Molecular Basis of Inheritance Questions and Answers
![C₂H5OH ⇒ C₂H3OOH
Ethanol ------> Acetic Acid
Which of the following is true about this reaction?
(Hint: The equation should have same number of. O on both sides to be balanced]
This process occurs anaerobically.
This process requires O2.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/56094646-1659208077.5226352.jpeg?w=256)
Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceC₂H5OH ⇒ C₂H3OOH
Ethanol ------> Acetic Acid
Which of the following is true about this reaction?
(Hint: The equation should have same number of. O on both sides to be balanced]
This process occurs anaerobically.
This process requires O2.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIn fruit flies, the gene for white eyes is X-linked recessive. If a white eyed female is crossed with a red eyed male, what percentage of the males will have white eyes?
Not enough information
0%
50%
100%

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceScientists examined the folded structure of a purified protein resuspended in water and found that amino acids with nonpolar R groups were primarily buried in the middle of the protein, whereas amino acids with polar R groups were primarily on the surface of the protein. Which of the following best explains the location of the amino acids in the folded protein?
Polar R groups on the surface of the protein can form ionic bonds with the charged ends of the water molecules.
Polar R groups are too bulky to fit in the middle of the protein and are pushed toward the protein's surface
Nonpolar R groups that cannot form hydrogen bonds with water are pushed into the middle of the protein.
Nonpolar R groups from different parts of the protein form covalent bonds with each other to maintain the protein's structure.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhich of the following statements is/are CORRECT about excision repair?
DNA polymerase seals the nick left in the sugar-phosphate backbone of repaired DNA strand
DNA ligase forms the final phosphodiester bond
endonuclease removes the damaged nucleotides found at the end
the DNA molecule
two choices

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceTravis and Marcy, a Caucasian couple, are pregnant with their first child. Travis has a prior child with cystic fibrosis (autosomal recessive). He has refused to pursue carrier testing but Marcy has had negative carrier testing. Note: Carrier testing can identify 90% of carriers of CF accurately and approximately 1/25 Caucasian's are carriers of CF. What is the chance they will have a child with CF?
1/140
1/25
1/964

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIf the following snippet of mRNA is translated, what sequence of amino acids would be
produced? (Hint: Use a codon table to help find the answer.)
mRNA: 5'-GCGACU-3'
Ala-Thr
Ser-Ala
Arg.
Ser-Arg

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhat type of mutation involves a small part of the DNA sequence that is copied and
added, with the result that the gene grows larger with every generation?

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIsoforms are
different versions of proteins that reflect different exon combinations.
the patterns of acetyls, phosphates, and methyl groups that bind to a particular gene.
different types of RNA molecules.
technologies that sequence DNA at very low temperatures.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceEnsures that mistakes during DNA replication are corrected
adenine
antiparallel
chainreaction
cytosine
deoxyribose
Franklin
helix
hydrogen
leading
nucleotide
nucleus
kazaki
polymerase
repair
semiconservative

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhich of the following can form a pyrimidine dimer
A DNA sequence with a guanine followed by a guanine.
A DNA sequence with a guanine followed by a thymine.
A DNA sequence with a thymine followed by an adenine.
A DNA sequence with a cytosine followed by a thymine.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceThe frequency of allele R in an isolated population of 200 outcrossing grasses (no inbreeding) is 0.2. Immigrants from a population with a frequency of R = 0.5 are introduced at a rate of one new immigrant per generation. Assuming no other evolutionary processes and one-way gene flow, what will be the equilibrium frequency of R in the isolated population after many years (rounded to 3 decimal places)?
0.205
1.000
0.500
0.600

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIf mRNA has the codon AGU, what tRNA anti-codon will match with it in the ribosome? (Enter the anti-codon answer as three capital letters with no spaces or dashes between them.)

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceSelect the correct answer.
Which mutation does the given change in nucleotide sequence represent?
ATTGCATC → ATACGTTC
A translocation
B. substitution
C. inversion
D. duplication

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhat is true about the lagging strand during DNA replication?
It is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction.
It is synthesized before the leading strand.
It has the same sequence as the leading strand.
It contains Okazaki fragments.

