Vectors Questions and Answers

Math
VectorsFind the unit vector in the direction of 8 6 Write your answer in component form Do not approximate any numbers in your answer 0 0
Math
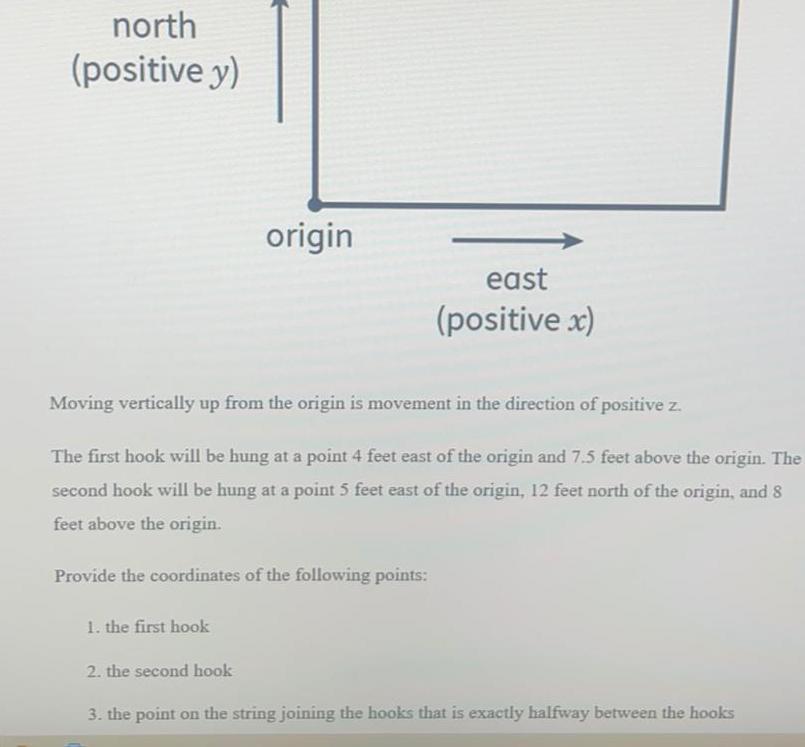
Vectorsnorth positive y 1 the first hook origin Moving vertically up from the origin is movement in the direction of positive z The first hook will be hung at a point 4 feet east of the origin and 7 5 feet above the origin The second hook will be hung at a point 5 feet east of the origin 12 feet north of the origin and 8 feet above the origin Provide the coordinates of the following points 2 the second hook east positive x 3 the point on the string joining the hooks that is exactly halfway between the hooks

Math
VectorsThe magnitude and direction of vectors t u and v are shown in the table Vector Magnitude Direction 5 250 t u V 335 305 155 1 0213 6 What is the direction of t u v Round to the nearest degree 12 60 330

Math
VectorsA vector has a magnitude of 50 and a direction of 30 Another vector has a magnitude of 60 and a direction of 150 What are the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector Round the magnitude to the thousandths place and the direction to the nearest degree 55 678 99 FESTO PU

Math
VectorsWhich of the below is are equivalent to the statement that a set of vectors v Vp in R is linearly independent Suppose also that A V V2 Vp A A linear combination of v Vp is the zero vector if and only if all weights are zero B The vector equation x V x2V2 XpVp 0 has only the trivial solution C There are weights not all zer which make a linear combination of the vectors V Vp the zero vector D The matrix equation Ax 0 has free variables E All columns of A are pivot columns The rank of A is equal to p F G The rank of A is equal to n

Math
VectorsVector u PQ has initial point P 3 17 and terminal point Q 9 2 Vector v RS has initial point R 30 6 and terminal point S 8 18 Part A Write u and v in linear form Show all necessary work 4 points Part B Write u and v in trigonometric form Show all necessary work 8 points Part C Find 7u 4v Show all necessary calculations 3 points

