Anatomy and Physiology Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Anatomy and Physiology
Nervous SystemWhich of the following is a response from the sympathetic division O Constricted pupils O Increased heart rate O Lower blood pressure O High gastrointestintal tract activity


Anatomy and Physiology
Nervous SystemThe parasympathetic division has postganglionic fibers preganglionic fibers and postganglionic fibers The sympathetic division has preganglionic fibers and

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologySelect all of the following receptors that have a nonencapuslated free nerve ending structure Hair follicle receptors Pacinian corpuscles Thermoreceptors O Nociceptors Meissner s corpuscles O Muscle spindles Merkel s discs

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyWhich of the following is TRUE regarding neurotransmitters Muscarinic receptors bind to norepinephrine The effect of ANS fibers releasing acetylcholine or norepinephrine is always inhibitory ONE binding to B2 receptors constricts blood vessels Acetylcholine binding to nicotinic receptors is always stimulatory

Anatomy and Physiology
Nervous SystemMatch the cranial nerve with its correct function Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Accessory Hypoglossal 4 A Provides motor function to part of the tongue for swallowing and conveys sensory impulses from the posterior part of the tongue B Sense of vision C Supplies motor functon for facial expression and conveys sensory impulses for the anterior 2 3 of the tongue D Supplies somatic motor fibers to the superior oblique muscle E Provides parasympathetic motor innervation to the heart lungs and abdominal viscera Transmits sensory impulses from the thoracic and abdominal viscera F Supplies motor fibers to the lateral rectus muscle G Motor fibers to four of the extrinsic eye muscles H Provides motor fibers to muscles of the tongue and controls tongue movements involved with manipulating food while chewing swallowing and speaking 1 Provide motor fibers to the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles J Conveys sensory impulses from the face and supplies motor fibers to muscles for mastication K Sense of smell L Transmits impulses for the sense of equilibrium and hearing

Anatomy and Physiology
SupexMatch the spinal nerve with its correct function Phrenic Axillary Radial Femoral Sciatic A Serves the deltoid and teres minor muscles B Serves the quadriceps anterior thigh C Serves the muscles of the posterior arm and forearm D One branch serves the back of the thigh hamstring muscles and the other branch lateral surface of the leg E Motor and sensory nerve for the diaphragm

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to Physiologyatch the receptor to its stimulus type Mechanoreceptor Thermoreceptor Photoreceptor Chemoreceptor Nociceptor A Pain causing stimuli B Touch pressure vibration stret C Light D Changes in temperature E Chemical

Anatomy and Physiology
EndocrinologyHormone release caused by altered levels of certain critical ions or nutrients Hormone release caused by another hormone The most common type of stimulus for hormone release by the major endocrine glands Hormonal Stimuli Example Luteinizing hormone causes testosterone release Example Stress causes corticotropin releasing hormone CRH release from the hypothalamus Humoral Stimuli Not terminated by negative feedback Involves tropic hormones Example Rising potassium levels cause aldosterone release Terminated by n feedback by a hc Terminated by negative feedback by the regulated substance Neural Stimuli Hormone release

Anatomy and Physiology
BrainThe most common type of stimulus for hormone release by the major endocrine glands Hormonal Stimuli Not terminated by negative feedback Example Rising potassium levels cause aldosterone release Hormone release caused by another hormone Terminated by negative feedback by a hormone Involves tropic hormones Hormone release caused by neural input Hormone release caused by altered levels of certain critical ions or nutrients Humoral Stimuli 4 Example Stress causes corticotro releasing hormone CRH releas from the hypothalamus Example Luteinizing hormone causes testosterone release Rese Neural Stimuli Terminated by negativ feedback by the regulat substance

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I Tracture Animations Regulation of Hormone Release Parathyroid gland Posterior lobe of pituitary gland II Hypothalamus Releasing and inhibiting hormones Anterior lobe of pituitary gland Target gland hormones Thyroid gland Stimulating hormones You labeled 2 of 8 targets incorrectly You seem to have confused No credit Inst Tocan Adrenal cortex Gonad

Anatomy and Physiology
EndocrinologyAdrenocorticotropic hormone ACTH Corticotropin releasing hormone CRH Cerebral cortex Epinephrine Thyrotropin releasing hormone TRH Cortisol Hypothalamus Posterior lobe of pituitary gland Adrenal cortex Anterior lobe of pituitary E Target cells HHH

