Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Basic PhysicsThis section contains 35 SIN O 3T The period of oscillation of a magnet in earth s field is T The period of oscillation when an extra field twice of the earth s field is applied in the same direction is 2T Read More O 3T questions Each question has 4

Physics
Electric Field and Potential2 Electric field at a point on the axis of an electric dipole is E If strength of dipole moment and distance are doubled then new electric field at new point will be dipole is ideal 1 3 2 E 2 E4

Physics
Electric Field and Potential4 Electric potential in a region varies with distance as V 3x2 The electric field strength at a point P 2 4 2 m is V 1 12 along ve Y axis m V 2 12 m V 3 12 along ve X axis V 4 12 along ve Y axis m along ve X axis

Physics
KinematicsA boat is moving with a velocity 5kmph relative to water And water in a river is flowing with a velocity 3kmph The ratio of times taken by boat to cover same distance in downstream and upstream is A 4 1 B 1 4 C 5 3 D 3 5

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialThe electric potential V in volt in a region of space is given by V ax ay 2az where a is a constant given by a 1 25 x 10 V m What is the radius in m of the circle of the equipotential line corresponding to V 6250 V and z 2m Z
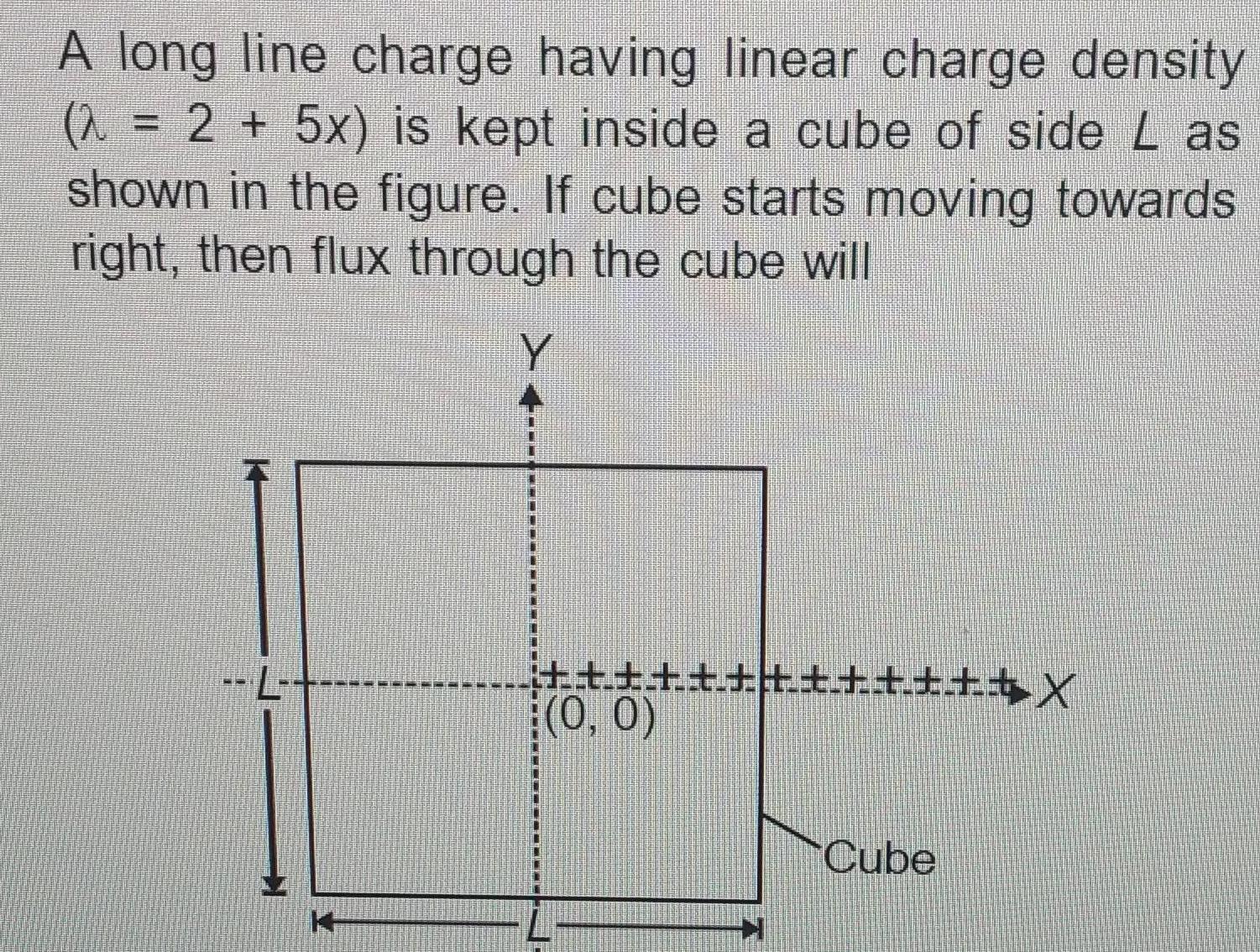
Physics
Gauss Law2 A long line charge having linear charge density 2 5x is kept inside a cube of side L as shown in the figure If cube starts moving towards right then flux through the cube will Y P 1 X 0 0 Cube
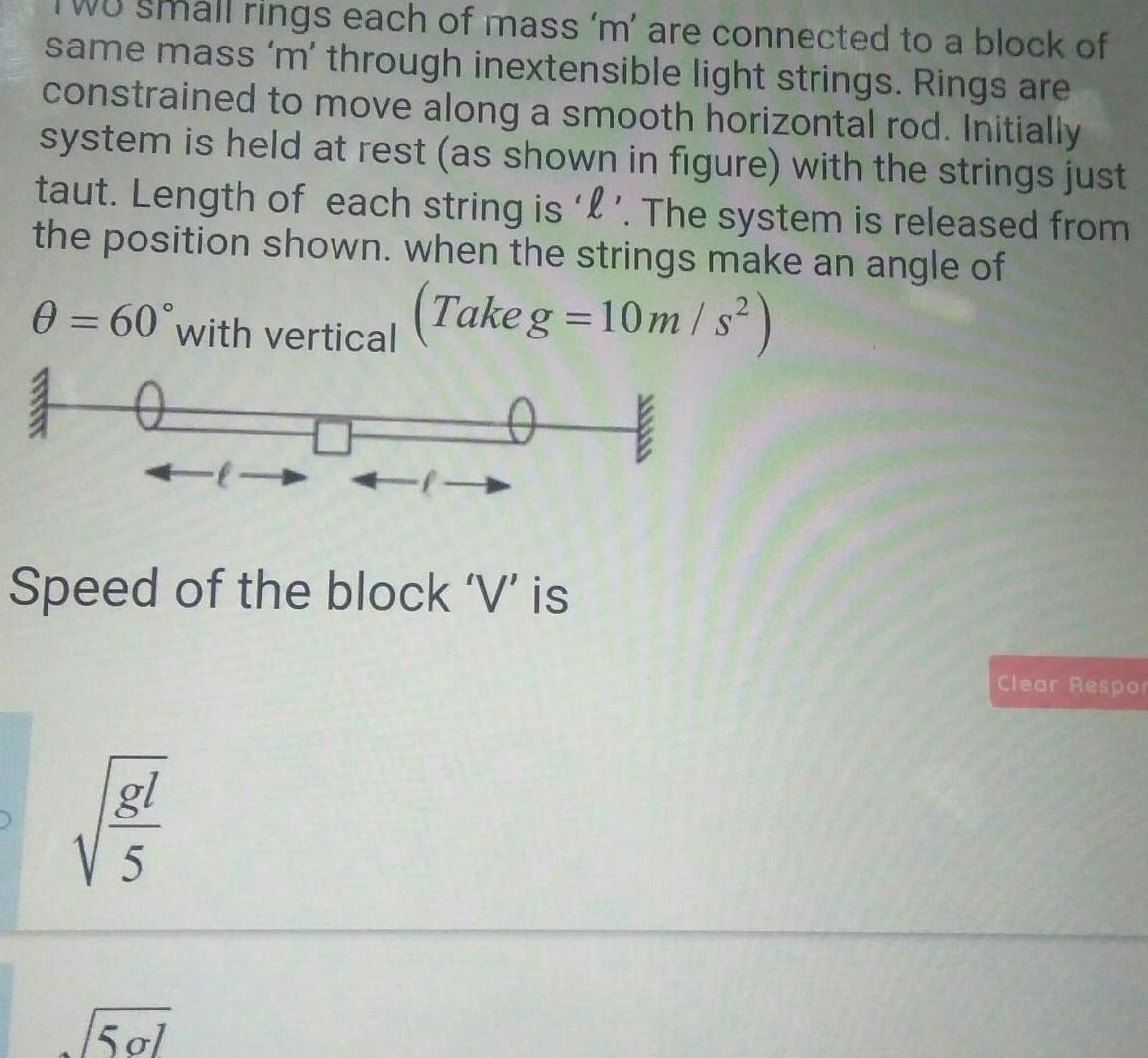
Physics
Simple harmonic motionrings each of mass m are connected to a block of same mass m through inextensible light strings Rings are constrained to move along a smooth horizontal rod Initially system is held at rest as shown in figure with the strings just taut Length of each string is l The system is released from the position shown when the strings make an angle of 0 60 with vertical Take g 10m s 10 t Speed of the block V is gl 505 15 gl Clear Respor

