Respiratory System Questions and Answers


Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System3 List the four major processes in cell respiration and where they occur in the eukaryotic cell Specific Location found in Cell A B C D Processes

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemWhere do you think the integrating center for control of ventilation might be located Why if you dont know the answer you can always make a SWAG a scientific wild ass guess

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systempulmonary diseases are characterized by a decrease in lung compliance or ability to change thoracic cavity volume

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemHypoventilation will cause an decrease carbon dioxide increase carbon dioxide increase oxygen in blood

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemMeasuring the rate of forced exhalation is used to diagnose obstructive lung diseases because O the positive pressure that exists during exhalation causes the airways to open fully and allows more ready movement of air into the lungs the negative pressure which occurs in the lungs during exhalation unmasks airway problems the positive pressure that exists during exhalation causes the airways to collapse which accentuates underlying airway problems O the negative pressure in the lungs during exhalation will pull airways open and mask airway problems

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System42 Which of the following statements 1 d e regarding pulmonary surfactant is TRUE It increases airway resistance It increases the compliance of the lungs It is secreted by type I alveolar cells It is thick mucus causing lung infections It is mixture of carbohydrates Bo b rak

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System8 Which structure is responsible for gas exchange in respiratory system Bronchi O Trachea Larynx Alveolar sacs Bronchioles Bo b rak

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systemmaxillary O etmoid sinus O sphenoid sinus O mastoid sinus O frontal sinus Question 27 Which membrane lines the body wall in the thoracic region O visceral pericardium O visceral pleura O parietal pleura O parietal peritoneum

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System31 18 Predict whether each condition would increase or decrease the delivery of oxygen to the tissues Left shift in the O2 Hb dissociation Decreased alveolar Poz curve Bohr Effect 75 saturation of Hb leaving the alveolus 0 Iron deficiency anemia Increased O Delivery to Tissues Decreased blood pH Increased hematocrit Increased tissue Poz 0 CO binding to heme Decreased temperature Decreased O Delivery to Tissues

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System0 23 Determine which set of capillaries each of the following processes would occur in Carbonic anhydrase is increasing the amount of carbonic acid Carbonic acid in RBCs converts back to carbon dioxide and water Carbon dioxide binds to plasma proteins Alveolar Capillaries Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood Decreasing carbon dioxide levels decrease the levels of HHb Chloride ion shifts into the RBC Systemic Capillaries Carbon dioxide is diffusing into the blood Oxygen is diffusing into the blood

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemWhich one of the followings is NOT true about samsara and karma Hinduism understands morality like scientists see the physical world The karmic law what goes around comes around exists as part of dharma the cosmic law or principle or order Thus just like everyone is bound to a law of physics we all live under the karmic principle In Hinduism the karmic principle is known as a creation of Brahma the god of creation However the law was set to work on its own Thus Brahma is not responsible for its working Samsara is the endless wheel of birth and re birth Karma literally means action and typically prefers to the sum of an individual s actions in his or her state of existence O An individual s status in the next life is determined by how much karmic cr dits the person has earned or lost in the present life

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systemtrue you know about the metabolic theory of autoregulation which of the following stateme increased levels of CO will cause vasodilation increased levels of O will cause vasoconstriction tissues with higher metabolic activity will get more blood all of the choices are correct

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemFor questions 6 through 8 fill in constrict or dilate then and arrows 6 Acetylcholine will bronchioles resistance air flow Histamine will 7 resistance 8 resistance air flow Epinephrine will air flow bronchioles bronchioles

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemIntrapulmonary pressure s or during inspiration What pressure is always negative and helps to keep the lungs flated pressure If transpulmonary pressure equals zero what will a appen to the lungs b This is known as a an When the bronchiole constricts what will happen to use arrows To air flow a sistance b use arrows

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemPart 2 After reading the chapters for the week what is one barrier to action that you feel you might experience Explain what you feel you can do to help yourself through it Respond to three other students post with one way they can still give assistance while experiencing a barrier to action

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemWhich of the curves in the following graph illustrates a condition of greater compliance A or B Volume EXCEL A Beeld B

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemThis might be a random or silly question to ask since I do not suffer from this but know people deal with it but when people suffer from an anx attack do you slowly stop getting oxygen or wou it be more like you are getting too much oxygen