Anatomy and Physiology
Endocrinologyneural rises hormonal negative humoral falls positive Glucose levels in the blood are tightly controlled An important hormone for controlling blood glucose is insulin which is released by the pancreas Increases in blood glucose cause insulin release This is an example of a hormone released in response to a stimulus Insulin release is terminated when blood glucose This is an example of feedback

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyJeremy has been feeling tired and cold for the last week His roommate offers Jeremy his bottle of thyroid hormone supplements and promises that they will make him feel better they don t Suppose that Jeremy s thyroid hormone levels were normal to start with and that the supplements actually did contain active thyroid hormones After taking these supplements for a week how do you think Jeremy s blood levels of thyroid stimulating hormone TSH and thyrotropin releasing hormone TRH would compare to normal levels View Available Hint s TSH would be higher but TRH would be lower than normal TSH would be lower but TRH would be higher than normal Both TSH and TRH would be lower than normal Both TSH and TRH would be higher than normal

Anatomy and Physiology
InfexParakeets Melanopsittacus undulatus come in many colors These birds may produce zero one or two types of pigment in their feathers a blue pigment and a yellow pigment Production of each pigment is due to one gene with two alleles Blue pigment is dominant to no blue pigment and yellow pigment is dominant to no yellow pigment These two pigment genes are not linked A parakeet that produces both blue and yellow pigment has green feathers A parakeet that produces neither blue nor yellow has white feathers Suppose you cross a homozygous yellow bird with a heterozygous green bird 1 Indicate the F genotypes and phenotypes 5 pts 2 You set up a cross with a yellow feathered F bird and a white feathered bird What is the probability of having an F bird with white feathers 2 pts

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to Physiologyhere at the arrow is known as an and the sex of the specimen here is a

Anatomy and Physiology
Infex1 Susan knows that there are laws that govern the refilling of diazepam which is a controlled substance How do these laws affect Mr Lehmke 2 What should Susan do to respond to this medication refill request 3 After talking with the patient Dr Penningworth has approved the request for one refill What is Susan s next step

Anatomy and Physiology
InfexExample Stress causes corticotropin releasing hormone CRH release from the hypothalamus Terminated by negative feedback by the regulated substance Hormonal Stimuli Not terminated by negative feedback Terminated by negative feedback by a hormone Example Luteinizing hormone causes testosterone release Hormone release caused by neural input Involves tropic hormones Humoral Stimuli Example Rising potassium levels cause aldosterone release The most common type of stimulus for hormone release by the major endocrine glands Hormone release caused by another hormone Neural Stimuli Hormone release by altered levels of critical ions or nutr

Anatomy and Physiology
EndocrinologyReleasing and inhibiting hormones Target gland hormones Hypothalamus Posterior lobe of pituitary gland Anterior lobe of pituitary gland Stimulating hormones Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Adrenal cortex Gonad

Anatomy and Physiology
EndocrinologyACTH travels in the blood to the adrenal cortex First step Adrenocorticotropic hormone is secreted from the anterior pituitary Glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids are secreted Hypothalamus secretes corticotropin releasing hormone Corticotropin releasing hormone travels through the portal system to the anterior pituitary Target cells produce metabolic and renal effects Last step