Physics
Magnetic Field54 A lona cylindrical conductor of radius R carries a current i as shown in figure The current density is a function of distance from the axis r according to j br where b is a constant Find an expression of the magnetic field B at a distance R measured from the axis 2 iemes Unbr 2 3 LD MobR 312 29

Physics
Electric Field and Potential21 Uniform electric field of strength 20 is present in a region as shown in the figure Points A and B are separated by 20 3 cm If potential at point A is 40 volt then potential at B is equal to A B 2013 cm 30 THER V E 20 m

Physics
CapacitorsThe time constant for a circuit containing 99 capacitance C and resistance R is t In this time an uncharged capacitor can be charged to about x per cent of the maximum charge 90 or a charged capacitor having charge q can be discharged to about y percent of q Then A x y 100 C x y 63 1 B x y 1 1 D x y 0 100

Physics
Kinematicsare projected horizontally with same speed v as shown in figure At the time when 2 touches ground at co ordinate L 1 m q h h m q 2 time elapsed T V x coordinate of 1 L x axis y coordinate of particle 1 is h h gL V2

Physics
Work, power & energyOne end of a block placed on a horizontal smooth surface is attached with a spring of force constant 100 N m Other end of the spring is attached with a wall as shown in figure Initially spring was in natural length Suddenly a constant horizontal force of 10N started acting on the block towards right and as a result the block started moving towards right The energy stored in the spring when the block stops for the first time is

Physics
Electric Field and Potential5 If W work is done in rotating a dipole in uniform electric field from its stable equilibrium position to an angle 30 then torque needed to hold this dipole at an angle 60 in the same electric field is 3W 1 2 3 3 3W 2 3 2 4 2 3 W 3 2 3 W 3

Physics
Magnetic Field6 Two coaxial circular loops 1 and 2 which form same semi vertical angle 0 at point O Same charges are uniformly distributed along the circumference of both the loops The loops are rotating with same angular velocity in same direction about their axis through centre of mass and perpendicular to their plane If B and B are magnetic field due to the loops 1 and 2 respectively then O X K 2x B 1 B 3 20 B B 2 8 W 1 1 1 00 2 4 B 1 B 2 B f B 4 2

Physics
Magnetic FieldFigure shows a uniform magnetic field B normally into the paper If the charge q is incident on the boundary MN at an angle 60 as shown then the deviation produced to the path of the charge on emergence is Region of magnetic field is finite upto the left boundary MN only 1 60 2 180 M X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X D q 60 X X X X X X X X X X X X XX X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X N 2 240 4 300

Physics
Basic PhysicsFor a body thrown horizontally from the top of tower h height v velocity of projection A the time of flight depends both on h and v B the horizontal range depends only on v but not on h C the time of flight and horizontal range depends on h but not on v

Physics
Basic Physics23 A 20 C charge is kept at centre of a square as shown in the figure The work done in moving a charge 2 C from point D to B is 7 C 1 18 x 10 J 3 72 10 3 J D 1 A 20 C 2 36 10 J 4 Zero

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentA triangular ent carrying loop i is placed in a uniform and transverse magnetic field as shown in the figure X A 30 C F 1 F 3 120 X X 30 X xB If the magnetic force on the sides AC CD and DA respectively have a magnitude of F F and F3 then 2 F and F have an angle of 120 between them 3 F 3 F

Physics
Basic Physicsperson swims at 30 with normal to river flow to meet target on reaching opposite point The ratio of river water velocity to the person s velocity is A 3 2 B 2 3 C 1 2 L 1

