated at the TY center of the see saw The masses of the thre girls were 30kg 40kg and 50kg respectivel Where should Rakesh sit on the other side seesaw so as to balance it Given the mass Rakesh is 80kg a 2m c 1 91m b 1 5m d 1 75m

Physics
Center of mass and momentum4m L 6 A hammer consists of an evenly thick wooden shaft with length L and mass m which is pressed into a hollowed out evenly thick iron head with height L 6 and mass 4m The left end of the shaft goes edge to edge with the head see figure above How far away from the right end of the shaft is the center center of gravity of the hammer x x x x 23L 30 5L 6 11L 19 E 2L 3 L x 1 H

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA ball of mass m initially at rest falls from a height h through a curved path to ground level see figure Then it is damped by a spring with a constant of elasticity k until it stops Using the law of conservation of mechanical energy find the velocity of the ball just before it touches the spring and the distance the spring is compressed from its equilibrium length to when the ball stops k

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA smooth ball of mass m strike a horizontal surface with a velocity v in a direction making an angle q with the normal to the surface as shown in the figure If the coefficient of restitution for the collision between the ball and the surface is e and the ball was in contact with the surface for a small time At the average force acting on the ball during collision is 30

Physics
Center of mass and momentuminclined plane m has coefficient of friction 0 1 with the surface while m has u 0 2 The masses are simultaneously released when their initial separation is 0 4 m and m is at a height of 2 3 sin 5 A m The angle of inclined is completely inelastic collision occurs between the two The velocity of masses just after collision is 0 8 n m s Then n is Take g 10 ms 2m 0 4m sin A