Probability Questions and Answers
Math
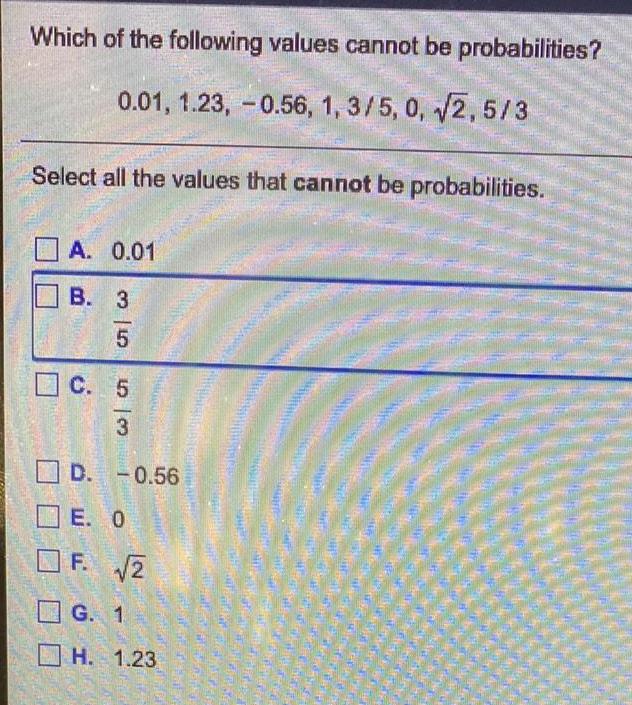
ProbabilityWhich of the following values cannot be probabilities?
0.01, 1.23, -0.56, 1, 3/5, 0, √2, 5/3
Select all the values that cannot be probabilities.
A. 0.01
B. 3/5
C. 5/3
D. -0.56
E. 0
F. √2
G. 1
H. 1.23

Math
ProbabilityBelow,n is the sample size, P is the population proportion, and P is the sample proportion. First, check if the assumptions are satisfied to use the normal distribution for probabilities. If appropriate, use the Central Limit Theorem to find the indicated probability.
n=101
P=0.27
It (Choose one) appropriate to use the normal distribution for probabilities.
is
is not
P(0.26 <p<0.30)=

Math
ProbabilityIf a die is rolled one time, find the probability: P(greater than 3 or an odd number) =
3/6
5/6
5
1/6
Math
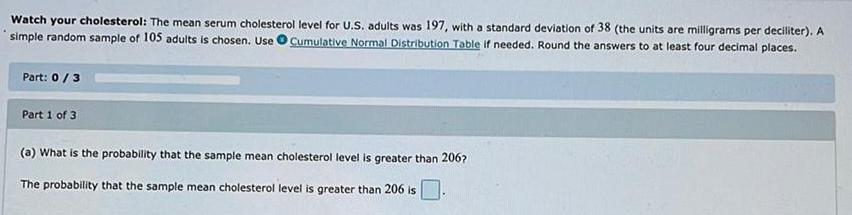
ProbabilityWatch your cholesterol: The mean serum cholesterol level for U.S. adults was 197, with a standard deviation of 38 (the units are milligrams per deciliter). A simple random sample of 105 adults is chosen. Use Cumulative Normal Distribution Table if needed. Round the answers to at least four decimal places.
(a) What is the probability that the sample mean cholesterol level is greater than 206?
The probability that the sample mean cholesterol level is greater than 206 is

Math
ProbabilityA math teacher gave her class two tests. 70% of the class passed both tests and 80% of the class passed the first test. What percent of those who passed the first test also passed the second test? This statement is an example of Supplementary Probability.
O True
O False

Math
ProbabilityA survey revealed that 50% of people are entertained by reading books, 31% are entertained by watching TV, and 19% are entertained by both books and TV.
What is the probability that a person will be entertained by either books OR TV?
81%
19%
62%
100%

Math
ProbabilityFor dinner, Javier will choose one of four fish options and one of five side dishes. His choices for fish are salmon, trout, tilapia, or halibut. His choices for side dishes are fries, carrots, asparagus, salad, or coleslaw.
(a) Draw a tree diagram for the sample space of all dinner combinations.
(b) How many choices for dinner combinations does Javier have?

