Anatomy and Physiology Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Anatomy and Physiology
CirculationUrinary bladder Uterus D Internal urethral sphincter ng and Stom m Peritoneum

Anatomy and Physiology
EndocrinologyArt labeling Activity Histology of the Female Urethra and Urinary Lumen of urethra Mucosa Lamina propria containing mucous glands Detrusor muscle Transitional epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium of mucosa Smooth muscle urethra Urinary bladder

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I TractUrinary System Lab Pre Lab Art labeling Activity The Renal Corpuscle Glomerular capsule Capsular epithelium Distal convoluted tubule Visceral epithelium podocyte

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I TractSystem Lab Pre Lab ling Activity Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephrons Papillary duct Proximal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Renal corpuscle Nephron loop Distal convoluted tubule Connecting tubules Juxtamedullary nephron Renal papilla Thin descending limb Thick ascending limb

Anatomy and Physiology
Embryosuppose local councils spend money only on roads and clean water The share of the expen ditures for clean water is a E 0 1 Voter preferences are Ui la pil where pi is the bliss point of voter i Suppose for men pi U 0 0 75 uniform distribution whereas for women pi U 0 25 1 There are equal shares of men and women in the population a Are these preferences single peaked b What is the policy outcome if only men can vote c What is the policy outcome if everyone can vote d Which outcome does better represent what women want

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenO a O b Believes that context counts and we should make pragmatic informed decisions Is a specific development methodology that believes in the rapid delivery of working solutions Oc Is only helpful for agile teams d Focuses on how to manage the flow of work by limiting work in process

Anatomy and Physiology
InfexO a States that the Scrum Master should replace the manager as the leader of the team b Is a lightweight development methodology described by a set of practices roles and artifacts c States that development cycles must be 2 weeks in length d Cannot be used on large projects because no documentation is required

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenWhich of the following is NOT a responsibility of a program manager a Ensuring strategic alignment of the program with the organization s strategy Establishing goals and success factors to ensure the program s benefits are realized c Monitoring and controlling project execution b d Engaging the program s stakeholders

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyWhat have we learned about the best way to motivate knowledge workers a Financial rewards are the best motivators b People working alone come up with the best solutions c Managers should create environments where there is no conflict Financial incentives are not effective at motivating teams to solve complex problems d

Anatomy and Physiology
EndocrinologyO a Describes a methodology to deliver projects in short increments b Describes a highly structured project management lifecycle process Believes that change should be limited to increase the predictability of project outcomes c O d Is a set of value statements that can be achieved through several different development approaches

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenA primary focus of Lean is a Eliminating waste and focusing on value Creating processes that increase the number of items being worked on simultaneously c Building in quality through rigorous testing at the end of the project b d Optimizing the flow of work

Anatomy and Physiology
Infexa Develop more efficient processes b Improve the flow of work by managing queue lengths c Understand the customer experience and identify ways to improve it d Deliver projects in short increments

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenWhich of the following is NOT associated with portfolio management a Making sure that projects are aligned to the organization s strategy b Selecting the best project managers to manage the most critical projects c Providing management oversight and governance of project execution d Reviewing project and investment options

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWho makes decisions about changes to the project a The project sponsor b The change control board c The change advisory board d It depends on the project

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenWhen conducting a net present value analysis or return on investment analysis what is the crucial lesson to remember a These two analyses do not have anything in common b It is better to recognize benefits sooner than later c The smaller the number the better d It is better to wait to recognize the full benefit rather than realizing benefits incrementally along the way

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe primary lesson to be learned from understanding your DISC profile is a DISC behaviors are the same as Myers Briggs but easier to understand People with a High D profile are very empathetic and concerned with the feelings of others c People with a High I profile are task oriented and focused on the details We can improve communications by understanding our natural behavior styles and those of our stakeholders Ob O d

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenWhen it comes to the Project Management Plan the project manager should O a Discuss the plan with all the stakeholders to ensure unanimous agreement Consider the context and customize or tailor the project management plan accordingly b c O d Follow the standard guidelines as established by the program management office Avoid collaborating with the project team when tailoring the plan to avoid conflict

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyYou are trying to decide about which project to pursue For which benefit measurement is a smaller number better a Return on investment Ob Net present value c Payback period d Benefit cost analysis

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenWe perform a quantitative risk analysis to O a Develop a risk exposure score b Estimate the cost or time impact of a risk event c Calculate the management reserve required for the project O d Determine when to implement our risk response strategy

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenRisks are O a Future events with a likelihood of occurring and potential impact b Only identified at the beginning of the project c Only negative things threats d Something that we cannot do anything about

Anatomy and Physiology
BrainWhat is true about the project budget O a The budget is the sum of the project cost estimates b The budget excludes estimates for risk events c The budget is established by the project sponsor O d Includes estimates for known and unknown risks

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyYou are assigned to manage a project the first thing you should do is a Understand what needs to be delivered b Create a schedule c Build your team d Start working on the first proiect deliverable

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenThe critical path is a Defined by the most critical and time sensitive activities on the project b Identified by senior management as milestones they want to track c The path of activities or tasks that determines the length of the project O d Only needed for agile projects

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyThe order planning a project is O Collect requirements Identify scope Identify sequence activities Create budget b Identify scope Collect requirements Create schedule c Create budget Create schedule Fit scope into the schedule a d Establish scope Collect requirements Create Schedule Create budget

Anatomy and Physiology
Abdomena Never updated b The same as the project schedule c Used by the project manager as a guide for executing the project d A standard set up practices used by all projects in the organization