Physics
Basic PhysicsA small block of mass m 1kg is attached with one end of the spring of force constant K 100Nm Other end of the spring is fixed to a rough plane having coefficient of friction 0 2 The spring is kept in its natural length by an inextensible thread tied between its ends as shown in Figure If the thread is burnt calculate the elongation of the spring when the block comes to rest for the first time g 10m s 0 8 37 4 cm 8 cm 12 cm Clear Respc

Physics
Basic Physics28 Select incorrect statement 1 Similar point charges always repel each other 2 Similar charged bodies always repel each other 3 Similar charged bodies may attract each other 4 Clouds get charged by friction

Physics
KinematicsA river is flowing from west to east at a speed of 8 m s A man on the north bank of the river capable of swimming at 16m s in still water wants to swim across the river in shortest time He should swim in a direction A Due south B Due north

Physics
Basic PhysicsA current carrying conductor of length I is bent into two loops one by one First loop has one turn of wire and the second loop has two turns of wire Compare the magnetic fields at the centre of the loops

Physics
ExperimentsThe displacement of a particle along the x axis is given by x asin cot The motion of the particle corresponds t 2 simple harmonic motion of frequency 30 2r AIPMT 2 1 simple harmonic motion of frequency art 3 non simple harmonic motion 4 simple harmonic motion of frequency w 2m

Physics
Basic PhysicsA particle at end of a spring executes simple harmonic motion with a period t while the corresponding period of another spring is t If two springs are connected in series then time period is T them which one is true Consider same mass of particle in all cases A B T t t2 T 1 1 CT t 1 T Correct Answer My Answer

Physics
Simple harmonic motion26 Average velocity of a particle executing SHM in one complete vibration is any velocity NEET 2019 2 Aw 2 zero 3 Aw Aw 4 2

Physics
Basic Physicsthe radial velocities of distant galaxies Example 10 1 What speed should a galaxy move with respect to us so that the sodium line at 589 0 nm is observed at 589 6 nm Av ll changes in v and 2 For

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle of mass 1kg is free to move along x axis under influence of a conservative force The potential energy function for the particle is U x 5x J If the total mechanical energy of the particle is zero Particle will remain between 5 m to 5 m 5 2 m to 5 2 m 2 m to 2 m Clear Resp

Physics
Basic Physics0 Stal electric flux through a closed surface enclosing a charge is equal to 1 Eo times the magnitude of the charge enclosed Assertion A Positive charge always moves from a higher potential point to a lower potential point Reason R Electric potential is a vector quantity

Physics
Optical Instruments2 Assertion A Focal length of a spherical mirror does not dpend on the material from which mirror is made but same for the lens depends on the material of lens Reason R law of reflection does not dpend on material and surrounding but law of refraction depends on refractive index of th materials Section R

Physics
Kinematicsparticle of mass m moves along a circle of radius r with constant tangential accelerati kinetic energy E of the particle becomes three times by the end of third revolution a eginning of the magnitude of tangential acceleration is celeration E 6 rm B C A E 12 rm E 24 rm E 3 rm D eef

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialThe electric field lines in a region is shown in the figure EA EB and Ec are the electric field strength at points A B and Crespectively Then B O EA EB Ec O EC EA EB O EA EC ER

Physics
Basic PhysicsTwo conducting plates have charge 3Q and 2Q and separation between them is x then potential difference between the two plates is plate area is A 3Q 2Q 1 A o 21 X X Q 2 2A o 3Q 4 X

Physics
Basic PhysicsTwo forces act on an object of mass M 4 00 kg as shown in the figure Because of these forces the object experiences an acceleration of a 8 00 m s in the positive x direction If 0 30 0 calculate the magnitude of F2 given that F 20 0 N F N M 0 1

Physics
KinematicsA car of mass m is driven with acceleration a along a straight level road against a constant external resistive force R When the velocity of the car is V the rate at which the engine of the car is doing work will be fed ER five V A RV B ma V a C R ma V D ma R V