Math
ProbabilitySuppose that 54% of all voters prefer the Democratic candidate. Let X be the number of people who prefer
the candidate when 31 people are surveyed at random.
Please show the following answers to 4 decimal places.
a. What is the probability that exactly 16 voters who prefer the Democratic candidate in the survey?
b. What is the probability that less than 16 voters who prefer the Democratic candidate in the survey?
c. What is the probability that at most 16 voters who prefer the Democratic candidate in the survey?
d. What is the probability that between 15 and 18 (including 15 and 18) voters who prefer the
Democratic candidate in the survey?
Math
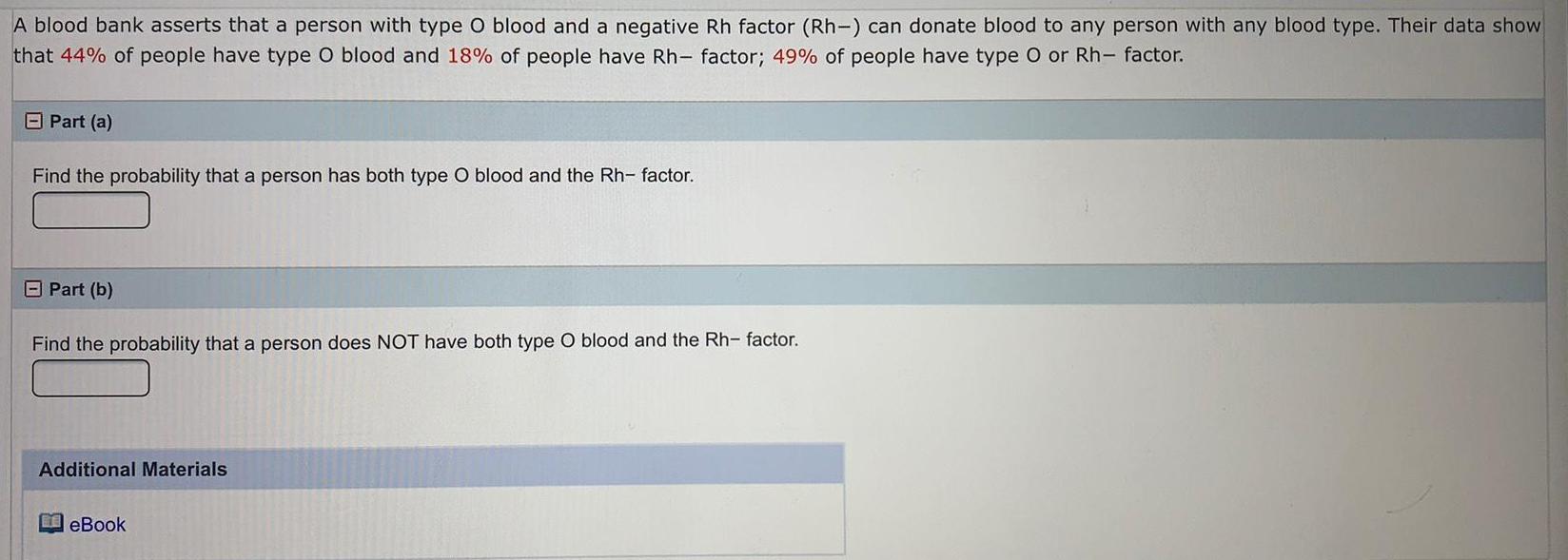
ProbabilityA blood bank asserts that a person with type O blood and a negative Rh factor (Rh-) can donate blood to any person with any blood type. Their data show
that 44% of people have type O blood and 18% of people have Rh- factor; 49% of people have type O or Rh- factor.
Find the probability that a person has both type O blood and the Rh- factor.
Find the probability that a person does NOT have both type blood and the Rh- factor.
Math
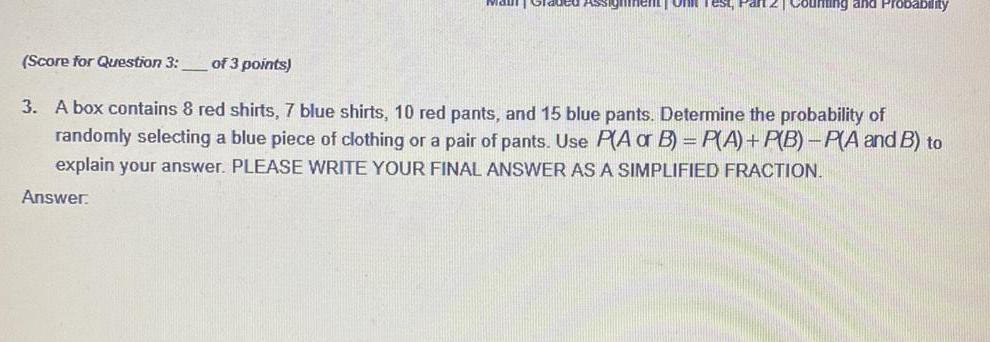
ProbabilityA box contains & red shirts, 7 blue shirts, 10 red pants, and 15 blue pants. Determine the probability of
randomly selecting a blue piece of clothing or a pair of pants. Use P(A or B)=P(A) + P(B)-P(A and B) to
explain your answer. PLEASE WRITE YOUR FINAL ANSWER AS A SIMPLIFIED FRACTION.