Anatomy and Physiology
JointsWhat is true about communications a We should select a communication method based on our stakeholder s needs b We should select a communication method based on what is easiest for the project manager O c Email is an excellent medium for communicating complex information d Face to face communication is no longer important

Anatomy and Physiology
Abdomena Created at the beginning of the project and does not need to be updated b Only lists the primary project stakeholders c A tool used by project managers to capture information about stakeholders d Only contains contact information about project stakeholders

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe primary reason for creating a Project Charter is a To get the project funded b Establish initial project expectations and outcomes c To identify all the project stakeholders d To define the final project scope

Anatomy and Physiology
BrainWhich is a primary characteristic of a project manager on a traditional project a Project managers are not needed on Agile projects b The project manager is a subject manager expert c The project manager is the functional manager of the team d The project manager is accountable for the project and its delivery

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenWhat are the primary characteristics of a project a We can use projects to manage delivery of services b A temporary undertaking to create a unique product service or result c A regular operation or process that is critical to the business d A collection of related tasks managed together

Anatomy and Physiology
Embryo6 A person has risk factors for illness The nurse teaches about risk factors to OLL a Help the person form healthy practices Control the person s decisions b c Show that the person has been making bad choices d Earn the person s trust 7 Which is true a Nonverbal communication uses the written or spoken word b Verbal communication is the truest reflection of a person s feelings nlan c Body language cannot be controlled d Touch means different things to different people 8 You touch a person on the forearm and smile Which response shows the touch was received well a The person pulls the arm away b The person moves your hand off of the arm c The person pats your hand and smiles back d The person says ouch and grabs the arm 9 Which shows that you are listening a You sit with your arms crossed b You have eye contact with the person c You avoid asking questions

Anatomy and Physiology
Brainb Everything will be fine This is a good nursing center d Go ahead I m listening 13 Which is a barrier to communication a Focusing b 169H stand know Asking questions Talking a lot when others are silent c d Using familiar language 23V1TD380 14 A person wants care given at a certain time and in a certain way Nothing seems to please the person Which response is best a Please stop being so picky b I m sorry I don t have time for this c Please tell me what you would like done d You are never happy with what I do 15 A person is angry You should a nislax3 Put yourself in the person s situation gel art sdnesd

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyIdentify the highlighted tissue villus Submit Previous Answers Request Answer


Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenBody Oblique muscle layer Pyloric antrum Pylorus Greater curvature Fundus Left gastroepiploic vessels Rugae Anterior surface

Anatomy and Physiology
Nervous SystemA Moving to anoth stion 19 The nucleus accumb a controlling slee

Anatomy and Physiology
Nervous SystemMoving to anothe tion 6 neuron s resting pot a the electrical sig


Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenQuestion 4 2 points In addition to what smooth and card generate O 1 weight


Anatomy and Physiology
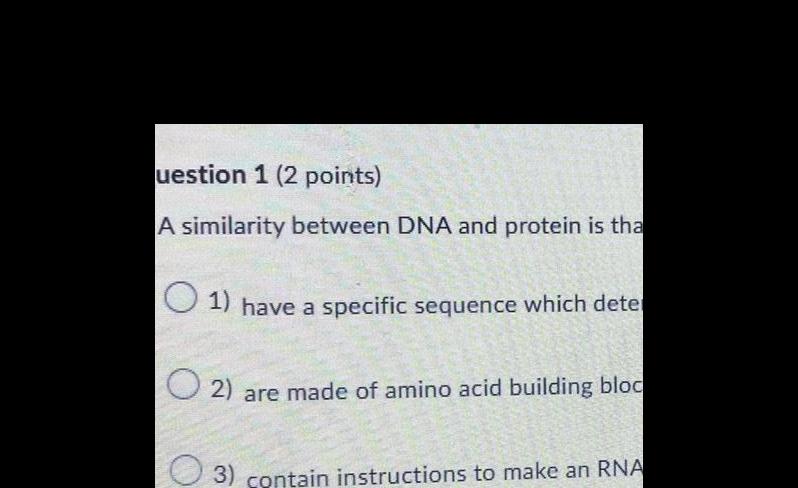
Introduction to Physiologyuestion 1 2 points A similarity between DNA and protein is tha 1 have a specific sequence which dete 2 are made of amino acid building bloc 3 contain instructions to make an RNA


Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyQuestion 10 2 points MARK ALL THAT APPLY Which of the disks 1 none of these answers

Anatomy and Physiology
BrainQuestion 13 2 points Saved During excitation of skeletal mus concentrations of sodium and cal O 1 sodium and calcium decre

Anatomy and Physiology
General Anatomy0 troponin L myosin tropomyosin actin on 16 2 points K ALL THAT APPLY Binding of neurotransmitter to channels on motor end es causes which ions to cross the membrane potassium 2 chloride 3 calcium 4 sodium

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyQuestion 17 2 points Which of the following has a head that moves during contraction O 1 myosin O2 actin 3 tropomyosin 4 troponin Question 18 2 points Binding of neurotransmitter to channels on motor end plates results in w channel gating 1 chemical O2 voltage

Anatomy and Physiology
General Anatomypotassium 2 sodium 3 calcium 4 chloride Question 20 2 points Which of the following prevents myosin from binding to actin 1 myosin 2 troponin 3 actin 4 tropomyosin

Anatomy and Physiology
Supexion 24 of the following is true about deliv outlines can have delivery cues

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I TractM Histology Digestive System Lab PAL Histology Digestive System Lab Practical Question 22 Identify the highlighted structure