Probability Questions and Answers

Math
ProbabilityLet p and q represent the following statements.
p: You study hard.
q: You graduate with honors.
Write the following statement in symbolic form: "You study hard or you don't graduate with honors."
To enter your response, select the appropriate statement in each of the dropdown boxes, and select the
appropriate operation in the middle. If only one statement is used, select "none" for the operation in the
middle and the statement in the second dropdown box. Be sure to enter the statements in the same order
as in the given sentence.

Math
ProbabilityAn American roulette wheel has 18 red slots, 18 black slots, and 2 green slots.
What is the probability that the ball lands on red, given that the ball does not land
on black?
has 4 freshmen, 6 sophomores, 5 juniors, and 3 senion
Math
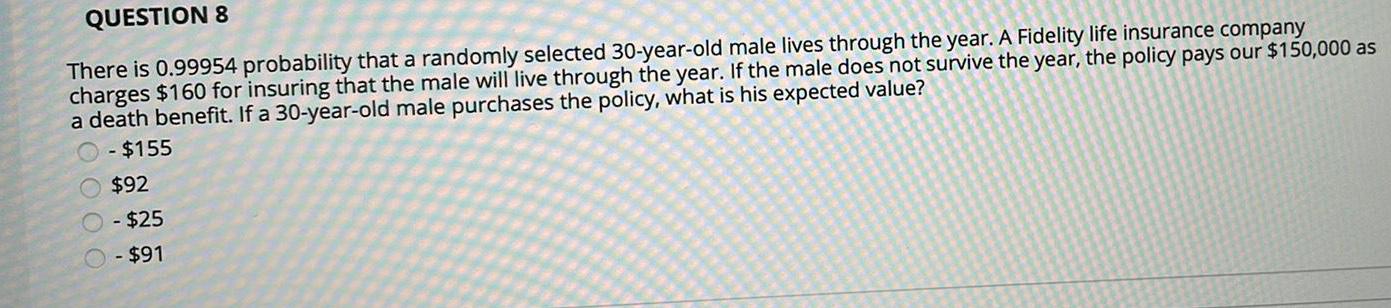
ProbabilityQUESTION 8
There is 0.99954 probability that a randomly selected 30-year-old male lives through the year. A Fidelity life insurance company
charges $160 for insuring that the male will live through the year. If the male does not survive the year, the policy pays our $150,000 as
a death benefit. If a 30-year-old male purchases the policy, what is his expected value?
- $155
$92
O-$25
O - $91

Math
ProbabilityIn a survey funded by the University of Washington School of Medicine, 98 of 1,400 adult Seattle residents said
they did not believe they could come down with a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Construct a 95%
confidence interval estimating the proportion of adult Seattle residents that do not believe they can contract an
STI. Round the answers to three decimal places.
Preliminary:
a. Is it safe to assume that n < 5% of all residents in Seattle?
O Yes
O No
b. Verify np (1-p) ≥ 10. Round your answer to one decimal place.
np (1 - p) =
Confidence Interval: What is the 95% confidence interval to estimate the population proportion? Round your
answer to three decimal places.
< p <

Math
ProbabilityA life insurance company sells a $200,000 1-year term life insurance policy to a 20-year-old female for $150. The probability that the
female survives the year is 0.999541. Compute the expected value of this policy to the insurance company.
$40.20
$52.80
$58.80
52.20
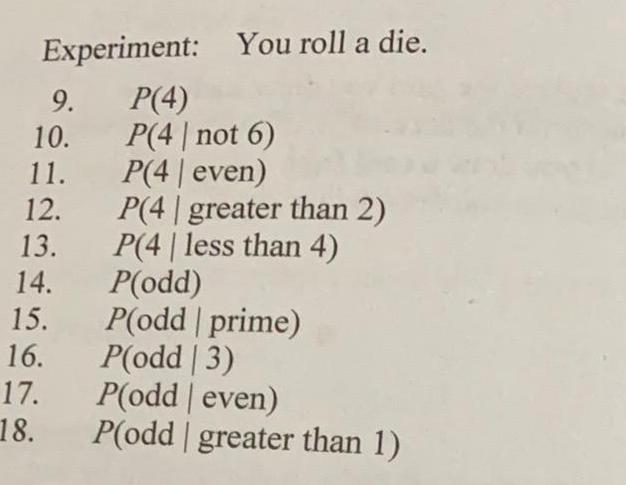
Math
ProbabilityExperiment: You roll a die.
9. P(4)
10. P(4 | not 6)
11. P(4| even)
12. P(4 | greater than 2)
13. P(4 | less than 4)
14. P(odd)
15. P(odd | prime)
16. P(odd | 3)
17. P(odd | even)
18. P(odd greater than 1)