Math
VectorsVectors t 6i 2j u 4i 8j and v 4i 12j are give Part A Find the angle between vectors t and u Show all necessary calculations 5 points Part B Choose a value for c such that c 1 Find w cv Show all necessary work 2 points Part C Use the dot product to determine if t and w are parallel orthogonal or neither Justify your a
Calculus
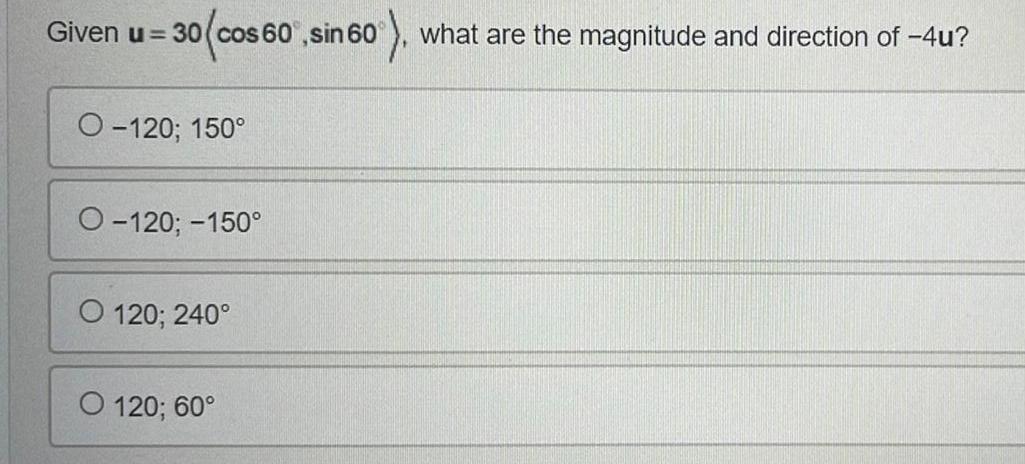
VectorsGiven u 30 cos 60 sin 60 what are the magnitude and direction of 4u O 120 150 O 120 150 O 120 240 O 120 60
Math
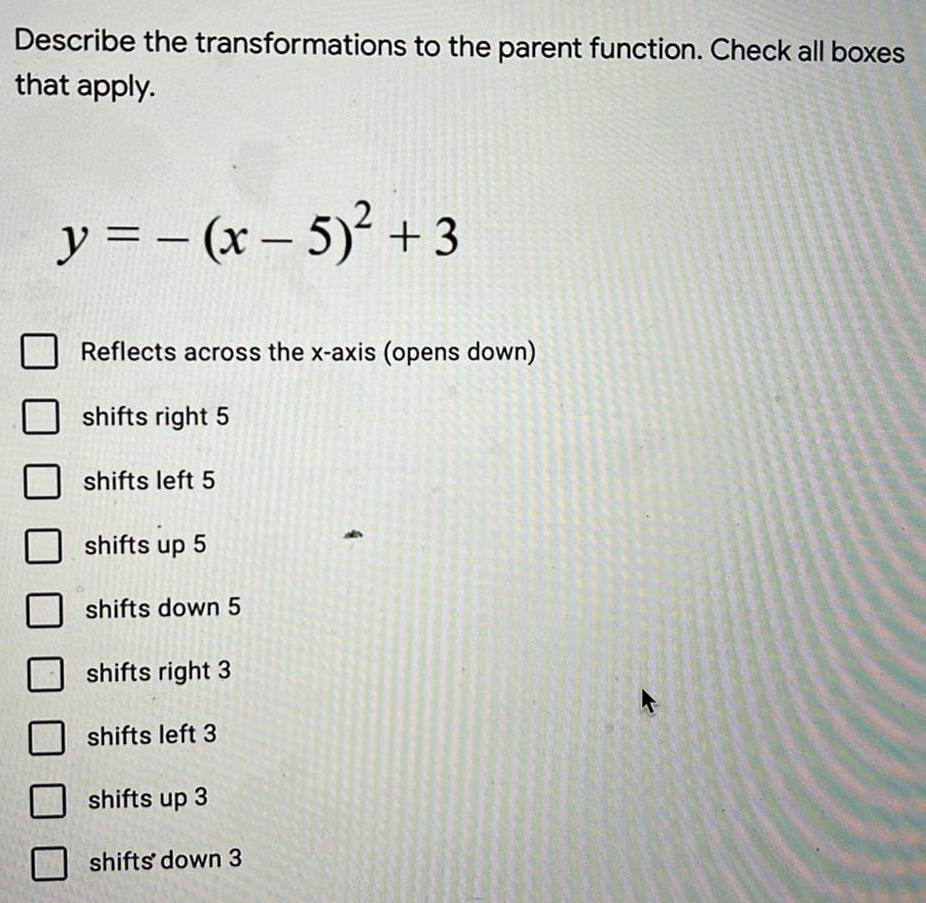
VectorsDescribe the transformations to the parent function. Check all boxes that apply.
y = -(x - 5)² +3
Reflects across the x-axis (opens down)
shifts right 5
shifts left 5
shifts up 5
shifts down 5
shifts right 3
shifts left 3
shifts up 3
shifts down 3
Math
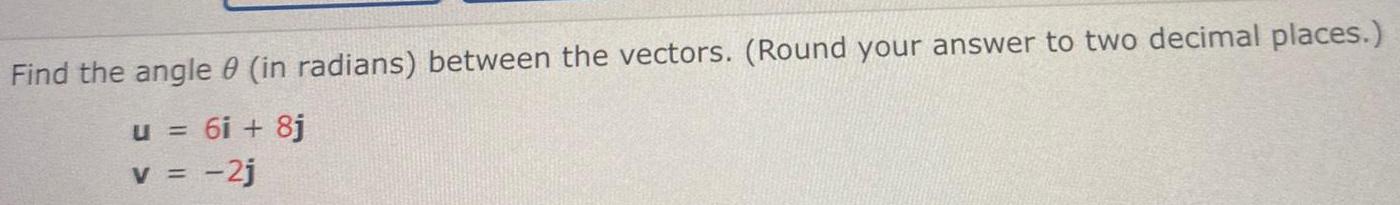
VectorsFind the angle 0 (in radians) between the vectors. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
u = 6i + 8j
v = -2j

Math
VectorsFind the projection of u onto v.
u = (4,8)
v = (6,-3)
Write u as the sum of two orthogonal vectors, one of which is projvu

Math
VectorsLet B =
be any 2 x 2 matrix.
and a such that
(i) Show that there are real numbers
as a scalar multiple of a unit vector, and hence find an
expression for u in terms of a and c.

