Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Electromagnetic InductionA 6 pole 50 Hz 3 phase induction motor running on full load develops a useful torque o 160 Nm when the rotor emf makes 120 complete cycles per minute Calculate the shaft power output If the mechanical torque lost in friction and that for core loss is 10 Nm Compute a the copper loss in the rotor windings b the input to the motor and c the efficiency The total stator loss is given to be 800 W

Physics
Basic PhysicsIn a situation the contact force by a rough horizontal surface on a body placed on it has constant magnitude if the angle between this force and the vertical is decreased the frictional force between the surface and the body will 1 increase 2 decrease 3 remain the same 4 may increase or decrease A 40 kg slah rests on a frictionless floor A 10 kg block rests on top of the slab The static coefficient of friction

Physics
FluidsAir is blown through a hole a closed pope containing liquid Then the pressure will 1 Increase on sides 2 Increase downwards 3 Increase in all direction 4 Never increases

Physics
Simple harmonic motionA particle is doing SHM with a time period of 0 80 sec and amplitude of 10 cm At t 0 it is 5 0 cm to the left of equilibrium and moving to the left Then at t 2 0 sec Its position is 5 0 cm to the right of equilibrium It is moving towards right Its position is 5 0 cm to the left of equilibrium

Physics
Frictiont 0 98 m s m s A body A of mass 1kg rests on a smooth surface Another body B of mass 0 2 kg is placed over A as shown The coefficient of static friction between A and B is 0 15 B will being to slide on A if a pulled with a force greater than 1 764 N B A 2 0 1764 N

Physics
Friction1 0 02 2 0 03 A block rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of 30 with the horizontal The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is 0 8 If the frictional force on the block is 10 N the mass of the block in kg is take g 10 m s AIEEE 2004 2 0 2 4 0 3 1 6 4 2 5 AIEEE 2005 longed at rest on a 45 incline and then slides a distance d The time taken to slide is n times incline The coefficient of friction is

Physics
Circular MotionD Og mass on a 20 cm long string oscillates as a pendulum It has a speed of 0 28 m s as it passes through the lowest point What maximum angle in rad does the pendulum reach g 9 8 m s Assume the motion is simple harmonic motion

Physics
Friction3 936 ms 2 2 936 ms 3 ms A gramophone record is revolving with an angular velocity o A coin is placed at a distance r from the of the record The static coefficient of friction is u The coin will revolve with the record if AIPMT 2 1 r go ug 3 TS H 4 r2 r ug w 2 ug Ona leyel circular track of radius R If u represents the static friction between in circular motion is given by AIPMT Main 20

Physics
Basic Physicsgu A block of mass m is in contact with the cart C as shown in the figure The coeff tion between the block and the cart is u The acceleration a of the cart that will prevent the block from AIPMT 2010 falling satisfies mg 5 0 g a 3 B m 4 a 201 g

Physics
Frictionn The upper half of an incline plane with inclination is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough A body starting from rest at the top will again come to rest at the the bottom if the coefficient of friction for the lower AIEEE 2005 half is given by 1 2 tan 2 tan 3 2 sin 4 2 cos ving on a straight road with a speed of 100 m s The distance at which car can be stopped AIEEE 2005

Physics
Friction42 0 2 4 0 3 1 6 A smooth block is released at rest on a 45 incline and then slides a distance d The time taken to slide is n times as much to slide on rough incline than on a smooth incline The coefficient of friction is AIEEE 2005 1 1 2 2 n 2 H 3 1 4 H n on is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough A body 2

Physics
Basic PhysicsPCP 3 x 1 A block of mass m is placed on a surface with a vertical cross section given by y 6 0 5 the maximum height above the ground at which the block can be placed without slipping is 3 1 8 m 2 m m 4 2 If the coefficient of friction is

Physics
FrictionA block W is held against a vertical wall by applying a horizontal force F The minimum value of F needed to hold the block is if u 1 1 Less than W 3 Greater than W 2 Equal to W 4 Data is in insufficient rough horizontal plane is acted upon by a horizontal force P and another force