Math
ProbabilityAn ice chest contains 6 cans of apple juice, 8 cans of grape juice, 7 cans of orange juice, and 6 cans of mango juice. Suppose that you reach into the container and randomly select three cans in succession. Find the probability of selecting three cans of grape juice.
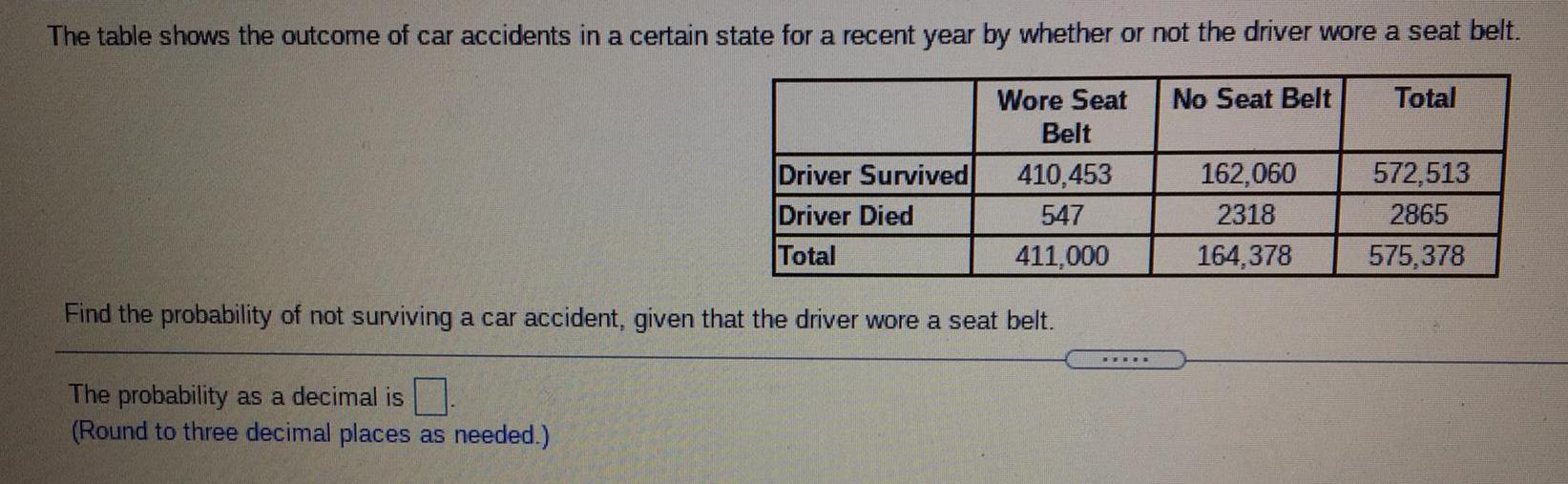
Math
ProbabilityThe table shows the outcome of car accidents in a certain state for a recent year by whether or not the driver wore a seat belt.
Find the probability of not surviving a car accident, given that the driver wore a seat belt.
The probability as a decimal is

Math
ProbabilityThe American Red Cross says that about 45% of the U.S. population has Type O blood, 40% Type A, 11% Type B, and the rest Type AB.
a) Someone volunteers to give blood. What is the probability that this donor
1. has Type AB blood?
2. has Type A or Type B?
3. is not Type O?
b) Among four potential donors, what is the probability that
1. all are Type O?
2. no one is Type AB?
3. they are not all Type A?
4. at least one person is Type B?