Math
ProbabilityA life insurance company sells a $130,000 1-year term life insurance policy to a 20-year-old female for $180. The probability that the female survives the year is 0.999212. Compute the expected value of this policy to the insurance company.
$80.86
$77.56
$63.86
$61.68

Math
ProbabilityBattery lifetime is normally distributed for large samples. The mean lifetime is 500 days
and the standard deviation is 61 days.
a) Find the distribution by filling in the blanks:
X~N(
)
b) Find the probability of batteries that have lifetimes longer than 561 days? Round to 4
decimals.
c) Find the probability of batteries that have lifetimes at most 497 days? Round to 4
decimals.
d) Find the 75th percentile. Round to 1 decimal.

Math
ProbabilityThe duration of a professor's class has continuous uniform distribution between 49.2 minutes and 55.5 minutes. If one class is randomly selected and the probability that the duration of the class is longer than a certain number of minutes is 0.592, then find the duration of the randomly selected class, i.e., if P(x> c) = 0.592, then find c, where c is the duration of the randomly selected class. Round your answer to one decimal places.

Math
ProbabilityA doctor gives a patient a 90% chance of surviving bypass surgery after a heart attack. If the patient survives the surgery, then the patient has
a 40% chance that the heart damage will heal. Find the probability that the patient survives the surgery and the heart damage heals.
The probability is
(Type an integer or a decimal.)
*****
Math
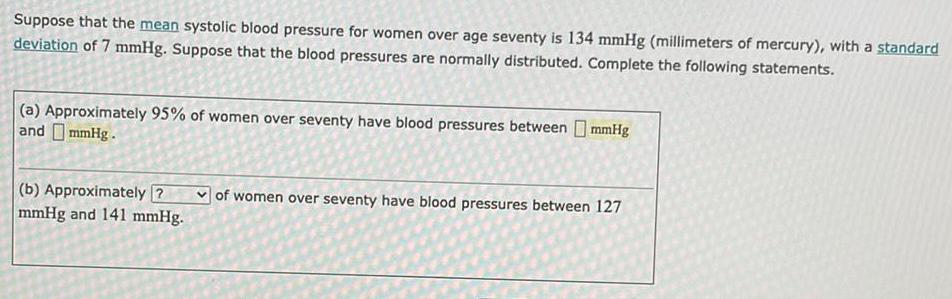
ProbabilitySuppose that the mean systolic blood pressure for women over age seventy is 134 mmHg (millimeters of mercury), with a standard
deviation of 7 mmHg. Suppose that the blood pressures are normally distributed. Complete the following statements.
(a) Approximately 95% of women over seventy have blood pressures between mmHg
and mmHg.
(b) Approximately 2
mmHg and 141 mmHg.
of women over seventy have blood pressures between 127

Math
ProbabilityA student is listening to songs that are on his phone. On his phone, he has 10 county songs, 15 Pop songs, 5 R&B songs, 10 rap songs, and 5 techno songs (for a total of 45 songs). He set his phone to shuffle so that it randomly plays music. If the phone randomly selects the next song, what is the probability that it will play a Pop song?
2/9
1/3
1/9
2/3
Math
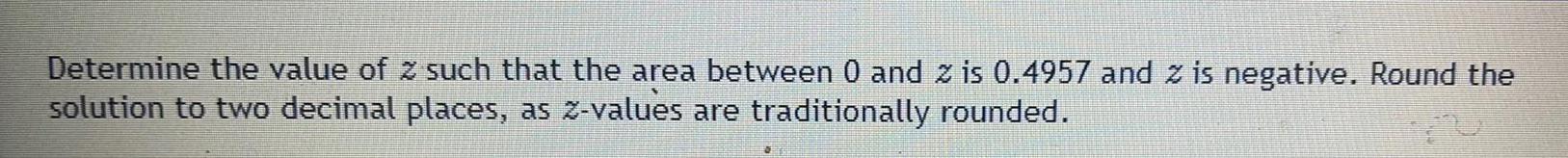
ProbabilityDetermine the value of z such that the area between 0 and 2 is 0.4957 and 2 is negative. Round the
solution to two decimal places, as z-values are traditionally rounded.