Physics
Electric Field and Potential3 Which of the following represents correct variation of electric potential due to an ideal electric dipole at large distance r from it 1 V 2 3 V x 1 r 2 Vor 4 V 1 2
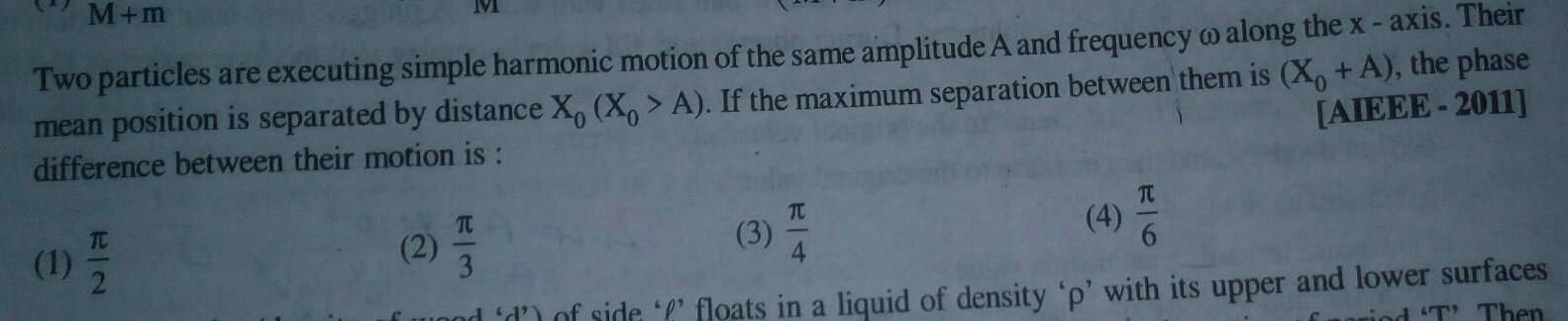
Physics
Simple harmonic motionM m Two particles are executing simple harmonic motion of the same amplitude A and frequency o along the x axis Their mean position is separated by distance X X A If the maximum separation between them is X A the phase difference between their motion is AIEEE 2011 1 7 2 M 2 T 3 3 TC 4 TU and d of side floats in a liquid of density p with its upper and lower surfaces rind T Then

Physics
Basic Physics21 An object 1 5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement with a concave lens the distance between two lenses is 8cm The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40cm Determine the magnification produced by the two lens system and the size of the image The focal length of concave lens
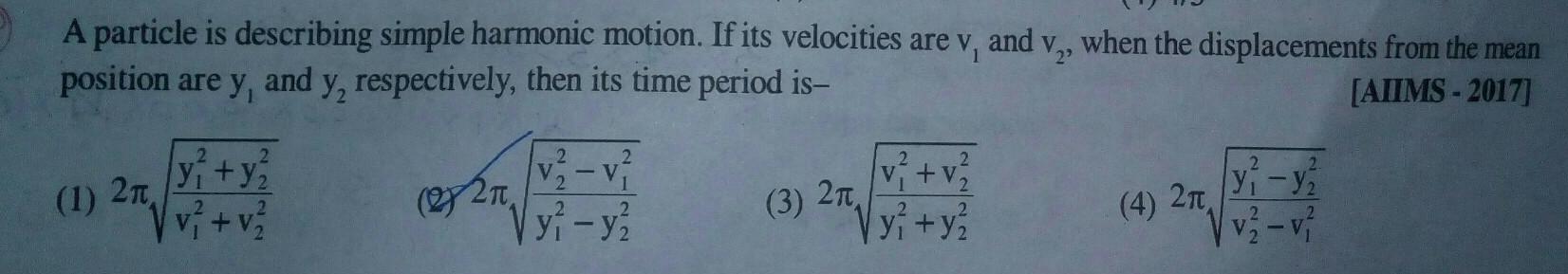
Physics
Simple harmonic motionA particle is describing simple harmonic motion If its velocities are v and v when the displacements from the mean position are y and y respectively then its time period is AIIMS 2017 1 2n 2 2 y y v v 22 2 2 v v y y 3 2 2 v v 2 y y 4 2 y y v2 v

Physics
Kinetic Theory of GasesAt what temperature is the R M S Velocity of Hydrogen molecule equal to that of a molecule at 47 C Molecular weight of hydrogen A 20 K B 80 K Molecular weight of oxygen 3 C 60 K D 40 K

Physics
CapacitorsCells in Series and Parallel Kirchhoff s 16 The charge in the 2 F capacitor at steady state is 1 Zero 2 2 C 3 4 C 4 6 C 1 V www PA Medal SE www 20 Division Aatucational