Math
ProbabilityThere are 5000 undergraduates registered at a certain college. Of them, 463 are taking one course, 660 are taking two courses, 564 are taking three courses, 1879 are taking four courses, 1342 are taking five courses, and 92 are taking six courses. Let X be the number of courses taken by a student randomly sampled from this population. Find the probability distribution of X. Round the answers to four decimal places as needed.
Math
ProbabilityA single die is rolled twice. Find the probability of rolling an even number the first time and a number greater than 3 the second time. Find the probability of rolling an even number the first time and a number greater than 3 the second time. (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.)
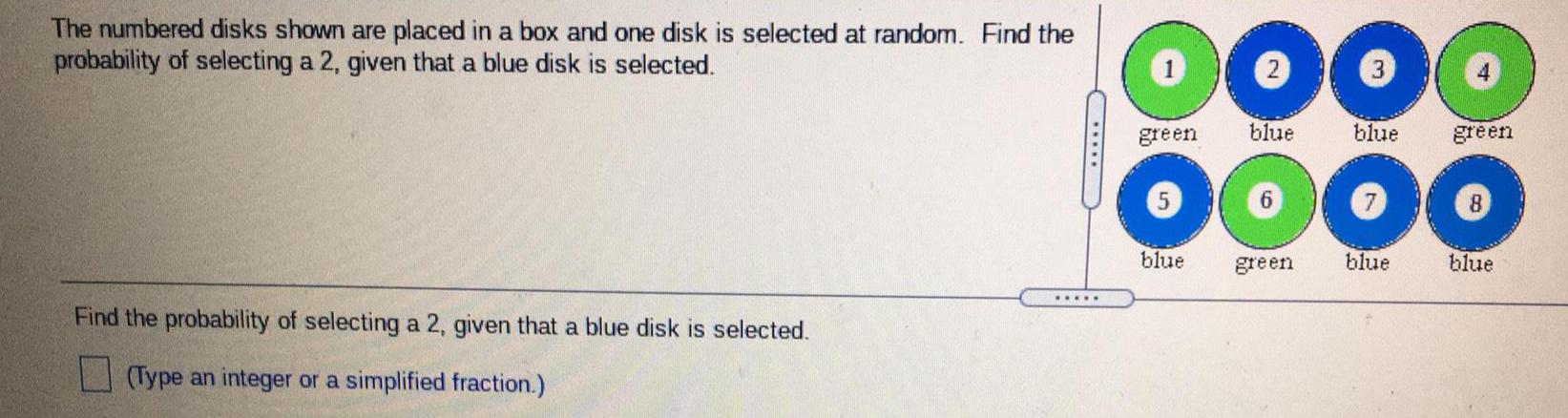
Math
ProbabilityThe numbered disks shown are placed in a box and one disk is selected at random. Find the probability of selecting a 2, given that a blue disk is selected.
Find the probability of selecting a 2, given that a blue disk is selected.

Math
ProbabilityAn ice chest contains five cans of apple juice, four cans of grape juice, five cans of orange juice, and six cans of mango juice. Suppose that you reach into the container and randomly select three cans in succession. Find the probability of selecting no orange juice. The probability of selecting no orange juice from the ice chest is

Math
ProbabilityYou and a group of friends are going to a five-day outdoor music festival during spring break. You hope it does not rain during the festival, but the weather forecast says there is a 10% chance of rain on the first day, a 20% chance of rain on the second day, a 30% chance of rain on the third day, a 35% chance of rain on the fourth day, and a 40% chance of rain on the fifth day.
Assume these probabilities are independent of whether it rained on the previous day or not. What is the probability that it does
not rain during the entire festival? Express your answer as a percentage to two decimal places.
Probability=
%

Math
ProbabilityA geologist has collected 25 specimens of basaltic rockand and 16 specimens of granite. The geologist nstructs a laboratory assistant to randomly select 10 of
the specimens for analysis.
(a) What is the probability that at least 3 of the selected specimens are granite?
(b) What is the expected number of granite specimens in the sample?
(c) If this same process is repeated every day, how many days (on average) will it take before getting a sample consisting entirely of granite?

