Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Unit & DimensionsIn the cube of side a shown in the figure the vector from the central point of the face ABOD to the central point of the face BEFO will be Z JEE Main 2019 a a i k Jby a c a k 1 d a k A KD X B 4016 O a 0 E Ha a a 2 2 F Y

Physics
Electromagnetic wavesA car is traveling 32 m s down a level road where Earth s magnetic field 5 0 x 10 5 T points north with an angle of 38 What is the maximum induced emf by the car s 63 cm antenna 6 01 x 10 4 V 5 50 x 10 4 V 7 94 x 10 4 V 5 75 x 10 4 V

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe square of the resultant of 4N and 3N exceeds the square of the resultant of the two forces by 12 when they are mutually perpendicular The angle between the vectors is 1 30 2 60 4 120 3 90

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentA charged particle is projected in air horizontally near the earth s surface at a point where horizontal component of magnetic field s absent Considering the effect of vertical omponent of the earth s magnetic field and the gravitational field due to the earth the path of the particle will be 1 circular 3 straight line 2 helical 4 parabolic

Physics
Kinetic Theory of GasesThe figure shows the plot of M 1 T T 3 T T PV vs P for oxygen gas at two different temperatures then nT PV nT 2 P more corved le 2 T T 1 4 May be 1 2 Otroch Tower 8 Pusa Road New Delhi 110005 PH

Physics
Basic Physics4 Internal energy per mole 23 The internal energy of 10 g of nitrogen at N T P is about 24 1 2575 J 3 3721 J The mean free path of a molecule of He gas is 2 2025 J 4 4051 J

Physics
KinematicsThe position of a particle moving along the X axis is given by X 18 0 t 2 2 0 t 3 where X is in meters and t in seconds What is the position of the particle when it achieves its maximum speed in the positive X direction O a 82 0 m O b 116 m O c 108 m O d 64 m O e 120 m

Physics
GravitationA ball is dropped down from the roof of a building and stimulus three are there ball is thrown in a horizontal direction when will the balls reach the ground a same time but different places b same time and same place

Physics
Unit & Dimensions4 The resultant of two vectors P and Q is R If the magnitude of Q is doubled the new resultant becomes perpendicular to P Then the magnitude of R is Kerala PET 2009 a P Q c P e P Q Lib Q d P Q 2

Physics
Electromagnetic waves3 The maximum electric field at a distance of 10 m from an isotropic point source of light is 3 0 Vm Calculate a the maximum value of magnetic field b average intensity of the light at that place and c the power of the source

Physics
Basic Physics2 A 20 kg cotton warp having moisture regain of 8 5 is sized with a paste of 15 concentration If a 10 add on the bone dry weight of the yarn is aimed then what should be the wet pick up How much water has to be evaporated so as to leave 8 moisture content in warp and size film Solution

Physics
Current ElectricityPre 13 The brightness of light bulb when a heating appliance is switched on will 1 decrease for non ideal source but remain same for ideal source 2 Increase for non ideal source but remain same for ideal source 3 Remain same for both ideal and non ideal source 4 Remain same for non ideal source but decrease for ideal source

Physics
Newton's law of motionA body hangs from a spring balance supported from the roof of an elevator a If the elevator has an upward acceleration of 2 45 m s and the balance reads 50 N what is the true wei of the body b Under what circumstances will the balance read 30 N c What will the balance read if the elevator cable breaks

Physics
Properties of matterTwo metal rods are fixed end to end between two rigid supports as shown in figure Each rod has length L and area of cross section is A When the system is heated up the junction between the rods does not shift y and y are young s modulus of materials o rods a and a are coefficients of linear expansion Find the value of THE M L a Y L a Y y 02 ROUP

Physics
Newton's law of motion2 A particle moves towards east with velocity 5 m s After 10 seconds its direction changes towards north with same velocity The average acceleration of the particle is CPMT 1997 AFMC 1999 Pb PET 2000 JIPMER 2001 MP PMT 2013 a Zero 1 c m s N E LIOT J2m1 8 1 d m s S W m s N W

Physics
Electric Field and Potential2 2 Initial charges with proper sign on the plates of two identical capacitors each of 1 F are as shown When both and S are closed the potential difference between A and B will S finally become A 2V R C 6V S A 2 C 4 C 6 C 12 C 6 CIF Figure 2 236 B 4V D OV S B

Physics
Work, power & energyA neutron of kinetic energy K undergoes a head on collision with a hydrogen atom at rest in ground state and is free to move k Neutron Then mark the correct option s H H atom at rest For K 20 4eV collision is perfectly elastic For K 20 4eV collision is perfectly inelastic For K 2 20 4eV collision may be elastic or it may be perfectly inelastic For K 24 18eV collision may be elastic inelastic or perfectly inelastic