Physics
Work, power & energyA particle is released from rest at origin It moves under influence of potential field U x 3x kinetic energy at x 2 is fog feen arren fagfaff af U x 3x i fx fr A 2 J B 1 J C 1 5 J D O J Your Answer

Physics
Simple harmonic motionThe displacement of a particle from its mean position in m is given by y 0 2 sin 10nt 1 5p cos 10nt 1 5n The motion of particle is A B C Periodic but not SHM non periodic Simple harmonic motion wit S Correct Answer
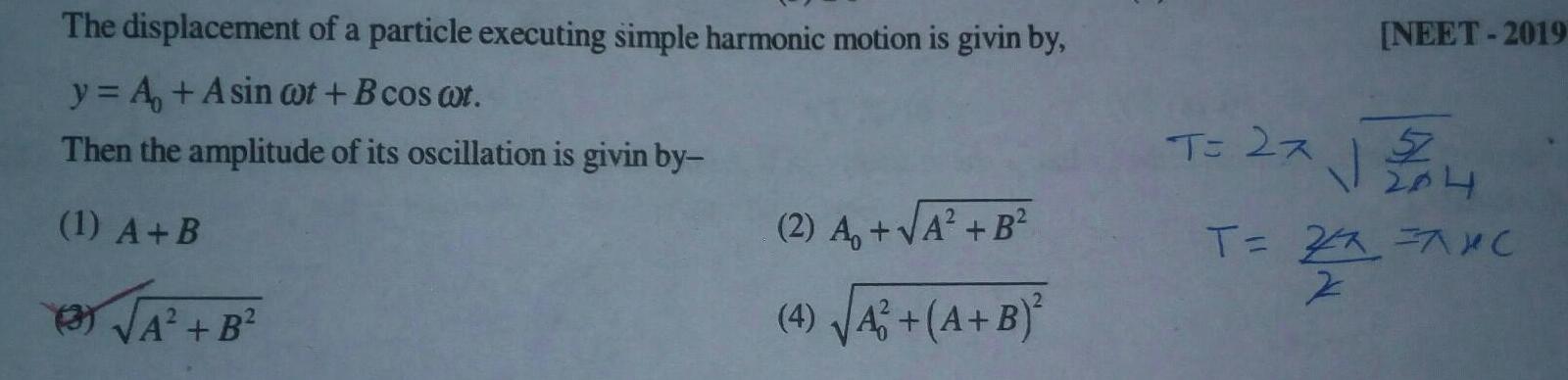
Physics
Simple harmonic motionThe displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion is givin by y A Asin wot B cos wt Then the amplitude of its oscillation is givin by 1 A B B 2 A A B 4 A A B NEET 2019 T 2x 27 2 04 T 27 7XC Z

Physics
Work, power & energyF 2x 3x 2 Choose correct option F 2x 3x 2 Hafa f A x 1 2 is position of stable equilibrium x 1 2fef B x 2 is position of stable equilibrium fref C x 1 2 is position of unstable equilibrium 3ff i x 1 2 D x 2 is position of neutral equilibrium fef Your Answer B

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialLinear charge density on circumference of half ring is If a particle of mass m and charge is kept at the centre of the ring then acceleration of particle is R radius of half ring Ay 1 3 xxxxx xx 1 noi 2 Rm xxxx 1 290 4 Rm 90 R m 2 a 4 a X 1 290 2 Rm 1 290 4TE Rm

Physics
Current ElectricityIn the circuit shown R 9 Q R 2 30 Q R 3 15 Q2 and the emfs 1 29 V 2 10 V and 3 15 V Calculate 13 Your result must be in Amperes and include 2 digit after the decimal point Maximum of 5 of error is accepted in your answer 1 R ww 1 E3 T

Physics
Optical InstrumentsAssertion A A reflecting type telescope is preferred over refracting type in astronomy Reason R reflecting type telescope is free from chromatic aberration and parabolic surfaces are us to avoid spherical aberration

Physics
Work, power & energyA uniform cylinder of mass m and length having area of cross section a is suspended lengthwise with the help of a massless spring of constant k The cylinder is half submerged in a liquid of density p A small push and release makes it vibrate with small amplitude The frequency of oscillation is kang A m apg 1 k apg

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialA charge q is kept in a closed surface as shown If flux through each plane surface is o then flux through curved surfaces is 1 3 q 380 9 30 EO q 2 4 9 20 280 q d GO