Math
VectorsDetermine whether u and v are equivalent. Explain.
Vector Initial Point Terminal Point
Interpret your results.
u and v have the same magnitude and direction so they are equivalent.
u and v have the same magnitude but not the same direction so they are not equivalent.
u and v have the same direction but not the same magnitude so they are not equivalent.
u and v do not have the same magnitude or direction so they are not equivalent.
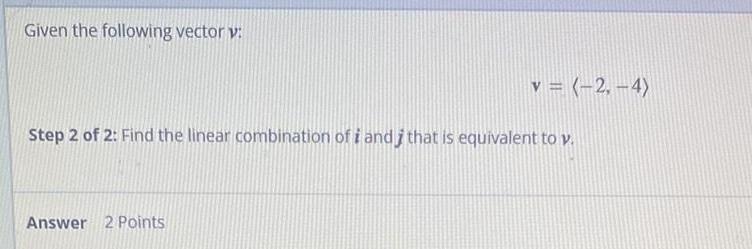
Math
VectorsGiven the following vector v:
v = (-2,-4)
Step 2 of 2: Find the linear combination of i and i that is equivalent to v.
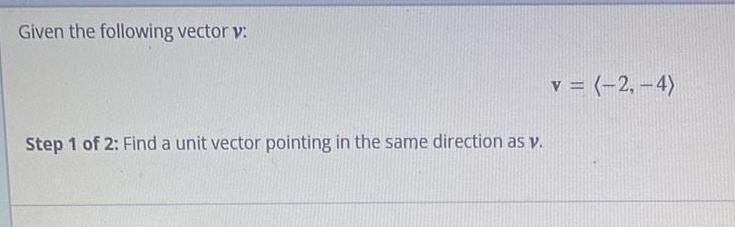
Math
VectorsGiven the following vector v:
Step 1 of 2: Find a unit vector pointing in the same direction as v.
v = (-2,-4)
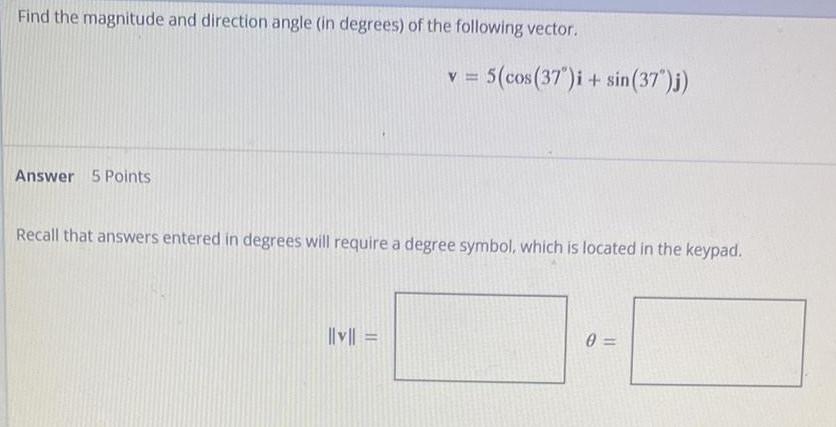
Math
VectorsFind the magnitude and direction angle (in degrees) of the following vector.
Answer 5 Points
v = 5(cos(37°)i + sin(37")j)
Recall that answers entered in degrees will require a degree symbol, which is located in the keypad.
|||v|| =
0=
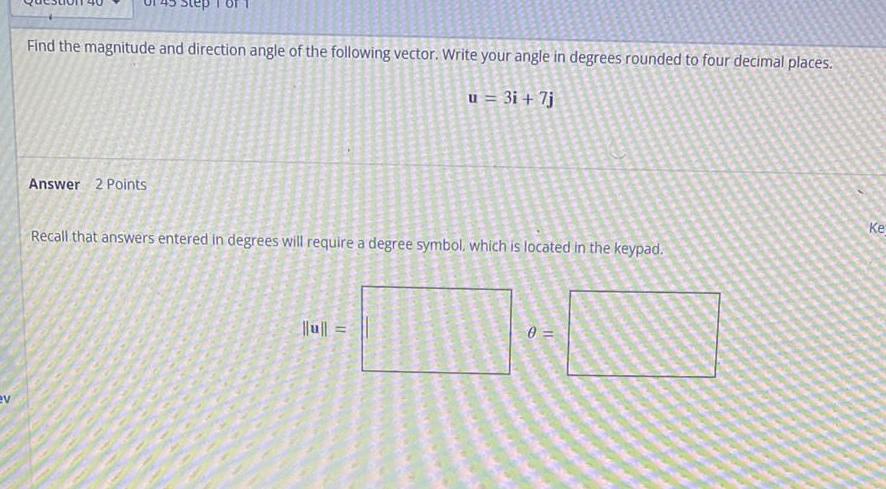
Math
VectorsFind the magnitude and direction angle of the following vector. Write your angle in degrees rounded to four decimal places.
u = 3i + 7j
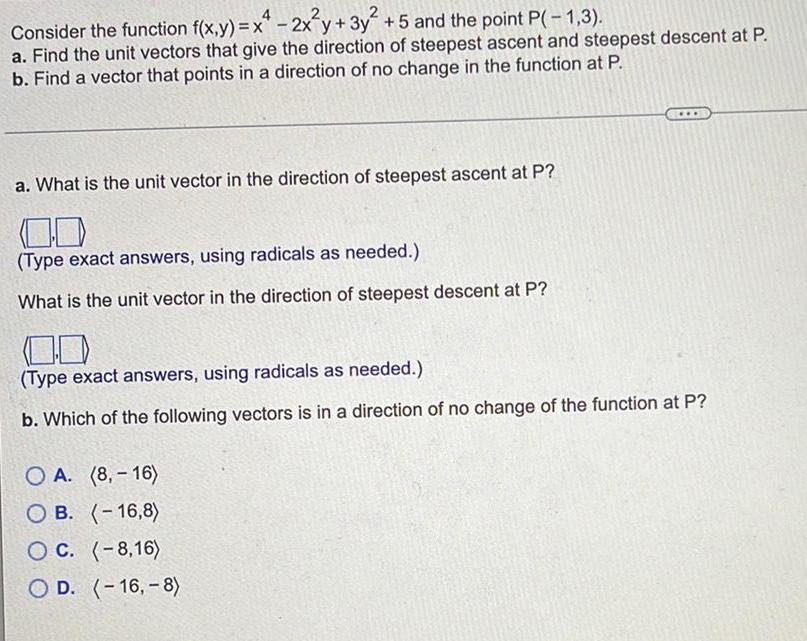
Math
VectorsConsider the function f(x,y) = x² - 2x²y+3y² +5 and the point P(-1,3).
a. Find the unit vectors that give the direction of steepest ascent and steepest descent at P.
b. Find a vector that points in a direction of no change in the function at P.
a. What is the unit vector in the direction of steepest ascent at P?
<_,_>
(Type exact answers, using radicals as needed.)
What is the unit vector in the direction of steepest descent at P?
<_,_>(Type exact answers, using radicals as needed.)
b. Which of the following vectors is in a direction of no change of the function at P?
A. (8,-16)
B. (-16,8)
C. (-8,16)
D. (-16,-8)