Physics
Geometrical OpticsA student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment At the end of the experiment on analysing the measurements which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw A Zi Ze Zr B Zi Ze r C Zi Ze Zr D ZiZe r

Physics
Newton's law of motion3 Greater than W 4 Data is in insufficient A block of mass m lying on a rough horizontal plane is acted upon by a horizontal force P and another force Q inclined at an angle to the vertical The block will remain in equilibrium if the coefficient of friction between and the surface is

Physics
Kinetic Theory of GasesIn an isobaric process of a monoatomic gas of heat is added to n moles of the gas to increase temperature from T to T The amount of work done by the gas in the process is 1 20 J 3 60 J 2 30 J 4 40 J 00 for an ideal

Physics
Newton's law of motion1 100 m 2 400 m The minimum force required to start pushing a body up a rough frictional coefficient u inclined plane is F while the minimum force needed to prevent it from sliding down is F If the inclined plane makes an angle from AIEEE 2011 the horizontal such that tan 0 2u then the ratio F F 1 I 2 2 3 3 is 4 4 Main I NEET AIIMS 29

Physics
Transmission of heat56 A composite slab consists of two different materials having equal cross sectional area but lengths in the ratio 2 1 and thermal conductivity K and 3K respectively as shown in figure The equivalent thermal conductivity of slab is 1 3 9K 7 3K A K 2L 2 4 3K 3K 2 3K L

Physics
Optical InstrumentsA student used a device X to obtain focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen S as shown below in the diagram Select the correct statement about the device X S 8 cm A This device is a concave lens of focal length 8 cm B This device is a convex mirror of focal length 8 cm C This device is a convex lens of focal length 4 cm D This device is a convex lens of focal length 8 cm
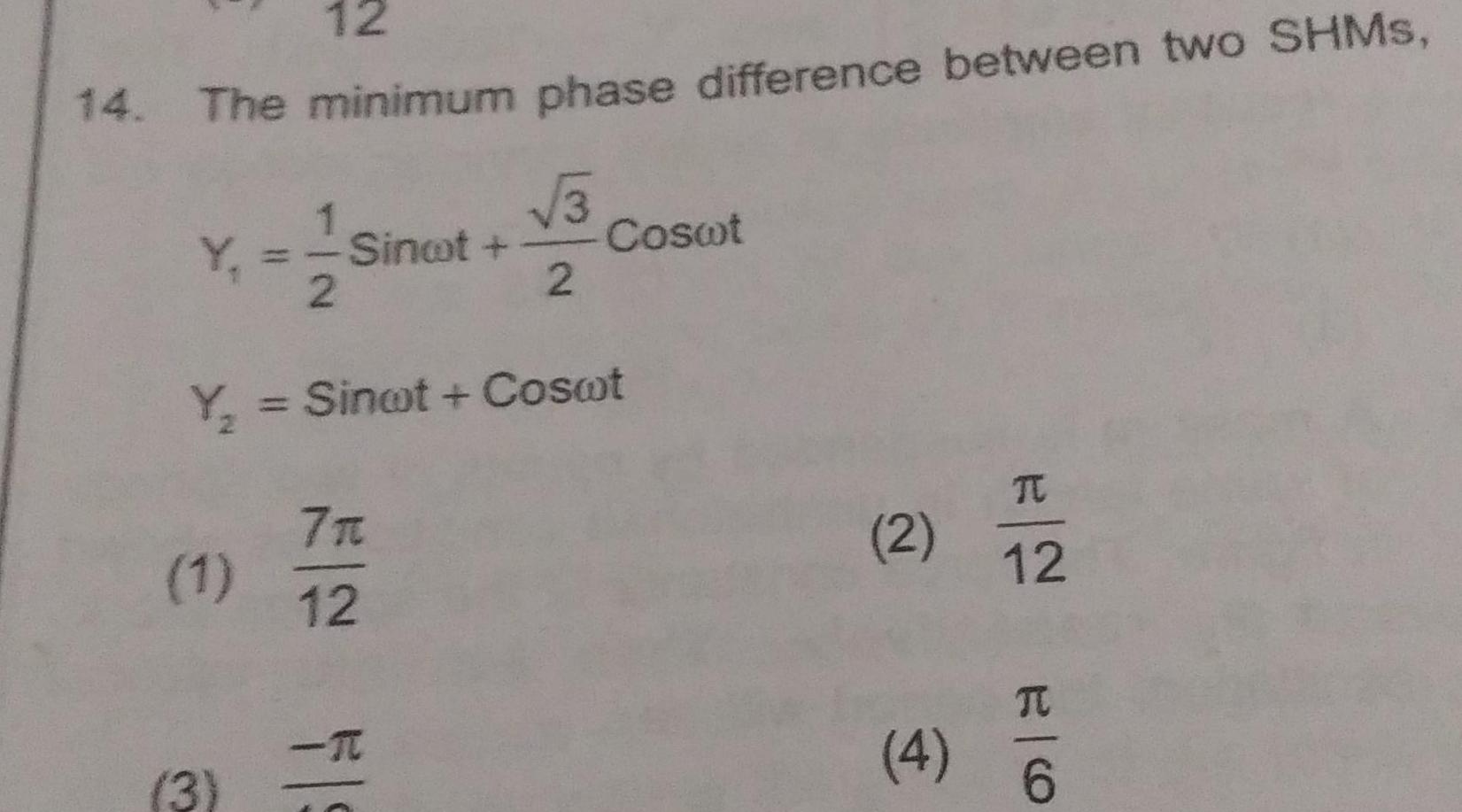
Physics
Simple harmonic motion12 14 The minimum phase difference between two SHMS 1 Y Sinot 2 1 Y Sinot Coswt 3 E FS 7 3 2 12 Coswt 2 4 TC 12 E O TU 6