Math
Probability41% of U.S. adults have very little confidence in newspapers. You randomly select 10 U.S. adults. Find the probability that the number of U.S. adults who have very little confidence in newspapers is (a) exactly five, (b) at least six, and (c) less than four.

Math
ProbabilityA random number generator picks a number from 2 to 18 in a uniform manner.
Find P(x>7.53)
0.681
0.654
0.612
0.692

Math
ProbabilitySixty-four percent of adults in a certain country believe that life on other planets is plausible. You randomly select five adults and
ask them whether they believe that life on other planets is plausible. The random variable represents the number of adults who
believe that life on other planets is plausible. Find the mean, variance, and standard deviation of the binomial distribution for the
random variable. Interpret the results.
02= 1.15 (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Find the standard deviation of the binomial distribution.
o= 1.07 (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Interpret the results.
On average, out of every 5 adults in the country believe that life on other planets is plausible. In most samples of 5 adults,
the number of adults who think life on other planets is plausible would differ from the mean by no more than
(Type integers or decimals rounded to two decimal places as needed.)
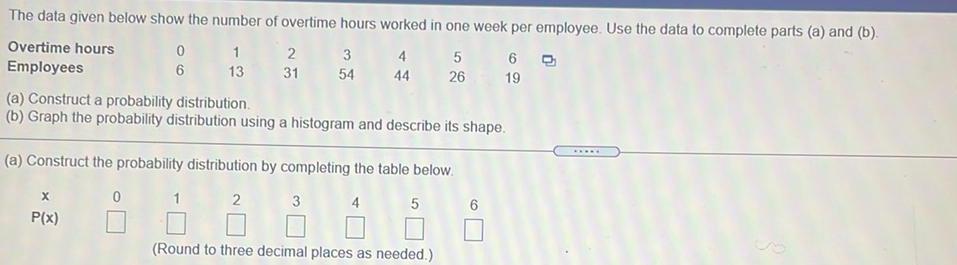
Math
ProbabilityThe data given below show the number of overtime hours worked in one week per employee. Use the data to complete parts (a) and (b).
Overtime hours
5
0 1 2 3 4
44 26
Employees
6
13
31
54
(a) Construct a probability distribution.
(b) Graph the probability distribution using a histogram and describe its shape.
(a) Construct the probability distribution by completing the table below.
0
1 2
5
X
P(x)
3
4
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
6 Q
19
6
www.

Math
ProbabilityF and H are sets of real numbers defined as follows.
F= {x|x≥4}
H= {x|x>8}
Write FUH and FOH using interval notation.
If the set is empty, write ø.

Math
ProbabilityA company prices its tornado insurance using the following assumptions:
• In any calendar year, there can be at most one tornado.
In any calendar year, the probability of a tornado is 0.14.
• The number of tornadoes in any calendar year is independent of the number of tornados in any
other calendar year.
Using the company's assumptions, calculate the probability that there are fewer than 2 tornadoes in
a 17-year period.

Math
ProbabilityOut of 100 people sampled, 10 had kids. Based on this, construct a 95% confidence interval for the true
population proportion of people with kids.
Give your answers as decimals, to three places
I am 95% confident that the proportion of people who have kids is between
A
and

Math
Probability23% of U.S. adults say they are more likely to make purchases during a sales tax holiday. You randomly select 10 adults. Find the
probability that the number of adults who say they are more likely to make purchases during a sales tax holiday is (a) exactly two,
(b) more than two, and (c) between two and five, inclusive.
*****
(a) P(2)= 0.294 (Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.)
(b) P(x>2) = (Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.)