Math
VectorsA football was thrown into the air at a speed of 37 miles per hour at an angle of 50 from the horizontal. Express this velocity in vector form. Round your answer to four decimals.
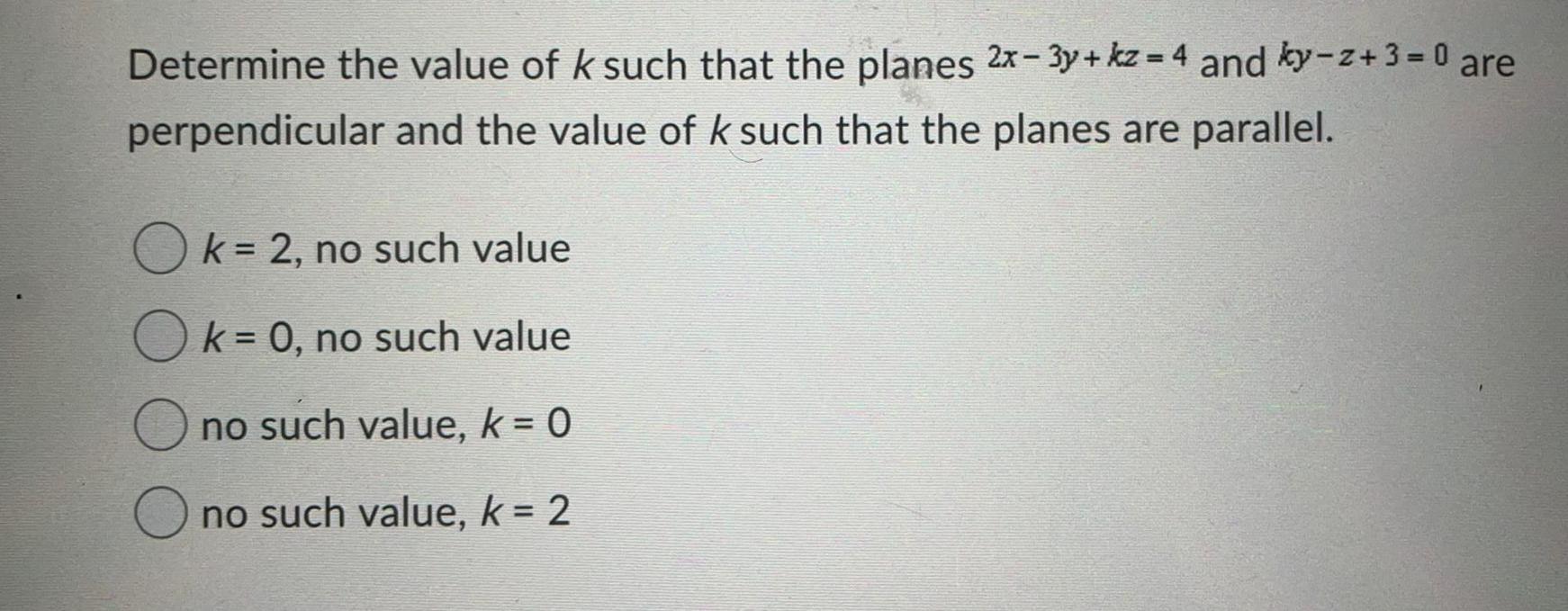
Math
VectorsDetermine the value of k such that the planes 2x-3y+kz=4 and ky-z+3=0 are perpendicular and the value of k such that the planes are parallel.
k = 2, no such value
k = 0, no such value
no such value, k = 0
no such value, k = 2

Math
VectorsThe area of the parallelogram whose adjacent sides are given by the vectors
a = 3i + j + 4k and b = i - j +k
(A) √50
(B) √42
(C) √44
(D) None of these
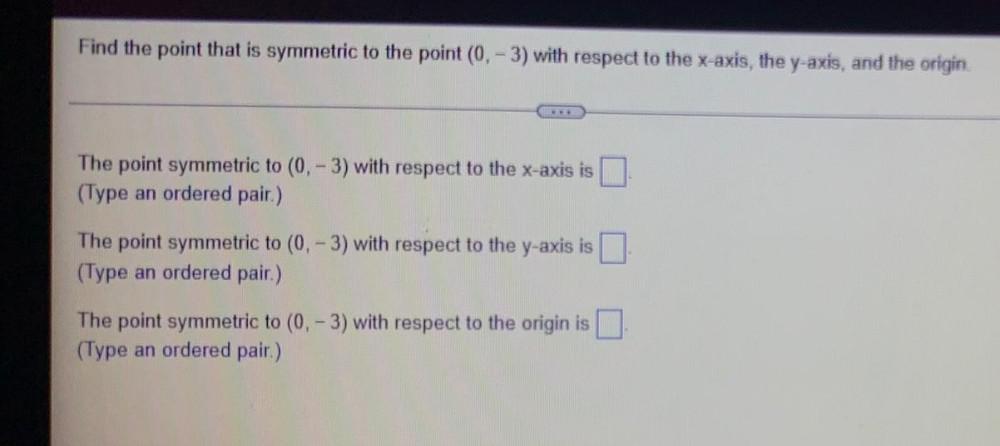
Math
VectorsFind the point that is symmetric to the point (0, -3) with respect to the x-axis, the y-axis, and the origin
The point symmetric to (0, -3) with respect to the x-axis is
(Type an ordered pair.)
The point symmetric to (0, -3) with respect to the y-axis is
(Type an ordered pair.)
The point symmetric to (0, -3) with respect to the origin is
(Type an ordered pair.)