Math
ProbabilityThe principle of redundancy is used when system reliability is improved through redundant or backup components. Assume that a student's alarm clock has a 17.1% daily failure rate. Complete parts (a) through (d) below.
a. What is the probability that the student's alarm clock will not work on the morning of an important final exam?
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
b. If the student has two such alarm clocks, what is the probability that they both fail on the morning of an important final
exam?
(Round to five decimal places as needed.)
c. What is the probability of not being awakened if the student uses three independent alarm clocks?
(Round to five decimal places as needed.)
d. Do the second and third alarm clocks result in greatly improved reliability?
OA. Yes, because total malfunction would not be impossible, but it would be unlikely.
B. Yes, because you can always be certain that at least one alarm clock will work.
C. No, because total malfunction would still not be unlikely.
D. No, because the malfunction of both is equally or more likely than the malfunction of one.

Math
ProbabilityThe prizes at a carnival tossing game are different stuffed animals. There are 34 tigers, 27 bears, 12 hippopotamuses, 16 giraffes, and 22 monkeys. The carnival manager randomly selects a prize when a player wins the game.
Determine the probability that the prize selected is not a hippopotamus. Give your answer as a decimal, precise to three decimal places.

Math
ProbabilityTay-Sachs disease (TS) is a fatal, recessive genetic disorder in which harmful quantities of a fatty waste substance accumulate in the brain, slowly progressing to death by age five. TS carriers are common among individuals of Eastern European Jewish
descent, with a carrier frequency of about 1 in 27. In the general population, the carrier rate is about 1 in 250.
(a) Give the probability that both parents are carriers in each of the given conditions. (Enter your answers rounded to six decimal places.)
P (both parents carriers | both mom and dad are of European Jewish descent):
P (both parents carriers | mom is of European Jewish descent but dad is not) :
P (both parents carriers | neither mom or dad are of European Jewish descent):
Question Source: Baldi de-The Practice of Statistics In The Life Sciences Publisher: W.H. Freeman
Math
ProbabilityTwo students will draw cards from a Deck. After the first student selects a card, this card is put back on the deck, before the second student selects a card. Find the probability that the first student gets a "Heart" and the second gets a "Diamond".

Math
ProbabilityProbability, p, is a quantitative measure of how likely an event is to occur.
Each of the subsequent questions details the likelihood of an event occurring. For each one, choose the value of p that best corresponds to that likelihood.
The event is impossible and never occurs.
p = 0
p = 0.01
p = 0.99
p = 0.3
p = 0.6
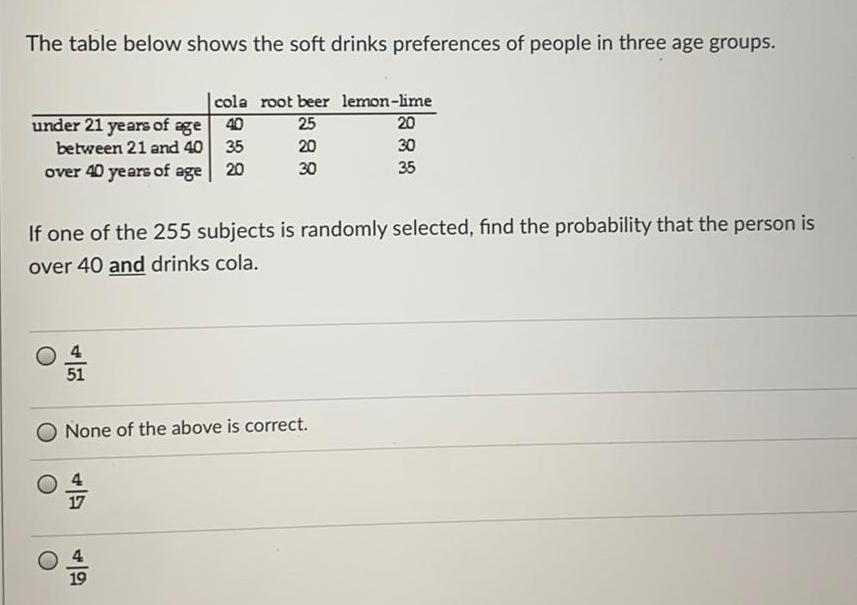
Math
ProbabilityThe table below shows the soft drinks preferences of people in three age groups.
If one of the 255 subjects is randomly selected, find the probability that the person is over 40 and drinks cola.