Math
ProbabilityA history professor decides to give a 20-question true-false quiz. She wants to choose the passing grade such that the probability of passing a student who guesses on
every question is less than 0.10. What score should be set as the lowest passing grade?
15
14
12
13
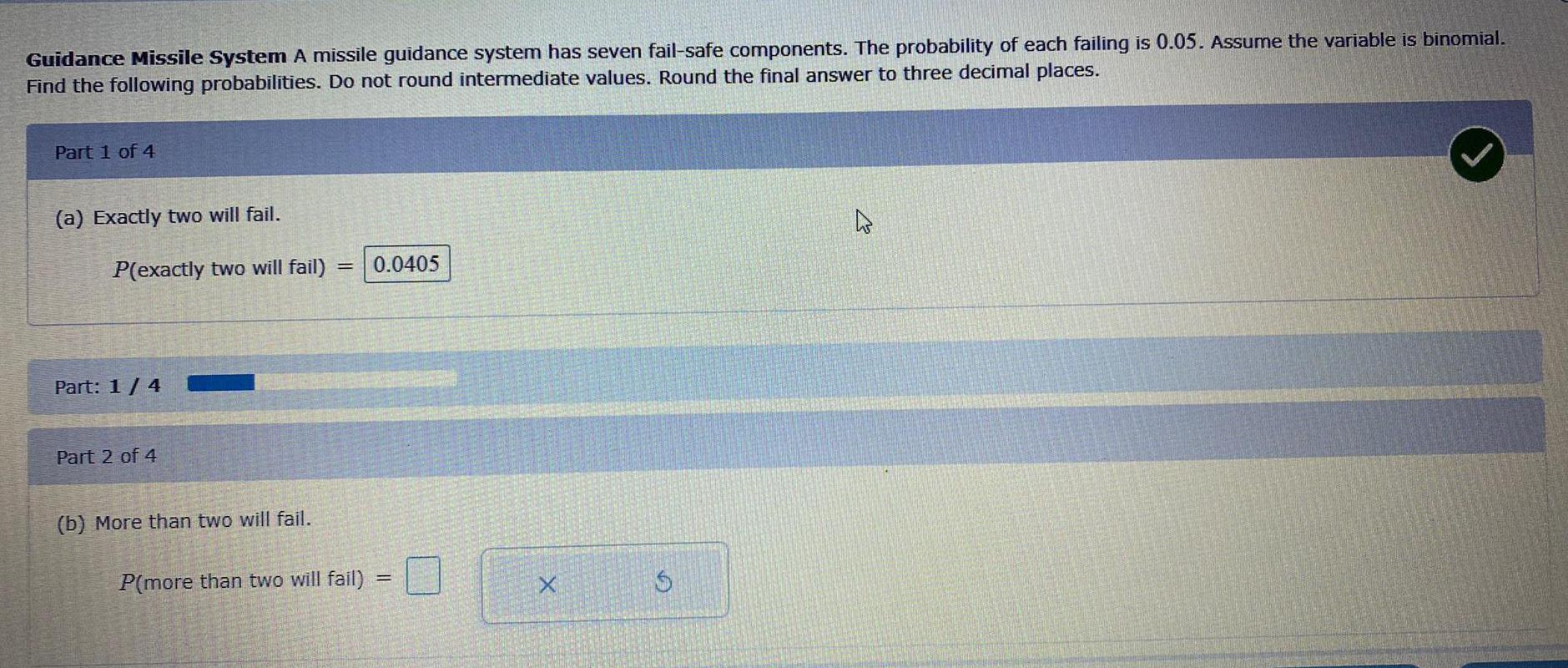
Math
ProbabilityGuidance Missile System A missile guidance system has seven fail-safe components. The probability of each failing is 0.05. Assume the variable is binomial.
Find the following probabilities. Do not round intermediate values. Round the final answer to three decimal places.
Part 1 of 4
(a) Exactly two will fail.
P(exactly two will fail)
Part: 1/4
Part 2 of 4
(b) More than two will fail.
= 0.0405
P(more than two will fail)
=
$
2
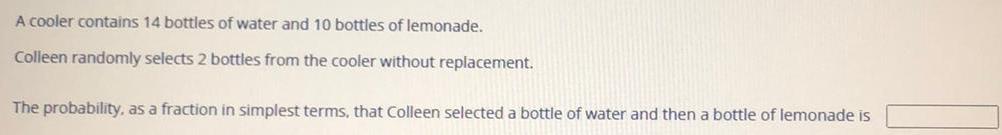
Math
ProbabilityA cooler contains 14 bottles of water and 10 bottles of lemonade.
Colleen randomly selects 2 bottles from the cooler without replacement.
The probability, as a fraction in simplest terms, that Colleen selected a bottle of water and then a bottle of lemonade is