Math
VectorsLet u and u be two vectors in an inner product space so that ||u||= 6, |v||=2 and the angle between the two vectors is 30°. Find the angle between vector u+3v and vector u-4v
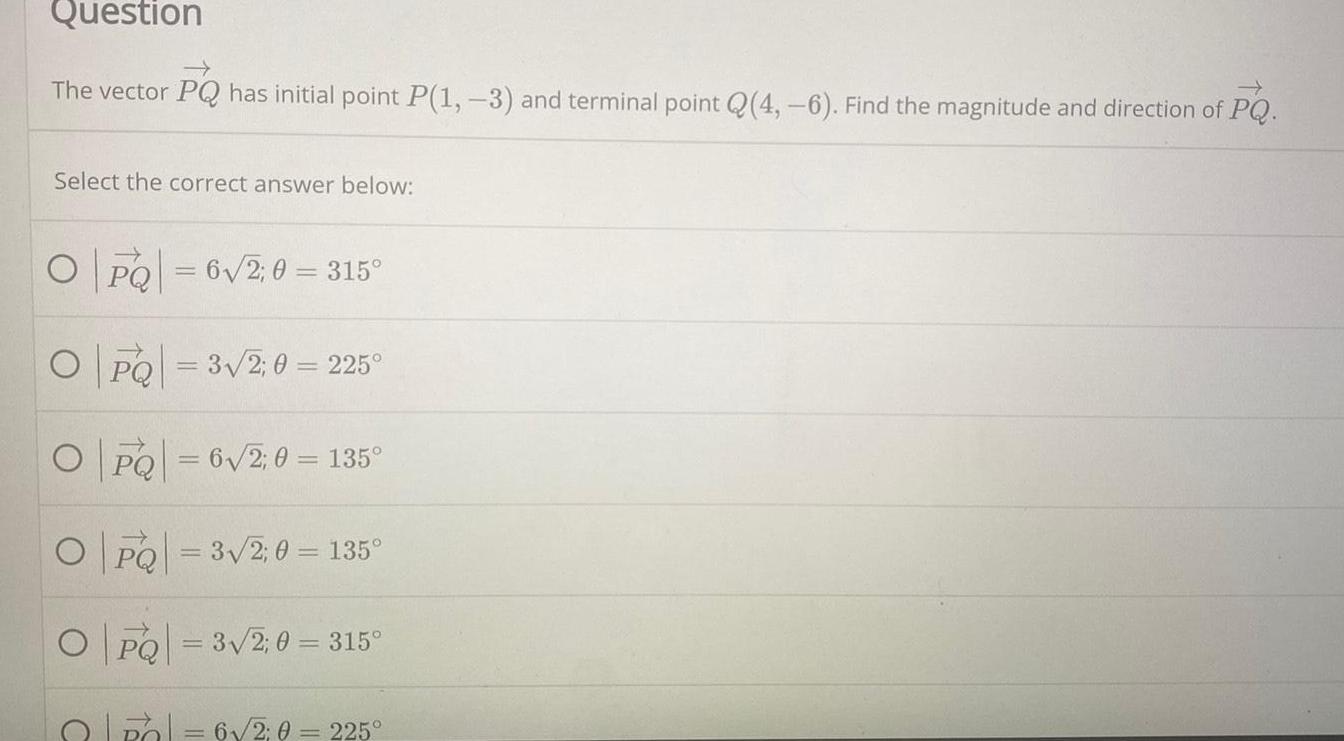
Math
VectorsThe vector PQ has initial point P(1, -3) and terminal point Q(4, -6). Find the magnitude and direction of PQ.
Select the correct answer below:
|PQ|=6√2; θ=315°
|PQ|=3√/2 θ = 225°
|PQ|-6√2; θ= 135°
|PQ|=3√2; θ= 135°
|PQ|=3√2; θ=315°
|PQ|=6√2; θ = 225°

Math
VectorsLet V be a vector space with dimension n. Consider the following statements.
(i) Every independent set in V is a basis for V
(ii) Every set in V that spans V must be independent
(iii) Every set in V with less than n vectors must be independent.
Which of the above statements is always true?
(a) (ii) and (iii) only (b) (iii) only (c) (ii) only (d) none of them
(e) (i) only