Math
ProbabilityThe 2011 National Youth Risk Behavior Survey provides insight on the physical activity of high school students in the United States. More than 15,000 high schoolers were asked, "During the past 7 days, on how many days were you physically active for a total of at least 60 minutes per day?" Physical activity was defined as any activity that increased heart rate. Let X represent the response. The survey results are given for the probability model for X.
Days 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Probability 0.15 0.08 0.10 0.11 0.10 0.12 0.07 0.27
(a) Which of the statements verifies why this a legitimate discrete probability model?
The eight probabilities have sum 1 (and account for all possible responses to the question).
The eight probabilities have sum 0 (and account for all possible responses to the question).
The eight probabilities have sum < 1 (and account for all possible responses to the question).
The eight probabilities have sum> 1 (and account for all possible responses to the question).
Math
ProbabilityA teacher has 25 students, and he wants to select two students for a pop quiz. To randomly select these two students, the teacher uses his calculator to generate a random number from the list (1,2,3..., 25), and then call the student that corresponds to that number in his roster. Then, the teacher repeats that procedure to select a second student. Hint: Since the teacher generates a random number from the list (1,2,3...,25) the second time as well, the number of the first student may be generated again. You may see this as two events with replacement. Johnny, is worried about being chosen twice. What is the probability that Johnny is called twice?
1/625
1/600
1/25
1/24

Math
ProbabilityA couple wants to have three children. Assume that the probabilities of a newborn being male or female are the same and that the gender of one child does not influence the gender of another child.
(a) There are eight possible arrangements of girls and boys. All eight arrangements are equally likely.
What is the sample space for having three children (gender of the first, second, and third child)? Use B for boy and G for girl.

Math
ProbabilityFor the use of a test for a certain disease, the sensitivity is 0.93, the specificity is 0.94, and the prevalence is 0.005.
a. Given that a test is positive, find the probability that a random patient has the disease.
b. Draw a tree diagram for a typical sample of 1000 patients.
c. Of the cases that are positive, explain why the proportion in error is larger if the prevalence is lower.

Math
ProbabilitySelect all of the statements that are axioms of probability.
The probability of any event is between 0 and 1 inclusively.
If two events A and B are mutually exclusive (disjoint), then P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B).
The probability of an event A is the number of outcomes in A divided by the number of
outcomes in the sample space.
The combined probability of all possible outcomes is equal to 1.
The probability of two events occurring is always greater than 0.

Math
ProbabilityA baseball player's batting average is the quotient of the number of hits and the number of times at bat. During the 2001 Major League Baseball season, Ichiro Suzuki of the Seattle Mariners batted 692 times and had a batting average of 0.350. How many hits did Suzuki have?

Math
ProbabilityOut of 40 boys, 23 have dark hair, 18 have brown eyes, and 26 have dark hair, brown eyes or both.
a Draw a Venn diagram to display this information.
b One of the boys is selected at random. Determine the probability that he has:
i dark hair and brown eyes
il brown eyes given that he has dark hair.

Math
ProbabilitySix papers are placed in a bag with names written on them. The names are: Lin, Mai,
Mai, Noah, Priya, and Priya. If one name is chosen at random, what is the probability
that it is Priya?

Math
ProbabilityA university class has 22 students: 3 are psychology majors, 9 are business majors, and 10 are history majors. The professor is planning to select two of the students for a demonstration. The first student will be selected at random, and then the second student will be selected at random from the remaining students. What is the probability that the first student selected is a business major and the second student is a history major? Do not round your intermediate computations. Round your final answer to three decimal places.
Math
ProbabilityA binomial experiment with probability of success p=0.45 and n=5 trials is conducted. What is the probability that the experiment results in exactly 3 successes?

Math
ProbabilityIn a lottery, the top cash prize was $655 million, going to three lucky winners. Players pick four different numbers from 1 to 52 and one number from 1 to 43.
A player wins a minimum award of $400 by correctly matching two numbers drawn from the white balls (1 through 52) and matching the number on the gold ball (1 through 43). What is the probability of winning the minimum award?

Math
ProbabilityAssume that random guesses are made for six multiple choice questions on an SAT test, so that there are n= 6 trials, each with probability of success (correct) given by p=0.45. Find the indicated probability for the number of correct answers. Find the probability that the number x of correct answers is fewer than 4.