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemBody mass kg Lung volume L O2 mL L in lung mL O2 in lungs mL O in lung mL 0 in lung V V Weddell seal 300 8 150 X 0 X 0 0 8 6 150 Human 70 6 150 0 0

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemMy question is why does our breathing change during exercising Why do we breathe more heavily

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemI was interested to learn more about respiratory disorders and how the lungs are susceptible to inhaled pathogens and debris It got me thinking about how our microbiome serves as an important biological barrier for the immune system Do individuals have different microbiomes in their lungs that can play a factor in immunity against inhaled pathogens It would be interesting to study the composition of the lung microbiome in those who suffer from lung disorders

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemM 1 BBC NEWS 2 3 4 Take a look at these characters Leaving Scooby Doo the dog out of your discussion choose 2 of the characters that would most likely have different lung volumes and explain how their volumes would differ and why the measurements would be different

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemWHAT IS THE EQUATION Body mass kg Lung volume L O2 mL L in lung mL O2 in lungs mL Q in lungs Lung Volume Body mass Weddell seal 300 8 150 X Human 70 6 150 O mL L in lung

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemWhy is it possible to find cytochrome oxidase in a facultative anaerobe a They can undergo aerobic respiration Ob This is due to anaerobic respiration c Because cytochrome oxidase uses inorganic molecules as a final electron acceptor d These microbes cannot respire aerobically therefore you will not find cytochrome oxidase Oe This is due to fermentation

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemQUESTION 37 Which of the following is false about aerobic respiration O a Oxygen binds with electrons to form water b Oxygen can combine with water to form hydrogen peroxide c The final electron acceptor is oxygen Od The electron transport chain is absent redox reaction

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systemspiratory Volumes and Capacities retory volume is the term used for verious volumes of air moved by or associated with the lungs at a given point in the piratory cycle There are four major types of respiratory volumes tidal residual Inspiratory reserve and expiratory reserve 2231 Tidal volume TV is the amount of air that normally enters the lungs during quiet breathing which is about 500 hers Expiratory reserve volume CRV is the amount of air you can forcefully exhale past a normal tidal expiration up to 1200 ters for men Imperatory reserve volume FV is produced by a deep inhalation past a tidal inspiration This is the extra pune that can be brought into the lungs during a forced Inspiration Residual volume TV is the al le in the lungs if you exhale much as possible The residual volume makes breathing coser by preventing the alveol from colapsing Respiratory volume dependent on a variety of factors and measuring the different types of respiratory volumes can provide important cues about a person s respiratory team oure 22 39 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 Inspiratory reserve volume Tidal volume Expiratory Volume Expiratory Reserve reserve volume Inspiratory capacity Functional residual capacity 500 Figure 22 18 Respiratory Volumes and Capacities These two graphs show a respiratory volumes and b the combination of volumes that results in respiratory capacity Volume Amount ml Vital capacity Lung Volumes Pre Lab Questions Complete the table below using the reading graph and chart on the previous slide You might have to do some math volume About 1100 ml b Total lung capacity Volume Description function test Spirometry Gas diffusion Spirometer Blood gas analyzer Forced vital capacity FVC Forced expiratory volume FEV Forced expiratory flow 25 75 percent Peak expiratory flow PEF Maximum voluntary ventilation MVV Slow vital capacity SVC Total lung capacity TLC Functional residual capacity FRC Residual volume RV Total lung capacity TLC Expiratory reserve volume ERV Arterial blood gases Figure 22 19 Pulmonary Function Testing Volume of air that is exhaled after ma Inhalation Volume of air exhaled during one force breath Air flow in the middle of exhalation Rate of exhalation Volume of air that can be inspired and expired in 1 minute Volume of air that can be slowly exhaled after inhaling past the tidal volume Volume of air in the lungs after maximum inhalation Volume of air left in the lungs after normal expiration Volume of air in the lungs after maximum exhalation Maximum volume of air that the lungs can hold The volume of air that can be exhaled beyond normal exhalation Concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood Lung Volumes and Spirometry Video

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systemis a disorder that primarily affects inhalation is a disorder more closely related to exhalation The first disorder however can lead to the second Asthma COPD Emphysema asthma TIL Retake question COPD pneumonia Pneumonia emphysema A Question 49 1 point Retake question Drinking too much alcohol can cause snoring due to a relaxation in which part of the respiratory system uvula epiglottis Opharynx