Math
Vectors4. X(-1, 2, 6) and Y(5, 5, 12) are two points in R³.
a). Determine the components of a position vector equivalent to YX.
b). Determine the components of a unit vector that is in the same direction as YX.
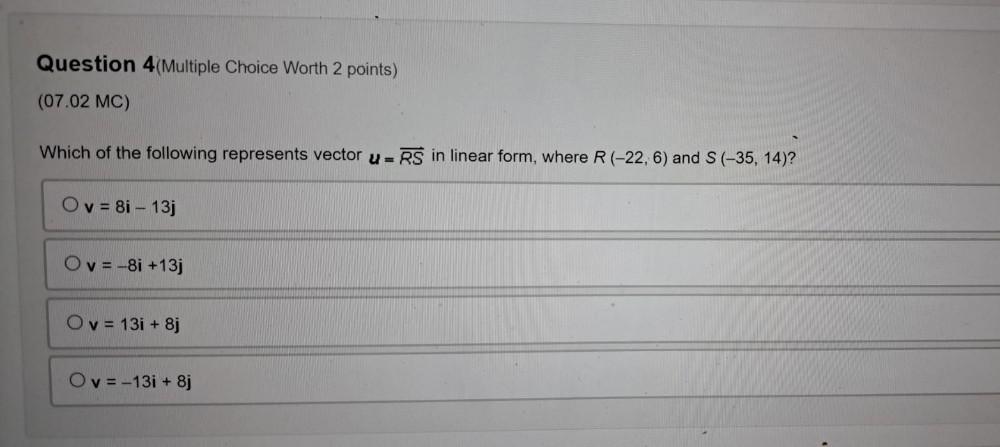
Math
VectorsWhich of the following represents vector u=RS in linear form, where R (-22, 6) and S(-35, 14)?
v= 8i - 13j
v= -8i +13j
v = 131 + 8j
v= -13i + 8j
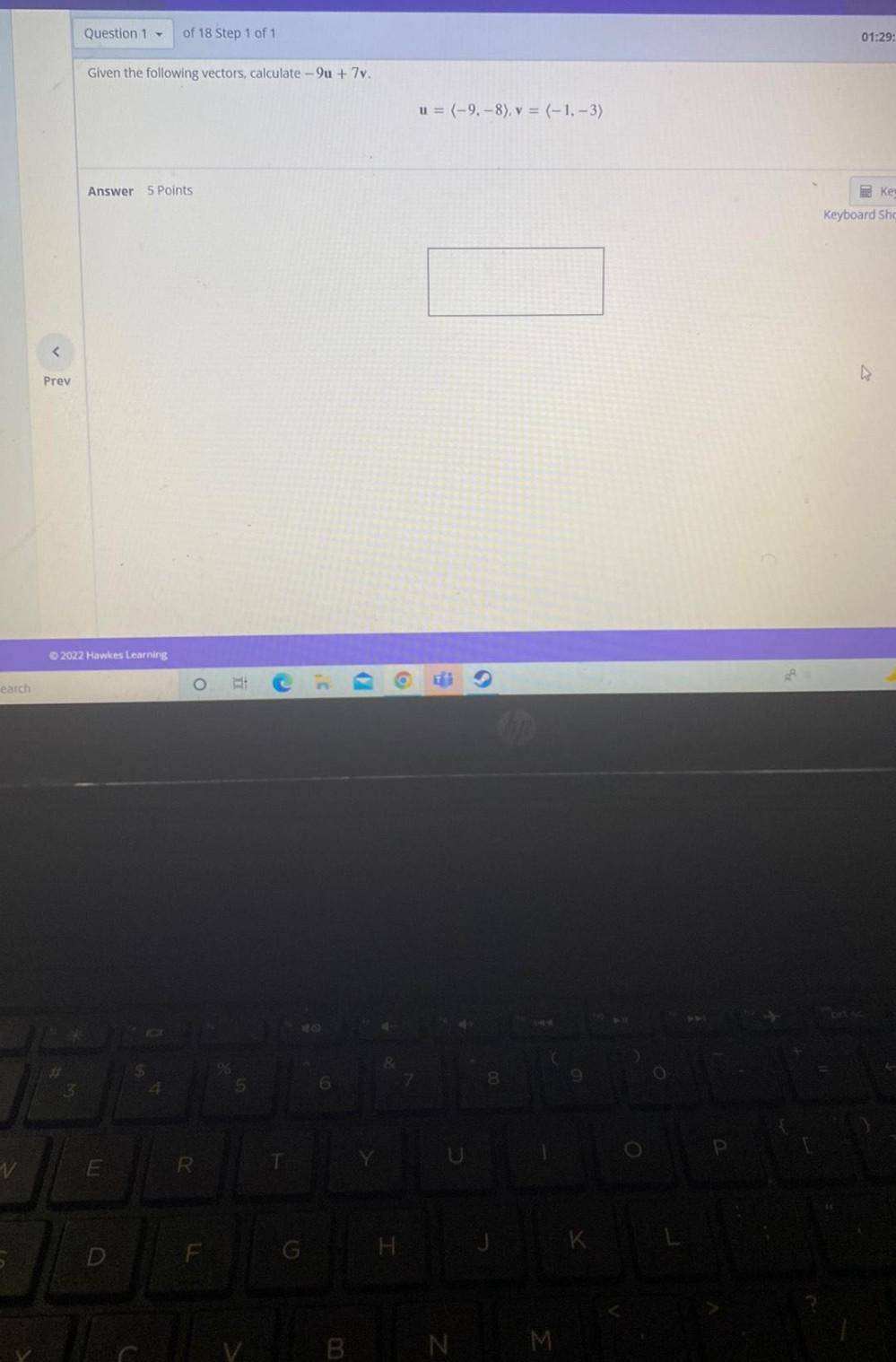
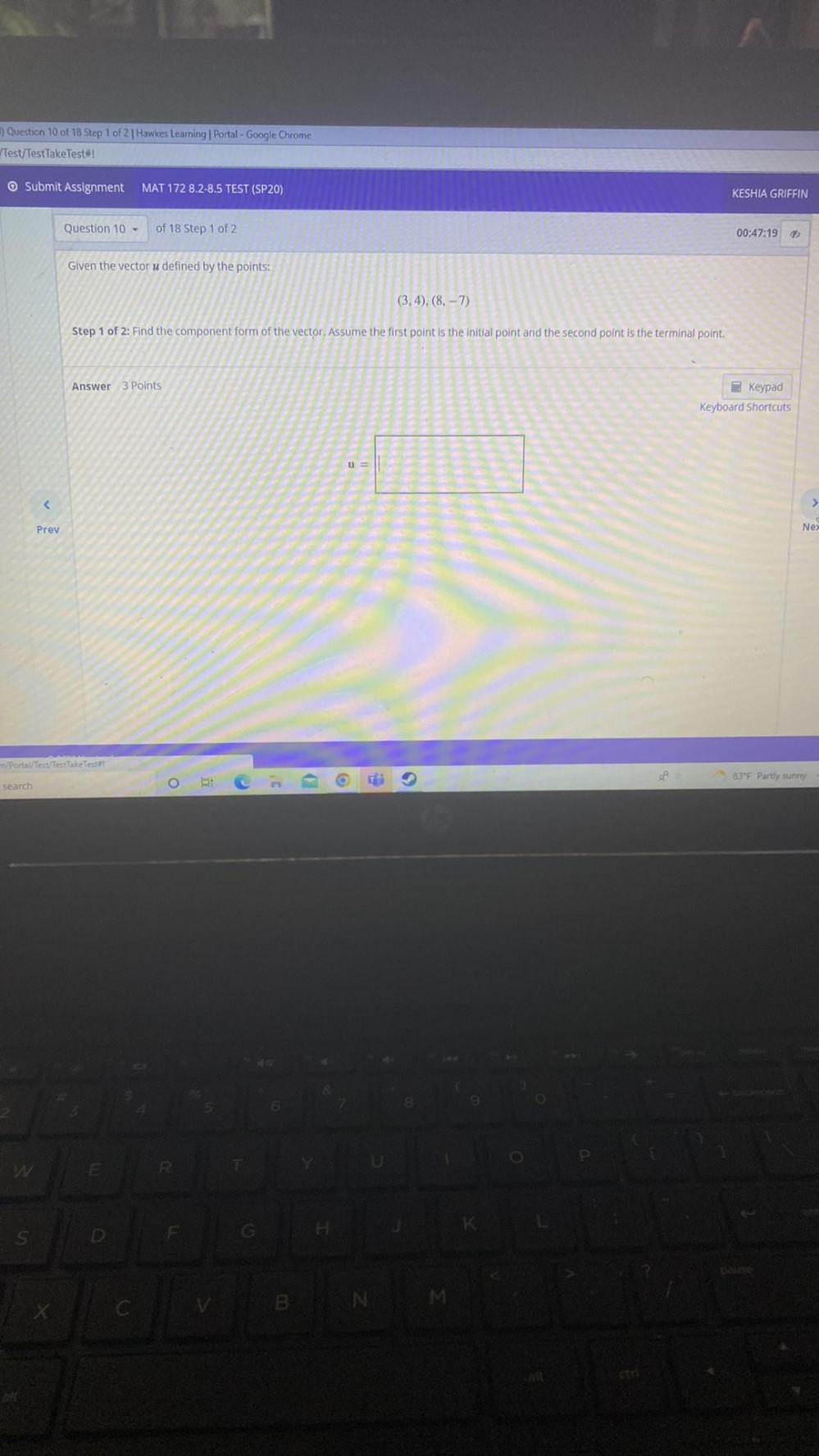
Math
VectorsGiven the vector u defined by the points: (3,4), (8, -7). Find the component form of the vector. Assume the first point is the initial point and the second point is the terminal point.