Math
ProbabilityIn the game of roulette, a player can place a $6 bet on the number 21 and have a probability of winning. If the metal ball lands on 21, the player gets to keep the $6 paid to play the game and the player is awarded an additional $210. Otherwise, the player is awarded nothing and the casino takes the player's $6. Find the expected value E(x) to the player for one play of the game. If x is the gain to a player in a game of chance, then E(x) is usually negative. This value gives the average amount per game the player can expect to lose.
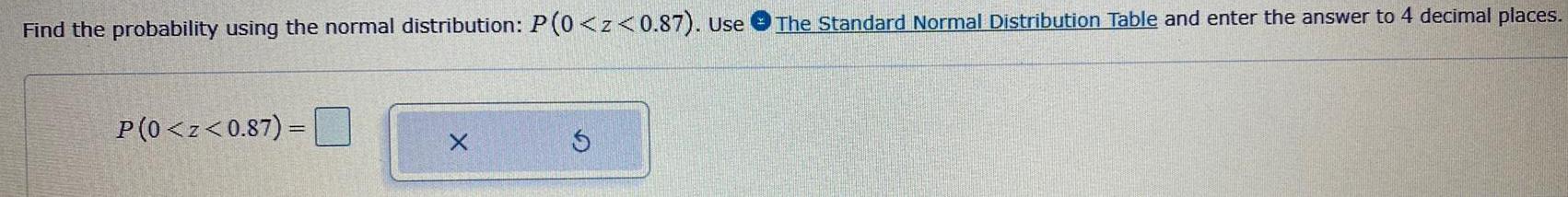
Math
ProbabilityFind the probability using the normal distribution: P (0<z<0.87). Use The Standard Normal Distribution Table and enter the answer to 4 decimal places.
P(0<z<0.87) =
X
S

Math
ProbabilityThe 50 yard freestyle times of a college swim team are normally distributed with a mean of 25.05 seconds and
a standard deviation of 3.71 seconds. Determine the probability that a randomly selected swimmer has a 50
yard freestyle time of 19.92 seconds or less. Round the solution to four decimal places, if necessary.
P(x≤ 19.92) =

Math
ProbabilityA frequency distribution is shown below. Complete parts (a) and (b).
The number of televisions per household in a small town
Televisions
0
2
3
Households 25
724
1403
(a) Use the frequency distribution to construct a probability distribution.
P(x)
XO-23
0
1
441
1
Math
ProbabilityA random number generator is used to select an integer from 1 to 100 (inclusively). What is the probability of selecting the integer 69?
The probability is
(Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)

Math
ProbabilityA school newspaper reporter decides to randomly survey 12 students to see if they will attend Tet (Vietnamese New Year) festivities this year. Based on past years, she knows that 18% of students attend Tet festivities. We are interested in the number of students, from the sample, who will attend the festivities.

Math
ProbabilityThere are two tests for aptitude in Data Management (and in particular probability). Test A gives a correct result 95% of the time. Test B is accurate 90% of the time. These tests are independent. If a student is given both tests, find the probability that
a. Only one of the tests will predict the correct result.
b. Test A or B will predict the correct result.

Math
ProbabilityAccording to the American Red Cross, 9.5% of all Connecticut residents have Type B blood. A random sample of 19 Connecticut residents is taken.
X = the number of CT residents that have Type B blood, of the 19 sampled.
What is the expected value of the random variable X?
1.596 1.805 1.957 1.634 2.014 2.09
Math
ProbabilityAccording to government data, the probability that an adult was never in a museum is 15%. In a random survey of 10 adults, what is the probability that at least eight were in a museum?
0.200
0.800
0.820
0.002

Math
ProbabilityFind the z value that corresponds to the given area in the figure below. Use The Standard Normal Distribution Table and enter the answer to 2 decimal places.
(Note: Figure not drawn to scale.)
Math
ProbabilityThe probability that an event will happen is P(E)=0.38. Find the probability that the event will not happen.
The probability that the event will not happen is
(Simplify your answer.)

Math
ProbabilityPeople with type O-negative blood are referred to as universal donors. Although if you give type O-negative blood to any patient, you run the risk of a transfusion reaction due to certain antibodies present in the blood. However, any patient can receive a transfusion of O-negative red blood cells. Only 7.2% of the American population have O-negative blood. If 7 people appear at random to give blood, what is the probability that at least one of them is a universal donor? Give your answer to four decimal places.
Math
ProbabilityYou are given a bag of jelly beans. There are 7 red, 8 blue, 4 yellow, and 10 pink. Find the probability of eating 3 yellow jelly beans in a row. (This implies you don't replace the jelly bean after you choose it.)