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemWhich measures can protect biodiversity Orestoration efforts O conservation efforts Oall choices are correct legal protections

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemDrag the tiles to the boxes to form correct pairs Match the respiratory disorders with their description lack of oxygen to some parts of the body deterioration of the alveoli inflammatory disorder triggered by allergens excess growth of cells leading to tumor formation asthma hypoxia lung cancer emphysema

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemQuestion 23 The abbreviation SOB means Question 24 The abbreviation CVA means Question 25

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System45 pleural effusion with pus is known as 46 The gonads include 47 what is the last section of the small intestine before it empties into the large intestine called 48 blood vessels that cary blood away from the heart are called 4 9 Experiencing pain in the right shoulder due to example of pain liver disease is an ex 50 Capillary beds are fed by the 51 Which cells are involved in the production of antibodies

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System8 Scenario A 75 year old male patient was admitted to the hospital with respiratory failure secondary to pneumonia After several days of being treated with steroids and antibiotics he has stabilized on 2 liters of oxygen via nasal cannula He has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD congestive heart failure hypothyroidism and rheumatoid arthritis all of which are currently medically managed The following medications were prescribed for the patient in the scenario Which ones are used to treat COPD Select all that apply 2 Points Tiotropium Spiriva Spironolactone aldactone Levothyroxine synthroid Indomethacin Indocin

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemWhich statement made by a client taking montelukast indicates the need for further teaching 2 Points I will take the medication when I first notice I am having trouble breathing I may be able to decrease the use of my metered dose inhaler I will need to have my liver function checked O I can take the medication with food or ith

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemGraph HR and SV as a function of VO L min Identify where 50 of VO2max is on each curve Describe the HR response to incremental exercise 1 2 sentences Describe the SV response to incremental exercise 1 2 sentences 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 HR and SV as a function of VO 0 66 0 36 0 23 0 80 1 07 1 15 1 16 1 42 1 45 1 58 1 67 1 78 2 18 VO2 l min 2 38 2 62 2 59 2 63 2 54 2 09 120 100 80 60 40 20 O SV mL

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System3 For the following questions FIRST writing down the app a For a female what is her IRV

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemMacmillan Learning The image shows a lipid bilayer with the polar heads represented by circles and the hydrophobic tails represented by lines Arrange the fatty acids in the lipid bilayer to indicate a structure that when incorporated into a phospholipid would result in a more fluid membrane with a lower melting point Be sure to insert the fatty acids into the bilayer in the correct orientation Not all the fatty acids will be used 50 00000 Answer Bank

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systemwww wwww Whew You were able to succes particles You are now passing beautiful it is after the snow tha the clean fresh air Starting at the nose and e

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systemerythropoietin clotting factors O hemoglobin O histamine O granulosen Question 8 0 5 pt Cell surface proteins that are foreign to the body and therefore cause a response from the immune system are known as

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System11 Explain the difference between a mild and severe airway obstruction 12 What should the nursing assistant do when a person is having a mild airway obstruction enco 13 What should a person do if a person is having a severe airway obstruction 14 Define abdominal thrust Hemich suver 15 When should chest thrusts be used wheat unable t


Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System32 What type of muscle tissue functions to pump out of the heart A cardiac muscle B skeletal muscle C single unit skeletal muscle D smooth blood

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemLabel and color the respiratory volumes and capacities depicted in Figure 23 1 using the terms from Exercise 23 2 p 611 Use your text and Exercise 23 2 in this unit for reference m m I

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemPAL Histology Respiratory System Lab Practical Question 2 Identify the highlighted structure Submit Request Answer