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentThe magnetic circuit of Fig 2 10 has cast steel core The cross sectional area of the central limb is 800 mm and that of each outer limb is 600 mm Calculate the exciting current needed to set up a flux of 0 8 mWb in the air gap Neglect magnetic leakage and fringing The magnetization characteristic of cast steel is given in Fig 2 16 1 400 mm I 500 turns T L Fig 2 10 1 mm 160 mm I I 400 mm 1 IN novatio

Physics
FrictionA plank with a box on it at one end is gradually raised about the other end As the angle of inclination with the horizontal reaches 30 the box starts to slip and slides 4 0 m down the plank in 4 0 s The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the box and the plank will be respectively NEET 2015 1 0 5 and 0 6 2 0 4 and 0 3 mg 3 0 6 and 0 6 4 0 6 and 0 5

Physics
FrictionA block A of mass m rests on a horizontal table A light string connected to it passes over a frictionles pully at the edge of table and from its other end another block B of mas m is suspended The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block A is sliding on the table the tension in the strng is NEET 2015 m m 1 g m m 1 2 m m 1 g m m 3 m m g m m 4 m um g m m

Physics
Basic Physics12 Three identical particles each of mass m are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side l The work done by external force to increase the sides of triangle from to 2l is 1 3 3GM l 3GM 2 3 3GM 2l 3GM

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialD A nonconducting sphere of radius 10 cm is charged uniformly with a density of 100 nC m What is the magnitude of the potential difference between the center and a point 4 0 cm away 12 V 6 8 V C 3 0 V d 4 7 V 22V a b

Physics
Properties of matter3 A steel ring of radius r and cross sectional area A is fitted on to a wooden disc of radius R R r It Young s modulus of steel is Y then stress in the steel ring is 1 3 RY r 2 4 R ry r F y

Physics
Kinetic Theory of GasesAn ideal gas heat engine operates in a Carnot cycle between 227 C and 327 C It absorbs 6 kcal at the higher temperature The amount of heat in kcal converted into work is equal to Question Type Single Correct Type 1 5 2 3 5 3 2 8