Physics
GravitationA ring of radius R 8m is made of a highly dense material Mass of the ring is mR 2 7 x 10 kg distributed uniformly over its circumference A particle of mass dense mp 3 x 10 kg is placed on the axis of the ring at a distance x 6m from the centre Neglect all other forces except gravitational interaction Determine speed in cm sec of the particle at the instant when it passes through centre of ring

Physics
Current Electricity5 In a potentiometer the null point is received at 7th wire If now we have to change the null point at the 9th wire what should we do 1 Attach resistance in series with cell of secondary circuit 2 Increase resistance in main circuit 3 Decrease resistance in main circuit 4 Decrease applied emf

Physics
Thermal Expansion64 Thermal Properties of Matter The coefficient of linear expansion of a crystalline substance in one direction is 2 10 C and in every direction perpendicular to it is 3 x 10 4 PC The coefficient of cubical expansion of crystal is equal to 1 5 x 10 4 C 2 4 x 10 4 C

Physics
Unit & DimensionsTwo vectors A and B have equal magnitudes The magnitude of A B is n times the magnitude of A B The angle between A and B is JEE Main 20191 a sin b cos Vc cos 2 1 1 d sin n n 1 n 1

Physics
Current ElectricityA bistable multivibrator with a saturation voltage 5V is shown in the diagram The positive and negative threshold at the inverting terminal for which the multivibrator will switch to the other state are a 5 11V 0 01 F b 10 11 2MQ 2MQ 200k to c SV d 11V

Physics
Kinematicsof a metre resistance two The resistance 3 17 The potential difference between points A and B in the circuit shown in figure 3 318 will be esistance A 1V C 3V 2592 ww 1592 B 10V 2 50 HH Figure 3 318 5V 2 592 B 2V DNone of these

Physics
KinematicsA particle moves from the point 2 01 4 0 m at t 0 with an initial velocity 5 01 4 0 ms It is acted upon E a constant force which produces a constant acceleratic 4 01 4 0 ms 2 What is the distance of the particle from the origin at time 2s La 20 2m JEE Main 2019 b 10 2m 1 16

Physics
Basic Physics31 A cylindrical rod has temperatures T and T at its ends The rate of flow of heat is Q cal s If all the linear dimensions are doubled keeping temperatures constant then rate of flow of heat Q will be 1 4Q Q 3 2 20 Q 4

Physics
Basic Physics9 In the figure the bigger block A has a mass of 40 kg and the upper block B is of 10 kg coefficient of friction between all surfaces of contact is 0 1 Choose the correct options Segr of string are perfectly parallel and perpendicular to the incline plane Use g 10m s 4x10x10 10 A magnitude of acceleration of B is twice of magnitude of acceleration of A 62 m s 25 C B acceleration of A is C Tension in the string is 92 8 N 124 m s 25 D acceleration of B is

Physics
Radioactivity15 Find the focal length of a plano convex lens when curved surface is silvered and the object is in front of plane surface A f behaves as concave mirror behaves as concave lens C R B D f behaves as convex mirror behaves as convex lens R 24
Physics
Gauss Law55 A circular plane sheet of radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform electric field of 5 x 105 N C making an angle of 60 with the field The electric flux through the sheet is a 1 36 x 102 N m C 1 b 1 36 x 104 N m C c 0 515 x 102 N m C d 0 515 x 104 N m C 1

Physics
Center of mass and momentum7 Force F is acting on a particle of mass m as shown in the force time curve The change in momentum of the particle over the time interval of 0 to 8 s is F N 6 3 0 3 2 4 6 8 time s D

Physics
Kinematics2 A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm Initially the block B is near the right end of block A as shown in the figure F 10 N B A A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A Assuming all the surfaces to be smooth find the time elapsed before the block B separates from block A

Physics
Kinematics4 Two blocks of masses m 2 0 and m 1 0 kg are in contact on a frictionless table A horizontal force N 3 0 N is applied to mass m m1 m Find the force of contact between m and m What would be the force of contact if force F is applied to m
Physics
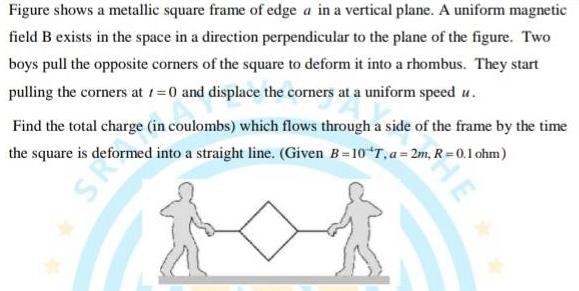
Gauss LawFigure shows a metallic square frame of edge a in a vertical plane A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the figure Two boys pull the opposite corners of the square to deform it into a rhombus They start pulling the corners at 1 0 and displace the corners at a uniform speed u Find the total charge in coulombs which flows through a side of the frame by the time the square is is deformed into a traightline Giv en 5 107 28 0 1 km HE

Physics
Capacitors2 8 A capacitor of capacitance of 2 F is charged to a potential difference of 200V after disconnecting from the battery it is connected in parallel with another uncharged capacitor The final common potential is 20V then the capacitance of second capacitor is A 2 F C 18 F B 4 F D 16 F