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance1. A strand of DNA in a skin cell contains the
bases:
A-T-G-C-C-A-T-C-G-G-T-A
After the cell is exposed to ultraviolet light, the
strand contains the bases:
A-T-G-G-C-C-A-T-C-G-G-T-A
Which statement describes the result of this
exposure?
(1) A new base has been inserted.
(2) A base has been deleted.
(3) One base has been substituted for another.
(4) There have been no changes in the bases.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceAmino acids have an amino group, a R group, a hydrogen and a carboxylic acid group attached
to a central carbon. Amino acids differ only in their R groups. Circle the R groups in the
following amino acids.
NAME
Glycine
ABBREVIATION
Gly

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceThe _ allele masks the
other allele it is paired
with.
A. recessive
B. biggest
C. most common
D. dominant

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceThe structure of
enzymes that just
includes folding AND
twisting is called a
secondary structure.
A. beta pleat
B. alpha helix
C. theta helix

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceBelow is a sequence of DNA on the CSF1PO locus.
CCTATCATGTAGTCAGGTACTGGACGGGTATGGTATGGTATGGTATGGTATGGTATGGTATGGTATAATCCGAGATGGA
A) What is the STR region in the above DNA sequence?
B) How many repeats does it have?
Biology
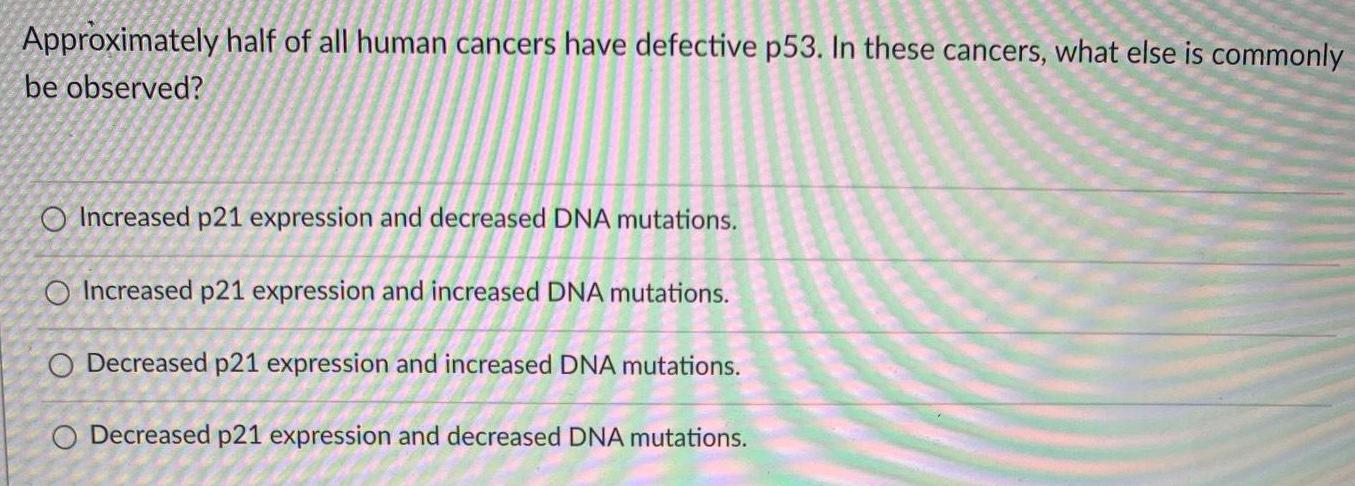
Molecular Basis of InheritanceApproximately half of all human cancers have defective p53. In these cancers, what else is commonly
be observed?
Increased p21 expression and decreased DNA mutations.
Increased p21 expression and increased DNA mutations.
Decreased p21 expression and increased DNA mutations.
Decreased p21 expression and decreased DNA mutations.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIf the haploid number for an organism is 24, the diploid number would be
A. 72
C. 12
B. 24
D. 48

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIn the fruit fly, vestigial wings (small and useless) and ebony (black) body colour are produced by two recessive genes located on different chromosomes. The normal alleles, long wings and grey body colour, are dominant. What offspring would be expected if a vestigial-winged ebony male is crossed with a homozygous normal female? If the F, from this cross were permitted to mate randomly among themselves, what offspring would be expected in the F₂?

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceDuring prophase, original maternal and paternal chromatids are matched up with ____.
A. their copies
C. chromatin
B. different contromeres
D. the mitotic spindle

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance2. Sickle Cell disease can result from a single mutation in the above DNA sequence. The underlined
thymine above is changed to a C below. Transcribe this section of DNA into mRNA and then translate
the mRNA into the correct sequence of amino acids. Answer the question below.
Mutated DNA: TAC CCT GAC TGA GGA CCC CTC TTC AGA
mRNA: AUG GGA CUG ACU CCU GGA GAG AAG ARG
amino acid sequence: MET, GLY, LEU, THR, PRO, GLY, GLU, LYS, ARG
What happens to the amino acid sequence because of this change from a T to a C?