Physics
Transmission of heat7 Figure shows a composite wall made of two walls A and B each of equal area and thickness Ratio of thermal conductivity of A and B is 3 2 Temperature of the common face is 1 30 C 3 35 C A B 1 40 C 20 C 2 32 C 4 37 5 C

Physics
Thermodynamics5 gm of ice at 0 C is mixed with 1gm 100 C The final temperature and composition of th mixture is 1 Water at 60 C 2 Water at 40 C 3 2gm water at 100 C and rest as steam 4 2gm water at 0 C and rest ice X

Physics
Newton's law of motion1 3 2F ELE m 3 Zero F 2m 0000000 m vovovor 4 Which among the following is correct for conservative forces Work done by a conservative force in a closed path is 1 Positive 2 Zero 3 Negative 4 All of these are possible 10 A spring of spring constant k is compressed by an amount of x and a mass m is just placed in contact with it and released Calculate minimum value of x for which the mass m completes the vertical circle in the circular track 1 2gR m m Natural length position F 2 smooth 5gR m k 2 3 5gR 4 None of these k Two blocks in contact with each other are being pushed by a external agent as shown 1 3 14 m F m m 3 m m m 12 A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path o fixed radius r such that its centripetal acceleration 1 Vo 3 a is varying with time as a k rt2 where ki constant The power delivered to the particle by th forces acting on it as a function of time t is 1 2 mk r t 2 mk r t mk4r215 Fv 1 Zero 2 Fv projection with speed resistance is 4 13 A body of mass 0 5 kg travels in a straight line w 3mv 4 1 velocity v ax3 2 where a 5 m 2 s The w done by the net force during its displacement fr x 0 to x 2 m is 2 50 J 1 1 5 J 3 10 J 4 100 J A body of mass m is projected vertically wi velocity vo If it passes through the poir m F m m 4 O Vo 1 2 the work done b 2 Foror 15 A massless spring when stretched by a force shows an extension of 1 5m This sp arranged as shown in figure A block of mas is released at rest on a frictionless incline down and compresses the spring by 3m coming to rest momentarily Distance by wi block slides before hitting the spring is 0 30 3mv 4 3mv 8 10Kg

Physics
Current Electricity2 The drift velocity of the free electrons in a conducting wire carrying a current I is v Consider a wire of the same metal but of double the ra dius and carrying a current 21 The drift velocity of the electrons for the second wire will be a v 4 b v 2 c v d 4y

Physics
Basic PhysicsThree concentric metallic spherical shells of radii R 2R 3R are given charges Q1 Q2 Q3 respectively It is found that the surface charge den sities on the outer surfaces of the shells are equal Then the ratio of the charges given to the shells Q Q2 Q3 is a 1 3 5 b 1 2 3 c 1 4 9 d 1 8 18

Physics
Photoelectric Effect3 A metallic surface when illuminated with light of wavelength A emits electrons with energies upto a maximum value E and when illuminated with light of wavelength A2 where A it emits electrons with energies upto a maximum value E2 Prove that plank s constant h and the work function of the metal are given by h E E A A C A and B A B A 1 1

Physics
Geometrical OpticsA man s face is at a distance p 15 cm in front of a concave spherical shaving mirror If the image is erect upright and 1 5 times largen than the object what is the radius of curvature of the mirror

Physics
Work, power & energy7 BC D E F X The force acting on a particle constrained to move along x axis varies as shown Identify the correct option s 1 E is a neutral equilibrium position 2 F is a stable equilibrium position A 3 B D are unstable equilibrium positin 4 Both 1 and 3

Physics
Photoelectric Effect4 Light of wavelength 800 nm is shone on a metal surface connected to a battery The work function of the metal is 1 25 eV Find the extinction voltage or retarding voltage at which the photoelectron current stops Find the highest speed of the emitted photoelectrons at this incident frequency Ans Vr 0 3 volt 3 2 105m s