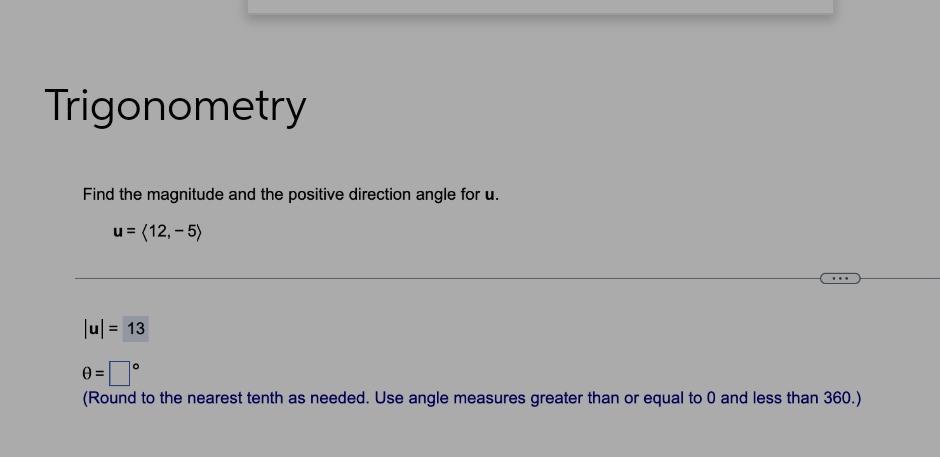
Math
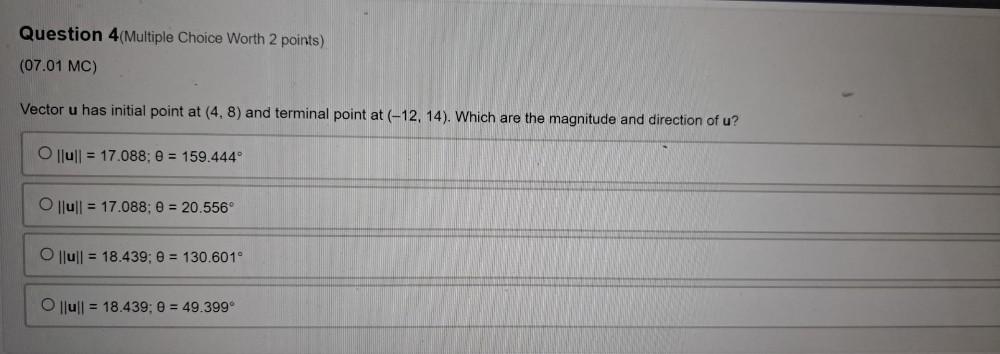
VectorsVector u has initial point at (4,8) and terminal point at (-12, 14). Which are the magnitude and direction of u?
a)lull = 17.088; θ = 159.444°
b)|lull = 17.088; θ = 20.556°
c)llull = 18.439; θ = 130.601°
d)|lull = 18.439; θ = 49.399
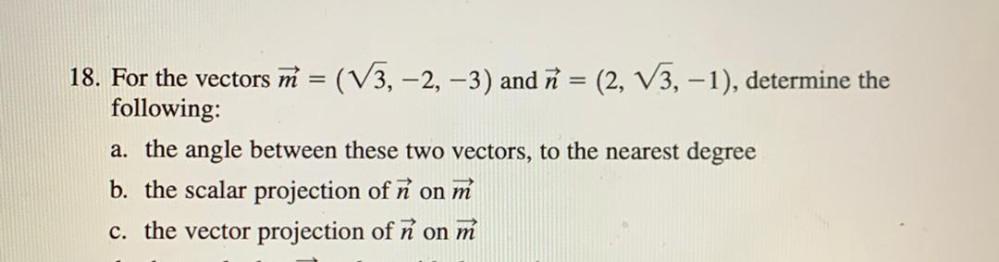
Math
VectorsFor the vectors M = (√3, -2, -3) and n = (2, √3, -1), determine the following:
a). the angle between these two vectors, to the nearest degree
b). the scalar projection of ñ on m
c). the vector projection of n on m