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritancePhenylketonuria is a rare genetic disorder that is caused by a mutation in the PAH gene. This
gene normally codes for the production of an enzyme that breaks down phenylalanine (found in
food). Patients with the disorder have a toxic level of phenylalanine in their bodies which causes intellectual disability and seizures.
Which of the following best explains why the mutation causes the severe symptoms?
A nonsense mutation interferes with the production of phenylalanine
A silent mutation impairs the enzyme's function due to improper folding
A frameshift mutation impairs the enzyme's function de to improper folding
A missense mutation causes too many copies of the enzyme to be transcribed
Biology
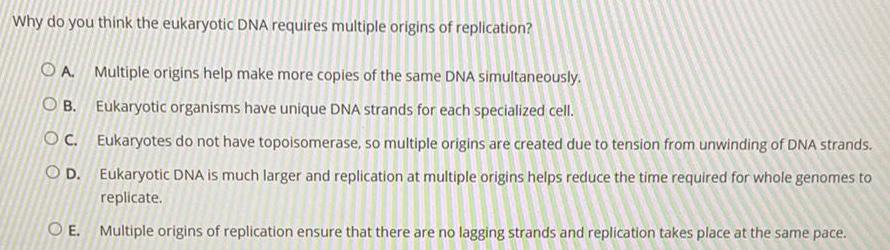
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhy do you think the eukaryotic DNA requires multiple origins of replication?
A. Multiple origins help make more copies of the same DNA simultaneously.
B. Eukaryotic organisms have unique DNA strands for each specialized cell.
C. Eukaryotes do not have topoisomerase, so multiple origins are created due to tension from unwinding of DNA strands.
D. Eukaryotic DNA is much larger and replication at multiple origins helps reduce the time required for whole genomes to replicate.
E. Multiple origins of replication ensure that there are no lagging strands and replication takes place at the same pace.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhen biologists speak of a UNIVERSAL GENETIC CODE they are referring to the fact that, in nearly all organisms:
A. The DNA sequences are identical
B. RNA information is transcribed
C. RNA specifies proteins the same way in all organisms
D. Phenotype is dependent upon genotype

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance(Pierce worked problem) Suppose that a consensus sequence in the regulatory promoter of a eukaryotic gene that encodes enzyme A was deleted. Which of the following effects would result from this deletion? Explain your reasoning.
A) Enzyme A would have a different amino acid sequence.
B) The mRNA for enzyme A would be abnormally short.
C) Enzyme A would be missing some amino acids.
D) The mRNA for enzyme A would be transcribed but not translated.
E) The amount of mRNA transcribed would be affected.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIn the 1920s, a dye (now called Feulgen stain) was developed that bound DNA in direct proportion to the amount of DNA present in cells. Upon binding, the DNA would gain in color intensity. This DNA staining technique
A) provided circumstantial evidence that DNA is the genetic material.
B) definitively proved that DNA is the genetic material.
C) demonstrated that all species have the same amount of nuclear DNA.
D) confirmed that DNA is an important component of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
E) led to skepticism that DNA is the genetic material.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIf a single bacterial cell that is sensitive to the antibiotic vancomycin is placed in a grown medium that contains vancomycin, it will die. Now consider another single bacterial cell, also sensitive to vancomycin, that is allowed to divide for many generations to become a larger population. If this population is placed into vancomycin-containing growth medium, some of the bacteria will not die, and indeed, they will grow. Why do you see growth in this case, but not with the transferred single cell?

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIf, in humans, the DNA sequence TTTCTAGGAATA encodes the amino acid sequence LYS-ASP-PRO-TYR, what amino acid sequence will that same sequence specify in bacteria? Explain the evolutionary significance of this.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceGiven the DNA sequence below, write out the nucleotides for the complementary mRNA segment that would be created as a result of transcription.
3' AGT TTA CGG 5'
5'.........................3'

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceAnswer the following using complete sentences.
a) How did Mendel's work gradually gain acceptance.
b) Describe how a cross between two closely related organisms may result in genetic problems.
c) Are there any advantages in breeding organisms from closely related species? Explain.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceGeneticists have discovered the existence of meiotic drive genes, which have alleles that, when present in a heterozygous state, are able to become incorporated into much more than 50 percent of the gametes. As a result, the offspring ratios are not what Mendel would have predicted. Which statement about these meiotic drive genes is true?
A) They violate the law of independent assortment.
B) They violate the law of equal segregation.
C) They alter dominance relationships.
D) They alter phenotypes.
E) They are an example of blending inheritance.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceA large population of animals is genotyped for many SNP loci across the nuclear genome. A high level of polymorphism is found at SNP loci over most of the genome. But on one chromosome, a particular long haplotype (a set of specific SNP alleles) is found at high frequency, and is homozygous in many individuals. Which of the following circumstances could help explain this situation? Select all correct answers; partial negative scoring for incorrect answers.
A) The chromosome carries a transmission ratio distortion system.
B) The chromosome has a higher mutation rate than the rest of the genome.
C) The chromosome carries an allele that was recently subject to strong positive selection.
D) The chromosome carries an inversion relative to other homologous chromosomes in the population.
E) The population was subject to a recent bottleneck and founder effect.
F) The chromosome was recently introduced from a different species.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhich kind of genetic element has repeated DNA with units composed of 2 to 6 nucleotides, copied from a few to about 100 times?
(A) minisatellite
(B) intron
(C) microsatellite
(D) transposon
(E) satellite