Physics
RotationAthin rod of length 2R is placed inside a smooth spherical shell of radius R The rod is vertical and i ends are in contact with the inner surface of the shell The rod is released from this position A Maximum speed of the mid point of the rod will be 3gR 2 2 B Angular velocity of the rod when it becomes horizontal is C At any moment all points of rod will have same speed D The maximum velocity of the ends of the rod will be 3gR 2 3g 2R

Physics
Kinematics2 The trajectory of a projectile in a vertical plane is y ax bx where a and b are constants and x and y respectively are horizontal and vertical distances of the projectile from the point of projection The maximum height attained by the particle and the angle of projection from the horizontal are tan b 1 3 b 2a a 4b tan a 2 4 a b 2a b tan 2a tan a

Physics
Rotationparticles 1 and 2 are allowed to descend on the two frictionless chord OA and OB of vertical circle at the same instant from point O The ratio of the velocities of the particles 1 and 2 when they reach on the circumference will be OB is diameter 1 sin a 2 tan a 3 cos a 4 independent on A B

Physics
Circular MotionWhy is centrifugal force called a pseudo force Calculate the centripetal force acting on a small mass of 0 25 kg rotating 1800 revolution min on a radius 200 mm Why does a cyclist bend inwards while riding along a curved road 2 2 2 2

Physics
Circular Motion3 A particle is moving in a circle of radius 3 m with an angular velocity 2 radian per second in clockwise direction as shown Find acceleration of particle at point Q y Q 60 X 1 61 6 31 m s 2 6 31 61 m s 3 61 6 31 m s 4 61 6 51 m 2

Physics
Basic Physicsb What are the advantages of Newton s divided interpolation formula over the Langrage s formula The strength of concrete block at different time is shown in the table Calculate strength when t 28 day Days Strength ksi 3 0 5 7 1 3 14 1 8 20 2 5

Physics
WavesTwo wires of different densities are joined at x 0 An incident wave Asin K x ot traveling from left to right is partly transmitted and partly reflected from the joint If the wave number in the second string is K2 find the amplitude of the reflected and the transmitted wave Show that a phase difference of occurs in the reflected wave if K K Advanced geometrical understanding of derivative is required Look up Resnick Halliday for hints this question may be above IIT JEE level

Physics
Newton's law of motion0 Can a dimensionless quantity have a unit Define Impulse of a force How is it related to momentum A 30 g bullet leaves a rifle with a velocity of 300 m s and the rifle recoils with a velocity of 60 c Find the mass of the rifle 3 1 2

Physics
Fluidsa The viscous force F on a spherical body moving through a liquid depends upon the velocity v of the body the radius r of the body and the co efficient of viscosity n of the liquid Derive the expression for the viscous force by dimensional method

Physics
Kinematics1 To a man walking at the rate of 3km h the rain appears to fall vertically When he increases his speed to 6km h it appears to meet him at an angle 45 with vertical The speed of rain is 1 2 3 km h 2 6 km h 3 3 2 km h 4 4 3 km h

Physics
FluidsC 5 State Hooke s law On what factors does the modulus of elasticity of a substance depend Define co efficient of viscosity and write down its SI unit What is meant by streamline and turbulent flow of a liquid What is critical velocity 3 1 1 3

Physics
Magnetic FieldA dip needle vibrates in the vertical plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian The time period of vibration is found to be 4 s The same needle then allowed to vibrate in the horizontal plane and the time period is again found to be 4 s Then the angle of dip is 60 30 90 45

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentc 0 28 A A conducting rod of 1m length and 1kg mass is suspended by two vertical wires through its ends An external magnetic field of 2T is applied normal to the rod Now the current to be passed through the rod so as to make the tension in the wires zero is Take g 10ms 2 a 0 5A 2 Kerala PET 2007 b 15A c 5A d 1 5A flows in a conductor from east to west The nints above the

Physics
Unit & Dimensions49 Figure a shows a ring of mass m and figure b shows half portion of the same ring Gravitational field at point P in figure b is I2 in magnitude and makes an angle o with line AB Gravitational field at point P in figure a is I in magnitude The ratio of It is 212 a sec o A P a b cos p 12 b c tan o A P B d sin o