Math
ProbabilityAt a dental office, the probability a patient needs a cleaning is 0.66. The probability a patient needs a filling is 0.45. Assuming the events "needs a cleaning" and "needs a filling" are independent, then what is the probability a patient needs a filling given that he/she needs a cleaning?
0.66
0.3
0.45
Additional information is required to determine the probability.
0.61
Math
ProbabilityWhat is your probability of winning given this situation: You are trying to win a stuffed animal. You have to hit a target two times in a row to win. The probability of you hitting the
target in one try is 63% .
23.3%
63%
106%
39.6%

Math
ProbabilityFrom previous records, it is known that a particular city can expect 1 hurricane every 4 years in the month of September. Use the Poisson probability equation to determine the probability that this city will experience exactly 3 hurricanes in September within the next 4 years. Round your answer to the nearest whole percent.
%

Math
ProbabilityAccording to the Neilson Company, approximately 30% of all US households had
a digital video recorder (DVR) in their homes in 2008. Suppose a random sample of 15 households are taken. After watching the video on calculating binomial
probabilities using the TI-84 graphing calculator, find the following:
a. Find the probability that exactly four of the sampled households have a DVR.
b. Find the probability that fewer than three of the sampled households have
a DVR.
c. Find the probability that more than one of the sampled households have a DVR.
d. Find the probability that exactly five of the sampled households have a DVR.
e. Find the probability that fewer than four of the sampled households have a DVR.
f. Find the probability that at least eight of the sampled households have a DVR.
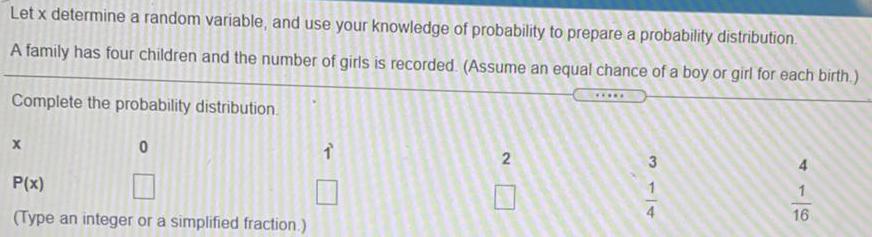
Math
ProbabilityLet x determine a random variable, and use your knowledge of probability to prepare a probability distribution. A family has four children and the number of girls is recorded. (Assume an equal chance of a boy or girl for each birth.) Complete the probability distribution
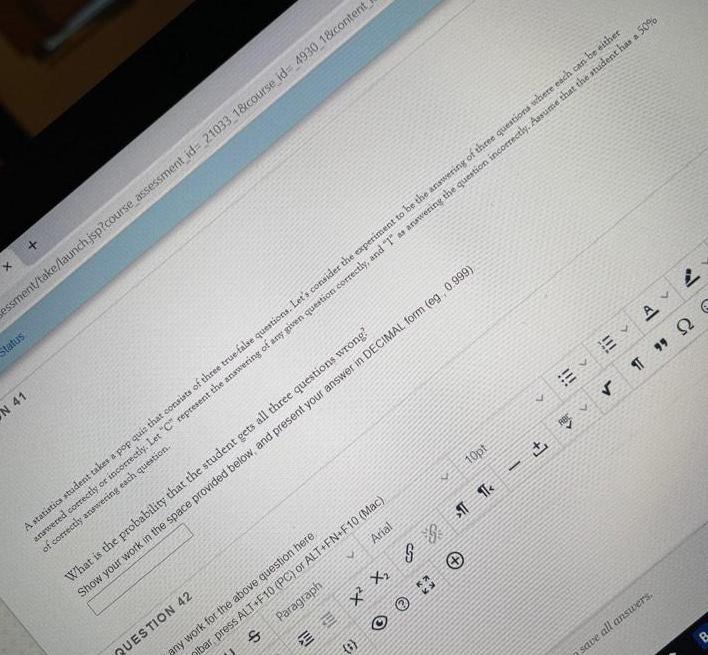
Math
ProbabilityA statistics student takes a pop quis that consists of three true false questions. Let's consider the experiment to be the answering of three questions where each can be either answered correctly or incorrectly. Let "C" represent the answering of any given question correctly, and "1" as answering the question incorrectly. Assume that the student has a 50% of correctly answering each question.
What is the probability that the student gets all three questions wrong?