Math
ProbabilityOne of the problems encountered by corporations in America is finding an adequate number of employees who want to move into management. Recent surveys of workers in America taken by the Department of Labor in Washington D. C. revealed that only 20% of employees would like to move into management and be the boss. Suppose that a random sample of 75 U.S. workers was taken and each person was asked whether or not they would like to move into management. Find the probability that at most 18 of the 75 sampled employees would not like to move into management.
0.0000
1.0000
0.8440
0.1660
None of the above
Math
Probabilityat the animal shelter where Miguel volunteers on the weekends, there were three Siamese cats, four tabby cats, eighteen mixed-breed dogs, and five iguanas i heir cages. If a customer picks any of these animals at random, find the probability that the animal is either a mixed-breed dog or a Siamese cat. Express you answer as a reduced fraction.
Math
ProbabilityAverage sales for an online textbook distributor were $71.75 per customer per purchase. Assume the sales are normally distributed. If the standard deviation of the amount spent on textbooks is $8.79, find these probabilities for a randomly selected customer of the online textbook distributor.
The probability that a randomly selected customer spent more than $63 per purchase is

Math
ProbabilityExplain why the t-distribution has less spread as the number of degrees of freedom increases.
Choose the correct answer below.
A. The t-distribution has less spread as the degrees of freedom increase because, for large values of n, n ≥30, the t-distribution and the normal distribution are the same.
B. The t-distribution has less spread as the degrees of freedom increase because, as n increases, less information is known about o by the law of large numbers.
C. The t-distribution has less spread as the degrees of freedom increase because, as n increases, s becomes closer to o by the law of large numbers.
D. The t-distribution has less spread as the degrees of freedom increase because the variability introduced into the t-statistic becomes greater as n increases.
Math
ProbabilityWhen Milo went to register for classes at the last minute, the only classes left to take were eight math courses, five computer science courses, four statistics courses, and six science courses. He shut his eyes and picked one at random. Find the probability that Milo selected either a science course or a math course. Express your answer as a reduced fraction.

Math
ProbabilityA literature teacher will use four books during the semester. The six possible books to use are War and Peace, The Hobbit, The Glass Menagerie, The Old Man and the Sea, Frankenstein, and The Tale of Two Cities. If the probability of selecting each books is equal, what is the probability that the class will read these four books in this order. The Glass Menagerie, The Hobbit, War and Peace, and The Tale of Two Cities?
1/4
1/24
1/360
1/15

Math
ProbabilityTimes for an ambulance to respond to a medical emergency in a certain town are normally distributed with a mean of 450 seconds and a standard deviation of 50 seconds. There are 288 emergencies in the town.
In about how many emergencies would response times between 400 seconds and 500 seconds?
The weights of bags of ready-to-eat salad are normally distributed with a mean of 300 grams and a standard deviation of 9 grams.
What percent of the bags weigh less than 282 grams?
2.5%
5%
13.5%
34%

Math
ProbabilityThe replacement times for cell phones are normally distributed with mean 3.1 years and standard deviation 0.8 years. What length of time separates the top 5% of cell phone replacements from the rest?
The replacement time cut-off for the top 5% is
11.1 years
3.2 years
4.7 years
4.4 years
5.2 years
Math
ProbabilityThe mean height of women in a country (ages 20-29) is 64.4 inches. A random sample of 70 women in this age group is selected. What is the probability that the mean height for the sample is greater than 65 inches? Assume a=2.78.
The probability that the mean height for the sample is greater than 65 inches is
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)

Math
ProbabilityA box contains green marbles and blue marbles. Yosef shakes the box and randomly draws a marble. He records the color in the table at the right and places the marble back into the box. Yosef repeats the process 50 times.
a. Develop a complete probability model for choosing a marble.
b. Based on the experimental probability, about how many times will Yosef draw a green marble if he draws a total of 75 marbles?
Math
ProbabilityThe heights of 10 year old children has a normal probability distribution with mean of 54.6 inches and standard deviation of 5.7 inches. What is the approximate probability that a randomly selected 10-year old child will be between 51.75 and 53.46 inches tall?
Refer: use the normal distribution calculator above.
0.1122
0.2345
0.4556
0.6677

Math
ProbabilityA particular fruit's weights are normally distributed, with a mean of 490 grams and a standard deviation of 35 grams. If you pick one fruit at random, what is the probability that it will weigh between 411 grams and 493 grams

Math
ProbabilityJill is running for student council. Fifty out of the eighty students in the class plan to vote for her. If Jill randomly polls five students, what is the probability that none plan to vote for Jill?
0.0059
0.0074
0.0881
0.0953