Math
VectorsFind the vector w w of length 6 6 in the direction of v = 8 i +7j. v=8i+7j. (Give your answer using component form or standard basis vectors. Express numbers in exact form. Use symbolic notation and fractions where needed.)

Math
VectorsFind the angle between the vectors (7, 2) and (9, -3). Carry your intermediate computations to at least 4 decimal places. Round your final answer to the nearest degree.

Math
VectorsFind the angle between the vectors (-9, -8) and (-8, 7). Carry your intermediate computations to at least 4 decimal places. Round your final answer to the nearest degree.

Math
VectorsLet u = -5i +2j and v=-5i-5j. Decompose u into two vectors u1, and u₂, where u1, is parallel to v and u2, is orthogonal to v.
Write your answers in the form ai+bj.

Math
VectorsFind the direction angle of the vector u = -3i+5j. That Is, find the angle between 0° and 360° that u makes with the positive x-axis (measured counterclockwise), when u is in standard position.
Do not round any intermediate computations, and round your answer to the nearest whole number.

Math
VectorsFind the direction angle of the vector w=6i-4j. That is, find the angle between 0° and 360° that w makes with the positive x-axis (measured counterclockwise), when w is in standard position.
Do not round any intermediate computations, and round your answer to the nearest whole number.

Math
Vectors(a) An angle measures 26°. What is the measure of its complement?
(b) An angle measures 150°. What is the measure of its supplement?

Math
Vectorsu =(-4,-5)
Find the magnitude of .
Enter an exact answer as an expression with a square root symbol or enter an approximate answer as a decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth.
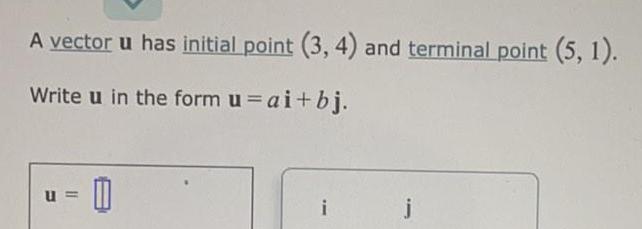
Math
VectorsA vector u has initial point (3, 4) and terminal point (5, 1).
Write u in the form u = ai+bj.
u=

Math
VectorsFind the direction angle of the vector v=-8i-7j. That is, find the angle between 0° and 360° that v makes with the positive x-axis (measured counterclockwise), when v is in standard position.
Do not round any intermediate computations, and round your answer to the nearest whole number.
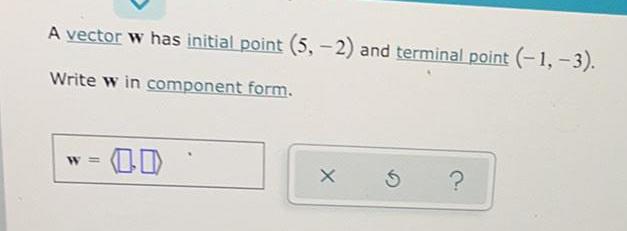
Math
VectorsA vector w has initial point (5,-2) and terminal point (-1, -3).
Write w in component form.
W =

Math
VectorsFind the direction angle of the vector u = -7i+4j. That is, find the angle between 0° and 360° that u makes with the positive x-axis (measured counterclockwise), when u is in standard position.
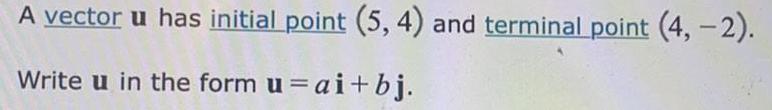
Math
VectorsA vector u has initial point (5, 4) and terminal point (4, -2).
Write u in the form u = ai + bj.


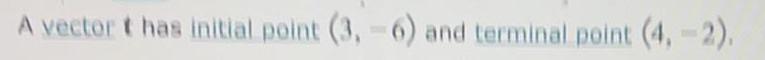

Math
VectorsFind the direction angle of the vector v=-3i-8j. That is, find the angle between 0 and 360° that v makes with the positive x-axis (measured counterclockwise), when v is in standard position. Do not round any intermediate computations, and round your answer to the nearest whole number.
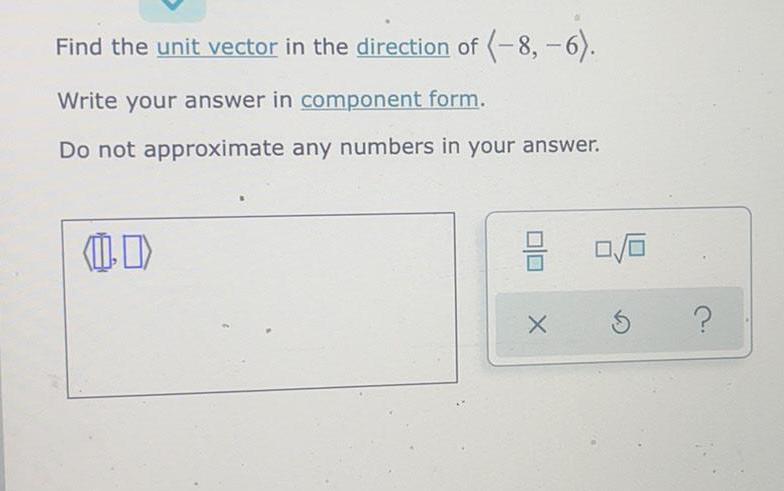
Math
VectorsFind the unit vector in the direction of (-8,-6).
Write your answer in component form.
Do not approximate any numbers in your answer.