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemMultiple Choice Heart venule medium vein large vein capillary conducting artery distributing artery arteriole heart Heart large vein medium vein venule capillary arteriole distributing a conducting artery heart Heart distributing artery conducting artery arteriole capillary venule la vein medium vein heart Heart conducting artery distributing artery arteriole capillary venule medium vein large vein heart Heart conducting artery arteriole distributing artery capillary large vein venule medium vein heart
Anatomy and Physiology
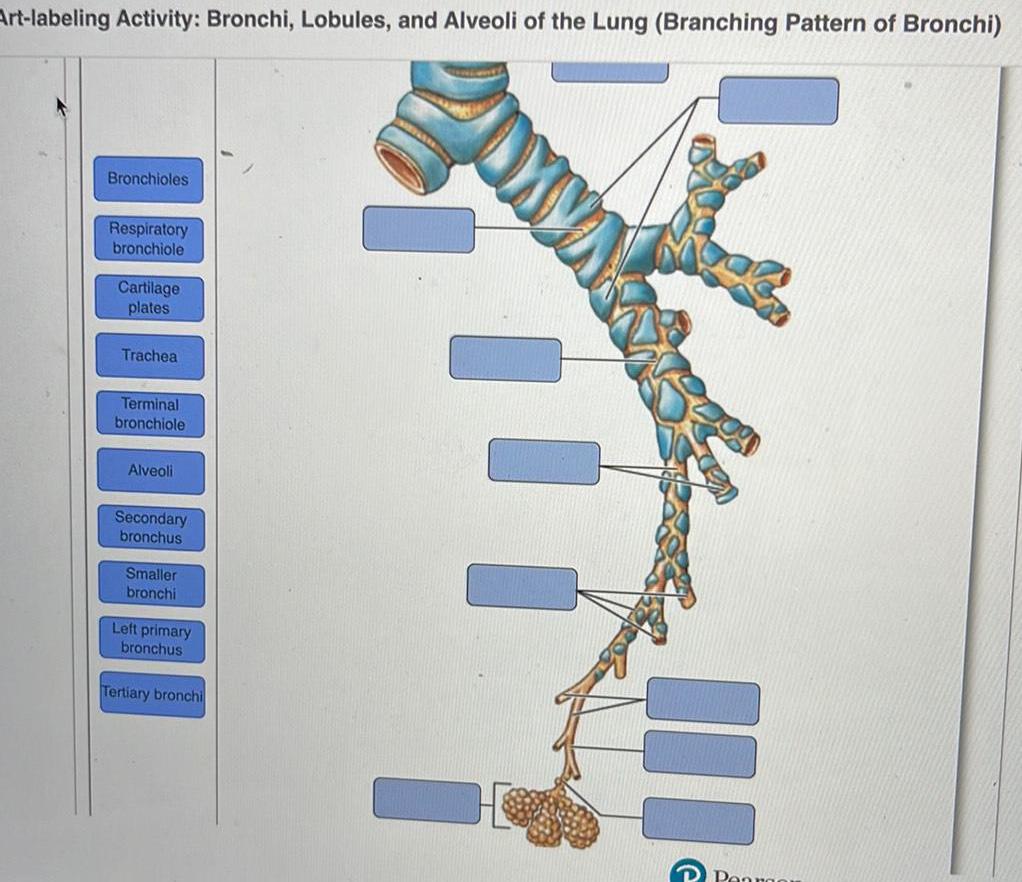
Respiratory SystemArt labeling Activity Bronchi Lobules and Alveoli of the Lung Branching Pattern of Bronchi Bronchioles Respiratory bronchiole Cartilage plates Trachea Terminal bronchiole Alveoli Secondary bronchus Smaller bronchi Left primary bronchus Tertiary bronchi G

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemAorta Inferior lobe Oblique fissure Pulmonary trunk Trachea Thyrohyoid ligament Heart Cricothyroid ligament Cardiac notch Superior lobe P Pearson 000

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemThyroid cartilage Epiglottis Superior lobe Inferior lobe Thyroid Hyoid bone Cricoid cartilage Middle lobe Oblique fissure Horizontal fissure 00100 of the Respiratory System 1000

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System15 The 16 How long should you count an apical pulse 17 Respiration means pulse is used for routine vital signs

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory System14 List the portals of exit and portals of entry used by pathogens to leave and enter the body A B C D E F 15 In medical asepsis an item or area is when it is free of pathogens 16 A resident with dementia does not practice aseptic measures well When do you need to assist the person with hand washing A B C D 17 Explain why hand lotions or hand creams are applied to the hands after practicing hand hygiene

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Systemuse soap and water or hand sanitizer How will you explain the difference 11 01 905 0 Wear ppe 2 6 6 ADDITIONAL LEARNING ACTIVITIES 1 List the measures you practice in your personal life to prevent infection