Math
ProbabilityAbout 30% of human twins are identical, and the rest are fraternal. Identical twins are necessarily the same sex - half are males and the other half are females. One-quarter of fraternal twins are both male, one-quarter both female, and one-half are mixes: one male, one female. You have just become a parent of twins and are told they are both girls. Given this information, what is the probability that they are identical?
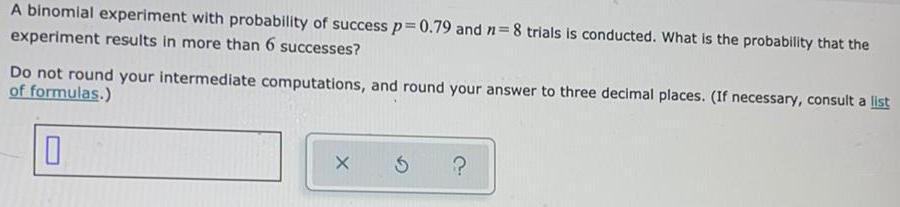
Math
ProbabilityA binomial experiment with probability of success p=0.79 and n=8 trials is conducted. What is the probability that the experiment results in more than 6 successes? Do not round your intermediate computations, and round your answer to three decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
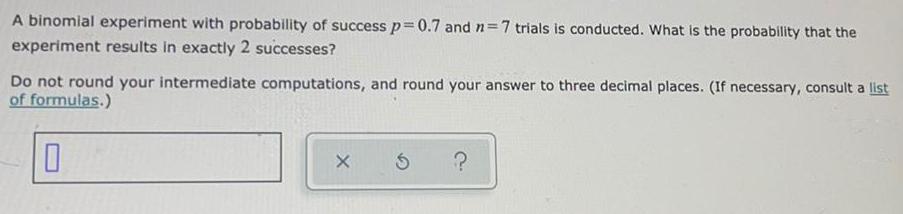
Math
ProbabilityA binomial experiment with probability of success p=0.7 and n=7 trials is conducted. What is the probability that the
experiment results in exactly 2 successes?
Do not round your intermediate computations, and round your answer to three decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)

Math
ProbabilityThe manufacturer of a fertilizer guarantees that, with the aid of the fertilizer, 70% of planted seeds will germinate. Suppose the manufacturer is correct. If 9 seeds planted with the fertilizer are randomly selected, what is the probability that more than 6 of them germinate? Carry your intermediate computations to at least four decimal places, and round your answer to two decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)

Math
ProbabilityNow suppose we wants to analyze the probability of going into the bowl twice selecting a yellow M & M on both selections. Here we have an and statement, it is the same as saying waht is the probability of selecting a yellow M & M on the selection and on the second selection. So we need to multiply probabilities, and before we can do so we need to determine if the events are dependent or independent. Well developing the first probability is not effected by dependence or independenc, the probability of selecting the first M & M and its yellow is 20/45 but the development of the next probability begs the question are the events dependent or independent so we need to ask ourselves if the first M & M that we selected was a yellow M & M does this effect the probability that the next M & M that we select is yellow? What will determine this is whether we decide to eat that first M & M or put it back in the bowl after we make our first selection. P(1st yellow and 2nd yellow) = 20/45 * 20/45 = 400/2,025 (If we replace M & M after 1st selection) P(1st yellow and 2nd yellow) = 20/45 * 19/44 = 380/1,980 (If we do not replace our first selection) Take notice that this theory will always solve the follow probabilty under the assumption that the previous event did happen. them Try the following problems for HW and submit them back to me via Blackboard email no later than Monday evening. Using the data above: 1. P(1st is red and 2nd is green) Assume dependent events 2. P(1st is yellow and 2nd is red) Assume independent events

Math
ProbabilityIt is known that 77% of all travelers at an airport are domestic travelers (staying
within the U.S.) while the rest are international travelers. If two travelers are
randomly selected, what is the probability one is a domestic traveler and one is an
international traveler?
Round your final answer to THREE decimal places.

Math
ProbabilityA survey of 50 NYU College students revealed that 5 liked Statistics class. What is the probability of selecting a NYU Student at random based on these results and he/she does not like Statistics class?
2. What is the probability of rolling a two on the single roll of a die?
3. What is the probability of guessing the correct answer on a true or false question?
4. What is the probability of selecting a NYU Student at random and he/she is a Senior?