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I TractBlood glucose increases to normal Body cells take up more glucose Liver takes up glucose and stores it as glycogen Pancreas releases glucagon Liver breaks down glycogen and releases glucose to the blood Blood glucose decreases to normal Pancreas releases insulin High blood glucose Glucose level Homeostasis Normal blood glucose level Glucose level Low blood glucose
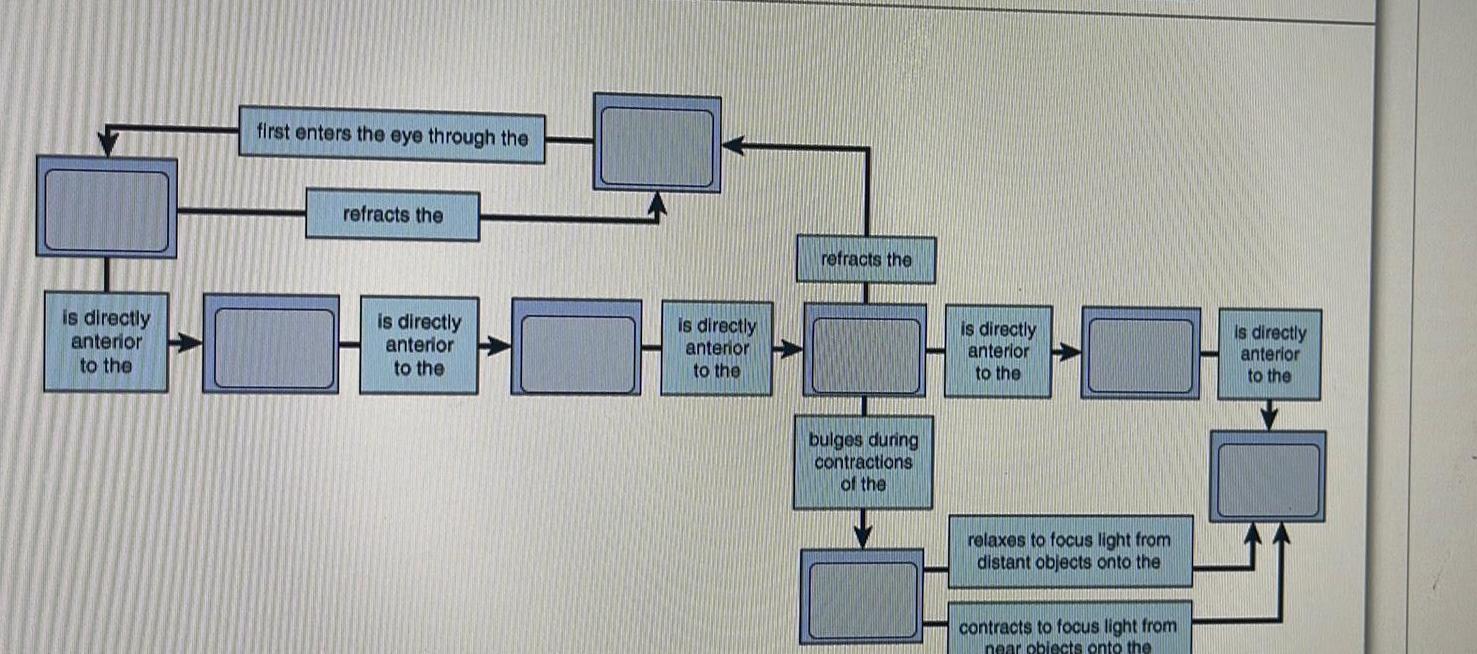
Anatomy and Physiology
General Anatomyis directly anterior to the first enters the eye through the refracts the is directly anterior to the is directly anterior to the refracts the bulges during contractions of the is directly anterior to the relaxes to focus light from distant objects onto the contracts to focus light from near objects onto the is directly anterior to the

Anatomy and Physiology
Nervous Systemuter ear pinna and ear canal describe s a region of the ear that include s the describe s a region of the ear that include s the describe s a region of the ear that include s the describe s a region of the ear that include s the middle ear describe s a region of the ear that include s the cochlea housing spiral organ oval window direct s sound waves In the air directly to the convert s sound waves into local vibrations and transmit s them to the transmit s vibrations to the inner ear at the change s the pressure of the fluid in the spiral shaped tympanic membrane contain s hair cells that convert mechanical energy into inner ear

Anatomy and Physiology
Braining Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets Produces hormones and is considered a neuroendocrine organ Produces the hormones that direct the production of the secondary male sex characteristics Produce hormones involved in electrolyte balance and the stress response Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain Produces the hormones that promote the development of the female secondary sexual characteristice at puberty

Anatomy and Physiology
SupexWhich action was justified by the ideas in Andrew Carnegie s theory of the Gospel of Wealth O the formation of monopolies and trusts the creation of a welfare system to help the poor government control over corporations an unwillingness to give back to the community

Anatomy and Physiology
ThoraxWhich of these lines from A Piece of String illustrates Matre Hauchecome s conflict A The heavy roll of the drum and the crier s voice were again heard at a distance B What grieved me so much was not the thing itself as the lying C The finder is requested to return same with all haste to the mayor s office

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe kidneys ability to secrete concentrated urine is possible because of the countercurrent multiplier Please mention the structures involved and explain how they work to secrete concentrated urine Hint what are the roles of the descending and ascending loop How are they different Lastly explain how is it possible for us to produce hyper concentrated urine TERM

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyIntroduction Match the territory with the description of the conflict Egypt Nicaragua Afghanistan Guatemala A CIA backed coup d tat resulted in civil war Conflict developed over access to a waterway Soviet supported Sandinistas fought the US backed Contras in a civil war Soviets led the invasion of an independent nation