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceChloramphenicol binds to the 50S subunit of a 70S ribosome, which will interfere with...
Transcription in prokaryotic cells
Transcription in eukaryotic cells
Translation in prokaryotic cells
Translation in eukaryotic cells
DNA synthesis

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceAccording to the video "The antibiotic apocalypse explained", what caused an increased bacterial resistance to the antibiotic colistin in China?
Colistin was an OTC (over-the-counter) medicine and people abused its use
Farmers were treating animals with colistin to prevent infections and this bad practice generated bacterial strains resistant to this antibiotic that were passed to humans
Colistin was treated to treat all the infectious diseases in China and after a while all the bacteria became resistant
it is unknown

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance7. A scientist wants to study the kinetics of a specific membrane protein. They ligate the DNA
coding region of the protein to the DNA coding region for GFP and introduce the DNA into
cells. A day or two later, they observe the cells under the microscope and they are
fluorescing green. They then shine a laser at a region of the cell repeatedly (or
continuously) that region loses its fluorescence. They monitor a separate region of the
cell and find that fluorescence never decreases in that area. What is the full name of the
technique that they performed? What can they conclude from their result?
a) What is the full name of the technique that they performed?
Flurorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP).
b) What can they conclude from their result?
Membrane proteins show lateral movement in the membrane. Due to this
movement of proteins, fluorescenc appears in the region of photobleaching.
c) List another photobleaching technique and briefly indicate how it is different from the
technique described here.
The other technique in FLIP (Fluorescence Loss in photobleaching) is a fluoresecne
microscopy technique used to examine movement of molecules inside cells and
membranes. A cell membrane is typically labelled with a flurescent dye to allow for
observation. The major difference between these two microscopy techniques issthat
FRAP involves the study of a cell's ability to recover after a single phtovleaching event
whereas FLIP involves study of how the loss of fluorescence spreads throughout the cell
after multiple phtobleaching events.
d) When or why might photoactivation techniques be preferred over photobleaching
techniques?
Biology
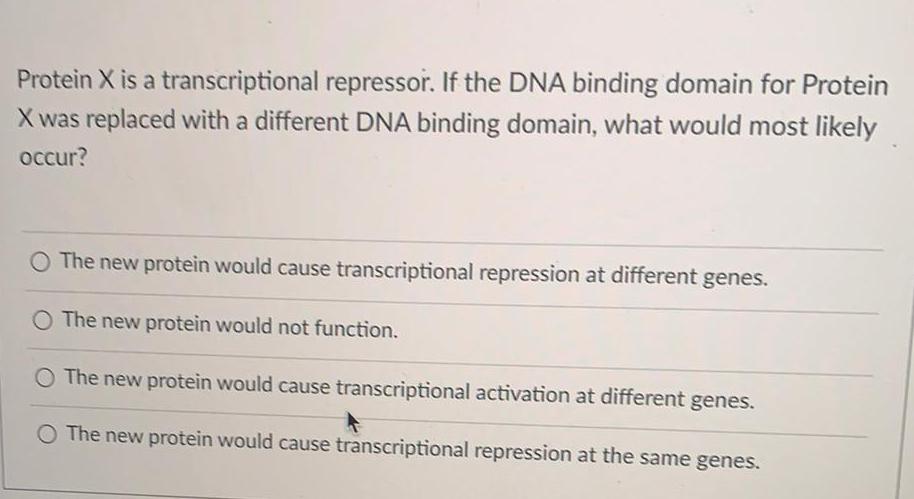
Molecular Basis of InheritanceProtein X is a transcriptional repressor. If the DNA binding domain for Protein
X was replaced with a different DNA binding domain, what would most likely
occur?
The new protein would cause transcriptional repression at different genes.
The new protein would not function.
The new protein would cause transcriptional activation at different genes.
The new protein would cause transcriptional repression at the same genes.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhich of the following would cause Drosophila cells to behave as they would
at night?
A chemical that increases the polyubiquitination of Tim.
A chemical that decreases the expression of Tim.
A chemical that prevents the degradation of Tim.
A chemical that increases the degradation of Tim.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceA scientist studying NTF2 starts to consistently add excess miRNA targeting NTF2 mRNA into a eukaryotic cell. What will eventually occur?
Nuclear import will decrease, and nuclear export will decrease.
Nuclear import will function normally, and nuclear export will decrease.
Nuclear import will function normally, and nuclear export will function normally.
Nuclear import will decrease, and nuclear export will function normally.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIn "the repressillator" (also known as "the represilator"), gene A is the Lac repressor. What should occur if cells containing the repressillator were continually maintained in very high (and excess) levels of allolactose?
The expression of B will be the opposite of the expression of C, but the expression will oscillate at long intervals.
The expression of B will always be high and the expression of C will always be low.
The oscillations of all proteins will occur with increasing amplitude.
The expression of B will be the opposite of the expression of C, but the expression will oscillate at short intervals.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceA proteasome inhibitor will...
decrease the number of multiubiquitylated proteins.
decrease the number of polyubiquitylated proteins.
increase the number of multiubiquitylated proteins.
increase the number of polyubiquitylated proteins.