Physics
Basic Physicspotential energy at any palace we ca nnot calculate potential energy at sp ecific space So give option a I think option d is right A positive charge is moved from low potential point A to a high potential point B Then the electric potential energy Increases Decreases Will remain same 5

Physics
GravitationA glass block measured 5 cm x 5 cm x 15 cm When block stands on one of its smaller faces and viewed directly from above it appear to be almost a cube Then find the refracting index of block

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialIf the potential difference of Coolidge tube producing X ray is increased then choose the correct option s The interval between Aka and Akp increases The interval between Aka and increases increases The interval between Akp and o does not change Here is cutoff wavelength and ka and Akp are wavelength of a and 2 characteristic X rays

Physics
Current ElectricityTwo cells of unequal emf E and E having 2 internal resistance r and r are connected as shown in figure E r E 1 Potential difference across any of the cell cannot be zero 2 Potential difference across cell of smaller EMF may be zero 3 Potential difference across cell of larger EMF may be zero 4 Potential difference can be zero only if EMF of both cell are same at 371 1

Physics
Kinetic Theory of Gases3 3 4 6 23 If a gas has degree of freedom the ratio of the specific heats of the gases 1 3 1 f 2 C C 2

Physics
Simple harmonic motionTwo masses m and m are suspended together by a massless spring of constant K as shown in figure When the masses are in equilibrium m is removed without disturbing the system Find the angular frequency and amplitude of oscillation of m2

Physics
Kinematicsof a metre resistance e two The resistance 3 17 The potential difference between points A and B in the circuit shown in figure 3 318 will be esistance A 1V C 3V 2592 ww ww 1502 B 10V 2 50 Figure 3 318 HH 5V 2 502 B 2V DYNone of these

Physics
Frictionthe bigge A Sh wedge of mass M slides or wedge initially resting on the smooth horizonta ground as shown in the figure The mass of the bigger wedge is 6M When the smaller wedge reaches the base of the bigger wedge the distance move by the bigger wedge is the fi JEE Fou 1 L M 21 6M 4L 2 4L 5 31

Physics
Magnetism and Matter4 Any value Two identical bar magnets each of same length and magnetic moment one bent into a semicircular are placed as shown If the angle made by the resultant magnetic moment with the magnetic axis of semicircular arc is 0 then 1 tane 1 3 tane 1 N SS 0 63 2 tane 1 57 4 tan0 0 5 2M E N 17 ja 9 12 Ho 3M 4 r 2M 4M 2

Physics
Kinetic Theory of GasesA box of negligible mass containing 2 moles of an ideal gas of molar mass M and adiabatic exponent y moves with constant speed v on a smooth horizontal surface If the box suddenly stops then change in temperature of gas will be 1 Y 1 MV 4R Mv 3 2 Y 1 R 2 4 YMv 2R Y 1 Mv 2R 5

Physics
Basic PhysicsTwo parallel conductors carrying current in the same direction attract each other while two parallel beams of electrons moving in the same irection repel each other Which of the ollowing statements cannot be the reason for his 1 The conductors are electrically neutral 2 The conductors produce magnetic fields on each other 3 The electron beams do not produce magnetic fields on each other The magnetic forces caused by the electron beams on each other are weaker than the electrostatic forces between them 8 A 1 2 Ach ch 3 4 MALTA Y GRI ala id fee

Physics
Magnetic FieldThe mean of marks obtained in an examination by a group of 100 students was found to be 49 96 The mean of the marks obtained in the same examination by another group of 200 students was 52 32 Find the mean of the marks obtained by both the groups of students taken together An assesses depreciated the machinery of his factory by 10 each in the first two years and by 40

Physics
Basic PhysicsA compartment of a train is lit by 20 identical 8 bulb in series one of the bulbs fuses and is removed from the chain The remaining bulbs now light the room The light in the compartment will 1 Increases 2 Decreases 3 Neither increases nor decreases 4 None Kirchoff s voltage law in a circuit indicates 9

Physics
Basic PhysicsMCQs 1 A man of 60 kg weight is standing at rest on a platform He jumps up vertically a distance of 1 m and the platform at the same instant moves horizontally forward with the result that the man lands I meter behind the point on the platform where they took the jump the total work done by the man at the instant he lands is a 300 J b 150 J c 600 J d zero

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe molar specific heat at constant pressure of an ideal gas is 7 2 R The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume is 2 97 87 4 7557

Physics
Basic Physics4 None of the above 20 If charges moved without collisions through 20 the conductor their kinetic energy would also change so that the total energy is 1 Changed 3 Doubled 2 Unchanged 4 Halved

Physics
KinematicsA car is moving on a straight road covers one third of the distance with a speed of 20 km h and the res a speed of 60 km h The average speed of the car is 1 40 km h 3 36 km h 2 50 km h 4 55 km h