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenDiscuss all the structural components of a nephron and explain what is happening in each section beginning with the glomerular capillaries and ending with the collecting duct What gets filtered absorbed and secreted in each of the sections for example TERM

Anatomy and Physiology
CirculationDefine and explain the principle topic of veracity Explain in detail how the principle may be utilized in Veracity How does this principle effect the profession of Nursing or care of clien Analyze how the issue may influence health as well as health care decis Provide an example or case study scenario of your principle or topic

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyMarquis Artis Attempt 1 The arrow is pointing toward which direction Toward the superior Toward the inferior Toward the posterior Toward the anterior Previous Page Next Pays

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyWhich of the following is NOT true about bones They form the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton They are innervated They are avascular

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyQuestion 20 1 point During cross bridge activity during muscle contraction what happens FIRST when ATP binds The thick and thin filaments slide past each other Muscle contractions stop ATP is an inhibitor The thick and thin filaments detach from each other dy to fire position

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyQuestion 11 1 point Which muscle can be used to make the head nod or rock up and down when it contracts brachialis supinator iliopsoas

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyQuestion 6 1 point Which of the following is NOT one of the major tissue types in the body Stranular Epithelial Muscle Nervous

Anatomy and Physiology
General Anatomy54 Which statement is false O a Vitamin B6 is part of the hormone epinephrine O b Vitamin B6 facilitates glycogen breakdown O c High amounts of vitamin B6 in the diet lower serum homocysteine levels O d People on very high protein diets may need higher intakes of vitamin B6

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to Physiology92 Dietary Vitamin K is absorbed in the small intestines and vitamin K is produced by bacteria in the colon Oa False b True

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to Physiology65 Which of the following statements is true a Calcitonin releases calcium from bones O b Parathyroid hormone PTH increases the excretion of calcium in urine O c Vitamin D increases intestinal absorption of calcium O d PTH decreases the production of calcitriol

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to Physiology59 Which of the following conditions results in increased ADH secretion O a Vomiting O b Protein consumption Oc Caffeine consumption Od Alcohol consumption

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to Physiology88 Most of sulfur in diet is contributed by O a phenylalanine and tryptophan O b isoleucine and lysine O c methionine and cysteine O d threonine and valine

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWhich chemical causes vasodilation of blood vessels in the penis leading to an erection Nitric oxide Epinephrine Cialis Renin Question 19 2 points Listen Which layer surrounds the oocyte and separates it from the follicular cells and is the layer that a sperm must penetrate during fertilization Corona radiata

Anatomy and Physiology
EmbryoThe lining of the uterus which sustains the embryo is the Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium Epimetrium

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWhich of the following is an example of an X linked sex linked trait Baldness Facial hair growth Color blindness Dwarfism Question 22 2 points Listen How is meiosis different in oogenesis than in spermatogenesis Oocytes have twice as many chromosomes Unequal sharing of cytoplasm in oogenesis forming polar bodies Occurs more quickly in spermatogenesis

Anatomy and Physiology
EmbryoWhich of the following is not a function of testosterone Secondary sex characteristics Development of the male reproductive system Descent of the testes All the above are functions Question 27 2 points Listen Which membrane surrounds the embryo and is filled with fluid Chorion Yolk sac Allantois

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I TractWhich hormone increases the production of gastric juice Gastrin Secretin Cholecystokinin Leptin Question 29 2 points 1 Listen Where would you find haustra Stomach Uterus Large intestine K

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWhat is the function of the appendix The appendix has no function Produces the enzyme appendix lipase O Stores useful bacteria that can recolonize the large intestine Regulates mucous production Question 32 2 points Listen Which cells produce testosterone in the testes Leydig cells Sertoli cells Interstitial cells Follicular cells

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I TractWhich substances are absorbed into lacteals Simple sugars Amino acids Salts Lipids Question 12 2 points 4 Listen Which cells release hydrochloric acid in the stomach Chief cells G cells Mucous cells

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenD Listen Where does fertilization occur Uterus Uterine tube Ovary O Cervix

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenListen Which hormone stimulates both the pancreas to release enzymes and the gallbladder to releases bile Secretin Gastric inhibitory peptide GIP Gastrin Cholecystokinin CCK

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWhat ions in pancreatic juice buffer chyme as it enters the small intestine Hydrogen Bicarbonate Chloride Sodium Question 24 2 points Listen Which structure implants in the uterus Morula Zygote Blastocyte