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance-hort tandem repeats are inherited from parents. The mother has 8 repeats of the TPOX STR on
one chromosome and 6 repeats of the TPOX STR on the other chromosome (alleles are 8,6) and
he father is homozygous with 5 repeats of the TPOX STR on both chromosomes (alleles are 5,5).
What alleles could the son could have for the TPOX STR?
8, 6 only
5,5 only
8, 6 and 5, 5
8, 5 and 6, 5

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhy does adding SDS and potassium acetate, followed by centrifugation precipitate the proteins and chromosomal DNA out of solution? Why does the RNA not precipitate out?
This is for an RNA isolation & electrophoresis lab. Below is the explanation given in the lab manual:
Detergents lyse membranes: SDS Cell membranes are composed of lipids and proteins rich in hydrophobic residues. SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) is a strong ionic detergent that solubilizes the plasma membrane. (Remember that in this protocol, E. coli, a prokaryote, is the source of RNA. Prokaryotes have cell walls which we need to break with lysozyme, but they do not have membrane bound organelles-meaning they do not have a nucleus-so we will need to separate the DNA from the RNA). In addition, SDS is also a strong protein denaturant as you learned when you isolated eukaryotic DNA in BIO130. In this protocol we use SDS plus potassium acetate to remove protein and other cellular constituents (discussed below under "Selective precipitation by SDS and potassium acetate").
Potassium acetate and SDS selectively precipitate protein and cell debris Sodium dodecyl sulphate is very soluble in water, while potassium dodecyl sulphate is very insoluble. In this procedure, we add potassium ions (potassium acetate), which form ionic bonds to produce insoluble potassium dodecyl sulphate. All of the molecules previously bound to SDS now precipitate from solution with the insoluble potassium dodecyl sulphate. By centrifuging this mixture, you remove most proteins, unbroken cells and fragments of cells, as well as most of the large, chromosomal DNA, which becomes trapped in the precipitate. Only very soluble molecules, such as RNA, small DNAs, and small salts remain in solution.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceDr. Stevens is examining the DNA sequences of a group of mice. He notices that in one of the mice, one nucleotide pair is substituted with another in the part of the DNA sequence that codes for fur color. However, despite the substitution, the mouse still has the same fur color as the other mice with the correct DNA sequence. Why
doesn't the substitution of nucleotides in the mouse change its phenotype, or physical characteristics?
A. The mouse has a completely different DNA sequence than the other mice.
B. The substituted nucleotide has the same directions as the original nucleotide.
C. DNA sequences don't determine the color of a mouse's fur.
D. Substitutions in the nucleotides of a mouse's DNA never affect their phenotypes.

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceChargaff's rule explains how the nitrogenous bases in DNA pair in complementary patterns. Adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine in order to maintain the same size of the base pairs throughout the DNA strands.
BASED ON THIS ANSWER CREATE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhich technique would be MOST useful in determining the father of a child in a paternity suit?
A. DNA Fingerprinting
B. Polymerase chain reaction
C. Computer generated parental punnett square
D. Karyotype of father and child

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceDuring the process of replication, a molecule of DNA unzips, forming two single strands. What makes up each individual strand of DNA?
A. nitrogenous bases attached to a sugar-phosphate backbone
B. paired thymine and guanine bases
C. paired adenine and uracil bases
D. sugar groups attached to individual amino acids